Quantum Cryptography
Think of a world where every private correspondence, bank transaction, and medical data is protected by the greatest shield there is. No hacker, no matter how strong, could ever get it open. Quantum cryptography is a security solution that doesn’t use complicated arithmetic problems but instead uses the principles of nature.
The number of cyberattacks is rising at an alarming rate. IBM’s 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report said that the typical data breach around the world currently costs more than $4.88 million. Encryption that has been around for a long time is strong, but it might not stay that way for long with the emergence of quantum computers. Quantum cryptography is becoming a possible game-changer.
In simple terms, what is quantum cryptography?
Quantum cryptography is a means to protect communication by employing photons, which are the building blocks of light. It doesn’t employ equations that can be solved eventually to keep secrets; instead, it uses a rule from quantum mechanics. According to this law, a photon changes its status when you see it or touch it.
It’s like writing a note on water. The ripples give it away as soon as someone tries to imitate it. Quantum cryptography is special and strong because it can tell whether someone is listening in.
Why we need quantum security right now
- Quantum computers are getting better. Researchers think that in ten years, large-scale quantum computers may be able to break common encryption methods like RSA.
- Data need to be safe for decades. Long after they are made, health records, military intelligence, and trade secrets are still useful.
- Actors in nation-states are gathering data right now. People think that intelligence groups are keeping encrypted traffic now in the hopes of breaking it in the future.
The science that makes it feasible
Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) is the basis of quantum cryptography. This is how it works:
- Alice sends Bob photons that have information in them.
- Bob randomly measures them with different filters.
- Alice and Bob then check a part of their results against each other to see if there are any mistakes.
- They know no one was listening if there are relatively few mistakes. The leftover photons become their secret key.
If an adversary tries to intercept, glancing at the photons changes them, which makes mistakes that are easy to see. This is why QKD is trustworthy.
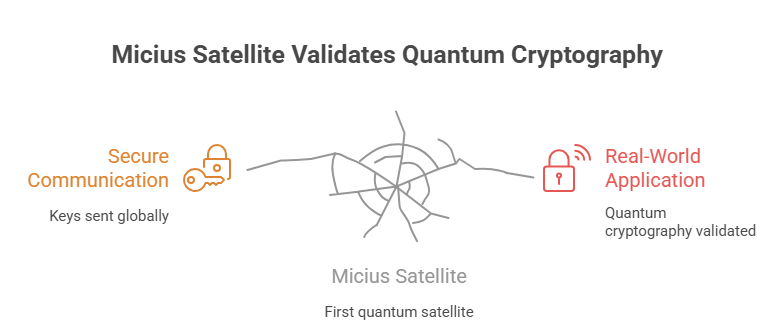
A look at China’s quantum satellite
China launched the Micius satellite in 2017. It was the first quantum satellite in the world. It was able to send safe keys between Beijing and Vienna, which are 7,600 kilometers apart. This discovery showed that quantum cryptography is not just a theory; it is a real way to communicate over the world.
Main benefits of quantum cryptography
- Physics, not math riddles, is what makes security work.
- It is easy to find out if someone is trying to snoop.
- It can stand up to attacks from quantum computers in the future.
- You can safely share keys without the usual problems.
Problems right now
- Distance barriers: Photons lose strength when they travel long distances through fiber. Satellites are helpful, but they cost a lot.
- Cost: Equipment is still quite specialized and costs a lot.
- Problems with compatibility: It’s hard to make quantum systems work with existing infrastructure.
- No standards: There are presently no global standards for quantum cryptography.
Industries that will gain the most
Banking and money
Banks deal with a lot of private information. Quantum cryptography can protect money transfers from both hackers and quantum attackers.
Medical care
Hospitals and research centers need to keep patient records for life. QKD makes sure that this information stays safe for many years to come.
Government and the military
Secret communication is important for national security. Defense groups all over the world are already testing quantum networks.
Cloud and phone
As more businesses move to the cloud, data centers can use quantum cryptography to keep server connections safe.
Comparing classical and quantum cryptography
| Feature | Classical Encryption | Quantum Cryptography |
| Foundation | Complex mathematics | Quantum physics |
| Vulnerable to | Quantum computers | No, if implemented correctly |
| Intrusion detection | Impossible | Always possible |
| Longevity | Limited to decades | Can remain secure indefinitely |
Global adoption efforts
- The EuroQCI initiative is helping Europe establish a quantum communication network.
- The US is giving money to several quantum projects through DARPA and NIST.
- China is still ahead with its vast satellite and city networks.
- Japan and South Korea are trying out business telecom apps.
Getting rid of common myths
- It replaces all encryption: False. The major use of quantum cryptography is to protect key distribution. Algorithms like AES still keep data safe.
- It is already common: Not yet. It could take years for full adoption.
- It’s not just for governments: Any group with important long-term data can use it.
The QKD workflow in steps
- Put quantum devices at each end of a fiber or satellite link.
- Exchange photons that might hold important vital information.
- Check to see if a little sample has been tampered with.
- Use methods to fix mistakes and protect your privacy to clean the key.
- Use the last shared key to encrypt and decrypt real communications.
How firms can get ready
- Keep up with changes by following research and government programs.
- Find important data and decide which data needs to be kept safe for decades.
- Try things out early by working with quantum-ready providers on test projects.
- Use a mix of security methods, like quantum cryptography and post-quantum algorithms.
- Teach your teams and make sure they know about the change in security that’s coming.
The road ahead
Experts say that by 2032, the global market for quantum cryptography will be worth $3.5 billion. Governments, banks, and telecom corporations will be the first to use it, but prices are likely to go down over time. A lot of people think that this will eventually lead to a quantum internet, where countries and businesses may share information safely without worrying about it being intercepted.
Important points to remember
- Quantum cryptography uses the laws of physics to keep communication safe.
- It finds out when others are trying to listen in right away.
- Finance, military, health, and the cloud are some of the best application cases.
- There are still problems like cost and distance, but things are moving quickly.
- Companies can get ready for the future by looking into hybrid methods.
Last thoughts
In the digital world, a new age is beginning where regular locks won’t be enough. Quantum cryptography is more than just technology. In a time where knowledge is the most valuable resource, it is about building trust. Businesses and governments can keep their secrets safe for decades by being ready today.
Hoplon Infosec can help your company become ready for the age of quantum security by coming up with tactics that will protect you against quantum threats.
Follow us on X (Twitter) and LinkedIn for more cybersecurity news and updates. Stay connected on YouTube, Facebook, and Instagram as well. At Hoplon Infosec, we’re committed to securing your digital world.



