Weekly Cybersecurity Review
Every week, cybersecurity changes as new threats and weaknesses endanger people, companies, and even governments. The digital world is always changing, from malware that targets mobile devices to zero-day exploits that impact enterprise systems. To keep you informed and ready, this Weekly Cybersecurity Recap compiles the most important updates.
A Tableau Server Vulnerability Causes Enterprise Concerns
Description: Tableau is a popular tool for data visualization, but there are concerns about a recently found flaw in its server component. The vulnerability could be used by attackers to get around authentication and access private dashboards and data without authorization. The impact of exploitation could be substantial because Tableau is integrated with important business intelligence systems. Businesses are advised to implement least privilege access, patch right away, and step up monitoring.
The macOS Installer Malware Increases the Attack Surface
Attackers are increasingly targeting the macOS ecosystem by inserting malware into installers that look like genuine apps. Users are especially at risk if they download software from unofficial sources. Once installed, the malware can open backdoors for remote attackers, compromise credentials, and gather data. Apple users need to make sure they only download from reliable developers, check signatures, and make use of built-in security features like XProtect and Gatekeeper.
Verification of Google Android Developers for 2026
Google has stated that a more stringent developer verification procedure will be implemented in 2026 in an effort to counteract the deluge of malicious apps that are making their way into the Play Store. Before being approved, developers will go through more thorough app reviews and improved identity checks. The goal of this change is to improve accountability and lessen fraudulent apps that deceive users into giving them risky permissions. While developers must get ready to comply with the new regulations, end users benefit from enhanced security.
The Development of Hook Android Trojans into Ransomware
The Hook Android malware was first created as a banking trojan but has since developed into a potent ransomware tool. It can now demand ransom payments, encrypt files, and lock users out of their devices. A new stage of cybercrime, where attackers adapt their strategies from desktop computers to smartphones, is heralded by the increasing sophistication of mobile ransomware. Users of mobile devices should use mobile antivirus software, be cautious when downloading apps, and stay away from dubious links.
Supply Chain Attacks
The Hidden Entry Point:Cybercriminals continue to target reliable third-party vendors in order to take advantage of supply chains. Hackers gain access to corporate systems by compromising a software update, service provider, or supplier rather than attacking a business directly. These attacks are risky because they enter through a reliable channel, circumventing conventional defenses. To identify suspicious activity, businesses need to implement a zero-trust security model, conduct frequent vendor risk assessments, and use sophisticated monitoring tools.
Taspen-Branded Malware Attack in Indonesia
Description: A number of malware campaigns have been found that use the name of Indonesia’s pension agency, TASPEN, to trick retirees and government workers. Fraudsters are using fake websites, phishing links, and fake documents that look like real TASPEN communications to get personal information. These dishonest tactics put the trust and financial security of vulnerable groups at risk. It’s important for people who might be victims and businesses to know how scams work and stay on guard.
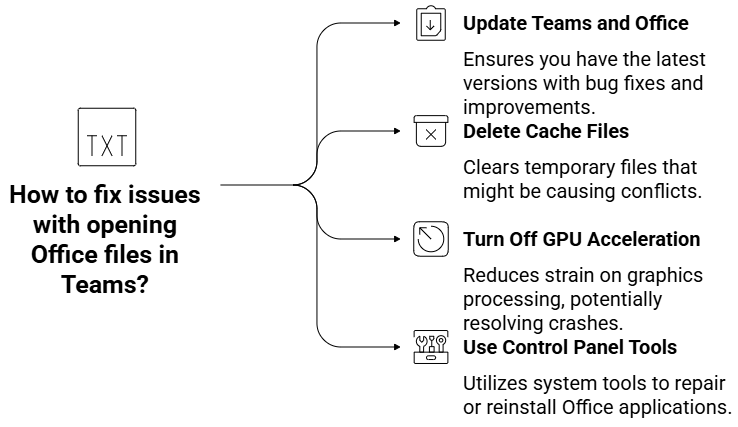
Microsoft Teams: Office files won’t open.
Description: People all over the world have been having trouble opening Word, Excel, or PowerPoint files directly in Microsoft Teams. The app might crash or not load content when you try to “Edit in Teams,” “Open in browser,” or “Open in app.” Some suggested fixes are to update your Teams and Office installations, delete cache files, turn off GPU acceleration, or use control panel tools to fix installations. As collaboration platforms are still important for getting work done, fixing these problems is necessary to keep productivity high.
Salesloft-Drift OAuth Breach Messes Up Salesforce Integrations
Description: In a complicated cyberattack, hackers used the SalesDrift integration between Drift and Salesforce to steal OAuth and refresh tokens. The breach, which lasted from August 8 to 18, 2025, let hackers steal sensitive information like AWS keys, passwords, and Snowflake tokens from several customer environments. Google’s Threat Intelligence Group called the group UNC6395, but other sources say it’s ShinyHunters. The breach shows how risky it is to use third-party integrations and how important it is to change passwords and check connected apps.
Chrome Use-After-Free Vulnerabilities Let Attackers Run Code Remotely
Description: Researchers found a number of serious “use-after-free” security flaws in different parts of Google Chrome, such as V8, Site Isolation, Blink, and media processing subsystems. Some important CVEs are CVE-2025-3066 (Site Isolation), CVE-2025-8578 (Cast component), CVE-2025-0445 (V8 engine), and CVE-2025-6555 (animation component). Attackers can run any code or crash systems by using specially made HTML content that has these bugs in it. Patches have been sent out, and users need to update their browsers right away to lower the risk.
Features for Lost Phone Security Protect Data
Numerous security features on contemporary smartphones lower the likelihood that the device will be misplaced or stolen. Biometric authentication, encrypted backups, and remote lock and wipe features guarantee that private and corporate data is kept safe. Many users wait until it’s too late to activate these features. Phone owners can keep control of their data even if their devices end up in the wrong hands by putting these safeguards in place beforehand.
Defending Against Attacks: QR Codes as the New Phishing Tool
With the emergence of quishing, a tactic that deceives users by using malicious QR codes, phishing has entered a new stage. These codes, when scanned, lead to malware downloads or websites that steal credentials. Because people tend to trust QR codes on websites, emails, and posters, quishing works particularly well. Employers should consider implementing tools that scan and validate QR code destinations, train staff to identify risks, and confirm QR sources.
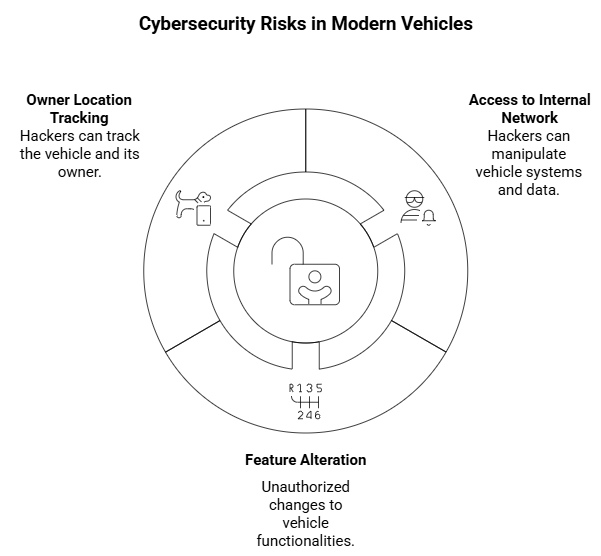
Cybersecurity Risks for Aftermarket Automobiles
Automobiles are now linked systems that are susceptible to cyberattacks rather than merely being mechanical devices. GPS trackers, remote-start devices, and entertainment modules are examples of aftermarket accessories that frequently lack adequate cybersecurity protections. These gadgets can be used by hackers to gain access to the internal network of the vehicle, change its features, or even locate the owner. Before installing third-party devices, drivers should confirm that they adhere to security standards and seek advice from experts on safe integration.
Exploit for Apache Tika PDF Parser XXE
Description: The PDF parser of Apache Tika, which is frequently used to extract content from documents, was recently discovered to be susceptible to an XXE exploit. Attackers might alter XML inputs to gain access to private data or interfere with services. This flaw has significant ramifications because Tika is frequently incorporated into enterprise document management workflows. Security teams should set up XML parsing settings to prevent external entity resolution and update right away.
Apple Zero-Day CVE-2025-43300
An urgent patch was released by Apple to address CVE-2025-43300, a zero-day vulnerability that was already being used against users. Attackers might install malicious code and obtain unauthorized system access if the system is not patched. Apple users should make updating a top priority right away because hackers frequently target those who put off updates. Maintaining device security in the face of active exploitation campaigns requires automatic updates and frequent patch checks.
AI Adoption and the GPT-5 Access Plan
The new GPT-5 Access Plan describes how businesses can use AI tools safely as it transforms cybersecurity. It provides businesses with organized choices for incorporating AI into their processes while upholding governance and compliance. AI improves automated response and anomaly detection, but if used carelessly, it can also be dangerous. In order to ensure ethical usage and oversight, businesses need to take a cautious approach.
IoT Devices Are Targeted by the RapperBot Botnet
Targeting insecure IoT devices such as routers, cameras, and smart appliances, the RapperBot botnet has been growing quickly. Following infection, these devices are enlisted in sizable botnets that are employed to launch distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. When it comes to security, IoT devices are frequently disregarded, but their default or weak passwords make them prime targets. To lower risks, owners must segment networks, update firmware, and change credentials.
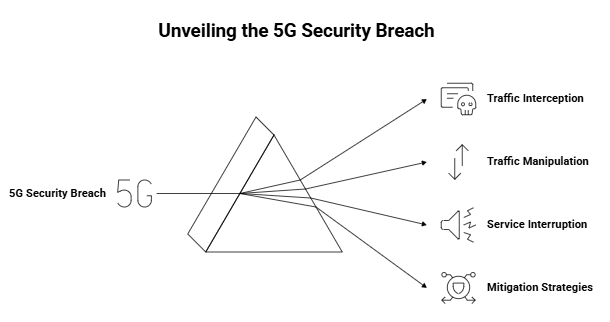
A New 5G Attack That Avoids Base Stations
Described: By evading base station authentication, researchers have discovered a new attack that compromises the security of 5G networks. Even sophisticated communication systems can be creatively attacked, as this exploit shows. Traffic interception, manipulation, and possible interruption of vital services are among the dangers. To stop real-world exploitation, telecom providers need to work with researchers, patch systems, and bolster encryption as soon as possible.
Action Table: Key Takeaways for Readers
| Threat / Update | Risk Level | Immediate Action |
| Tableau Server Vulnerability | High | Patch immediately, restrict user access, monitor dashboards |
| macOS Installer Malware | Medium | Download from trusted developers, enable Gatekeeper |
| Google Android Developer Verification | Medium | Developers prepare for 2026 rules, users check app permissions |
| Hook Android Trojan Ransomware | High | Use mobile AV, avoid suspicious apps/links |
| Supply Chain Attacks | Critical | Enforce zero-trust, audit vendors, secure updates |
| Lost Phone Security Features | Medium | Enable remote lock/wipe, activate backups |
| Quishing Attacks | High | Train staff, validate QR codes, use scanning tools |
| Aftermarket Car Risks | Medium | Verify aftermarket devices meet security standards |
| Apache Tika XXE Exploit | High | Update parser, block external entity resolution |
| Apple CVE-2025-43300 | Critical | Install patch immediately, enable auto updates |
| GPT-5 Access Plan | Informational | Plan ethical AI adoption with governance |
| RapperBot Botnet | High | Change IoT passwords, update firmware, segment networks |
| Novel 5G Attack | Critical | Telecoms patch networks, strengthen authentication |
Concluding remarks
The speed at which attackers are innovating to target both consumer and enterprise systems is highlighted in this weekly cybersecurity recap. The message is clear: cybersecurity needs to be proactive, whether it is achieved through IoT exploitation, supply chain manipulation, or phishing campaigns.
Businesses should prioritize vendor risk assessments, implement AI-driven defenses, and enforce zero-trust models. Customers need to update their software, be cautious when using the internet, and activate built-in device protections. The best way to lessen exposure to changing threats is to stay informed and take prompt action.
Follow us on X (Twitter) and LinkedIn for more cybersecurity news and updates. Stay connected on YouTube, Facebook, and Instagram as well. At Hoplon Infosec, we’re committed to securing your digital world.



