Recent research has revealed alarming evidence linking the Israeli firm Paragon Spyware Solutions to a sophisticated spyware operation exploiting a zero-day WhatsApp vulnerability. The investigation has exposed how this advanced spyware targeted journalists and civil society members around the globe. In this detailed blog post, we explore the background of Paragon Solutions, delve into the intricacies of Graphite spyware, and examine the sequence of events that led to the mitigation of this exploit. We also analyze the broader implications for privacy, digital security, and government accountability.
Background on Paragon Spyware Solutions
Founded in Israel in 2019, Paragon Solutions quickly became prominent in the surveillance technology industry. Its establishment was marked by the involvement of high-profile figures, including former Israeli Prime Minister Ehud Barak and Ehud Schneorson, known for his leadership in Israel’s renowned Unit 8200 intelligence unit. Under such influential leadership, the company’s inception has often been interpreted as a signal of the strategic significance of its operations.
Paragon Solutions has developed and marketed Graphite spyware. Unlike some of its competitors, the firm claims that Graphite is a more precise surveillance instrument designed to target specific messaging applications rather than take complete control of a device. This approach is notably different from NSO Group’s Pegasus spyware, which has infamously been linked to more intrusive, full-scale device takeovers.
A senior executive at Paragon has stated that the company maintains strict ethical boundaries, asserting that their products will only be sold to governments that abide by international norms and respect fundamental rights and freedoms. Despite these assurances, growing evidence suggests that the deployment of Graphite may have strayed from this ideal, leading to serious concerns about misuse.
Graphite Spyware and Zero-Day Exploits
At the heart of the recent controversy is the Graphite spyware, a tool engineered to infiltrate messaging platforms such as WhatsApp. Cybersecurity researchers discovered that the Paragon Spyware leveraged a zero-day vulnerability—a previously unknown flaw that had not yet been patched—in the WhatsApp messaging application. This vulnerability was exploited to allow the spyware to be deployed without any user interaction, a technique known as a zero-click exploit.
How the Zero-Day Exploit Works
The sophistication of the attack is underscored by its ability to bypass standard security measures. The malicious software was delivered via specially crafted PDF files sent to WhatsApp group chats. The vulnerability was automatically triggered upon receiving these PDFs, enabling the spyware implant to be loaded onto the target device without the recipient even realizing it was under attack. This exploitation is hazardous, as it circumvents traditional security protocols and leaves victims unaware of the breach.
Moreover, the Graphite spyware could escape the Android sandbox environment, an isolated space designed to protect applications from interfering with one another. Once the security barrier was breached, attackers gained unauthorized access to WhatsApp and other messaging applications on the compromised devices. This multi-layered penetration increased the risk profile for targeted individuals, making it a preferred tool for surveillance operations.
The WhatsApp Attack: How It Unfolded

The investigation into this high-profile attack began when cybersecurity researchers noticed anomalous behavior associated with WhatsApp communications. Their analysis revealed that around 90 potential victims across more than two dozen countries had been targeted through this zero-click exploit. The victims primarily included journalists and activists, groups that are often at the frontline of exposing human rights violations and government malfeasance.
WhatsApp’s Response and Mitigation
WhatsApp responded swiftly to the discovery. The company confirmed that the zero-day vulnerability had been exploited and immediately mitigated the issue. The vulnerability was patched on the server rather than through a client update. This decision meant users did not need to manually update their devices for protection, as the fix was implemented centrally within WhatsApp’s infrastructure.
Despite WhatsApp’s prompt action, the incident raised serious concerns about the resilience of even the most secure communication platforms. It underscored how advanced state-sponsored and commercial spyware operations could exploit undisclosed vulnerabilities to breach highly trusted applications.
Global Investigations and Evidence Collection
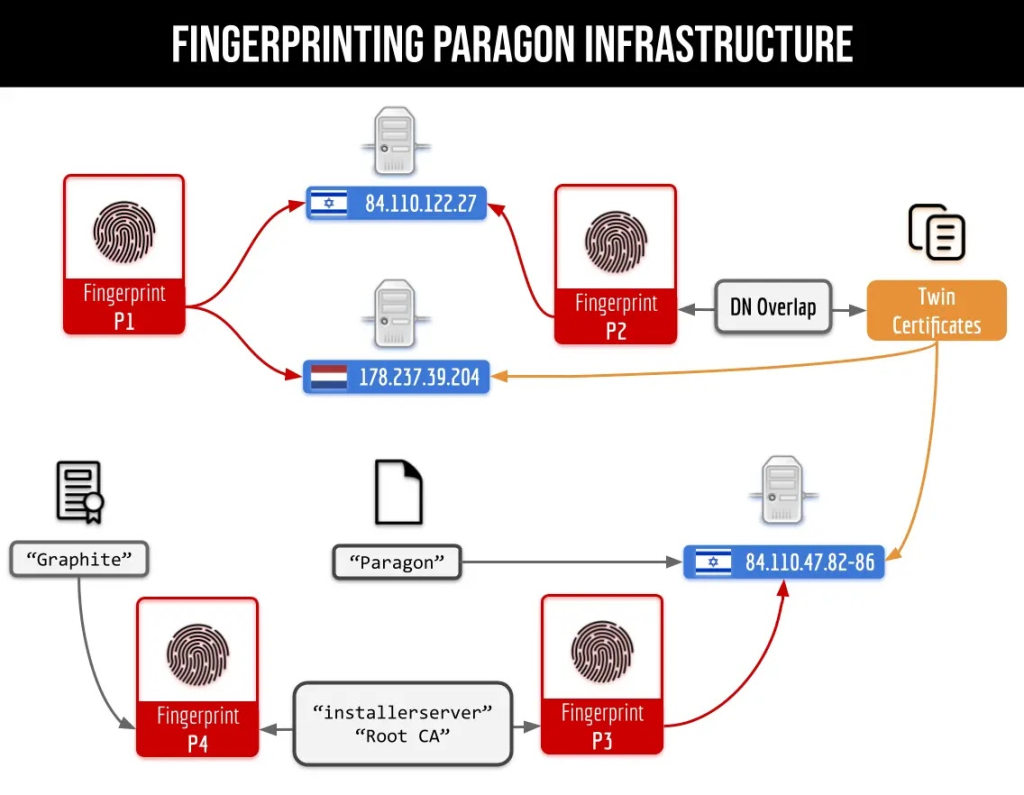
One of the pivotal elements of the investigation was carried out by Citizen Lab, a research group renowned for its work in digital security and surveillance. The investigation was initiated after a tip pointed to a distinctive server infrastructure that was not easily attributed to any known entity. Citizen Lab researchers used advanced fingerprinting techniques to identify approximately 150 digital certificates. These certificates were closely linked to Paragon Solutions’ command and control servers—a finding that directly implicated the firm in orchestrating the surveillance operation.
International Reach and Law Enforcement Connections
The investigation revealed that Paragon deployments were not limited to a single region. Evidence pointed to suspected spyware operations in multiple countries, including Australia, Canada, Cyprus, Denmark, Israel, and Singapore. This operation’s breadth highlights the technology’s global reach and suggests that the spyware was deployed in diverse geopolitical contexts. Such wide-ranging activity emphasizes the challenges governments and organizations face in regulating and overseeing surveillance tools.
Another intriguing investigation aspect involved the connections between Paragon and Canadian law enforcement. Researchers discovered suspicious IP address registrations under the name “Integrated Communications.” One of these registrations notably matched the address of the Ontario Provincial Police’s General Headquarters. This discovery aligns with earlier reports suggesting that Canadian law enforcement agencies have increasingly employed spyware technologies—often without sufficient public oversight or transparency.
Forensic Analysis and the Discovery of “BIGPRETZEL”
Forensic analysis played a crucial role in corroborating the presence of the spyware. In collaboration with Meta, the parent company of WhatsApp, cybersecurity researchers were able to identify a unique forensic artifact that was present on the compromised devices. This artifact, dubbed “BIGPRETZEL,” was a digital fingerprint, directly linking the infected devices to Paragon’s spyware operations.
Unraveling the Forensic Evidence
The presence of BIGPRETZEL was confirmed on multiple devices during the forensic examination process. For example, in Italy, several individuals who received WhatsApp notifications consented to have their devices analyzed for signs of infection. Among the affected users was Francesco Cancellato, the editor-in-chief of Fanpage. It and several members of Mediterranea Saving Humans, a humanitarian organization dedicated to rescuing migrants in the Mediterranean Sea.
The forensic findings were significant in establishing a tangible connection between the zero-day exploit and Paragon’s Graphite spyware. The ability to detect a consistent artifact across different devices and geographies provided compelling evidence of a coordinated operation. Moreover, this discovery underscored the critical importance of forensic analysis in uncovering sophisticated cyberattacks, especially when dealing with state-of-the-art surveillance tools that operate in stealth mode.
Government and Corporate Responses
In the wake of these revelations, corporate and governmental responses have been swift and decisive. On January 31, 2025, WhatsApp took the significant step of notifying approximately 90 accounts that were believed to have been targeted by Paragon’s spyware. This move not only alerted the victims but also demonstrated WhatsApp’s commitment to transparency and user safety.
Collaboration with Cybersecurity Experts
At the same time, the collaboration between independent researchers and Meta was instrumental in the broader investigation. By sharing detailed infrastructure analysis, the researchers enabled WhatsApp to mitigate the exploit and attribute it directly to Paragon Solutions. This cooperation between the private sector and independent cybersecurity experts is increasingly seen as a best practice in the fight against digital espionage.
Impact on Law Enforcement and International Policies
The repercussions of this case have also been felt on an international scale. For instance, in Canada, the investigation’s findings have further fueled debates about the use of spyware by law enforcement agencies. The association between suspicious IP addresses and the Ontario Provincial Police has intensified calls for more robust oversight mechanisms. Critics argue that using such advanced surveillance tools without adequate transparency or public accountability seriously threatens civil liberties.
Similarly, the incident has pressured European governments to reassess their cybersecurity policies. The Italian government, in particular, found itself at the center of attention when it was revealed that it had previously been a customer of Paragon Solutions. Although Italian officials initially denied targeting journalists and activists, they eventually confirmed their association with the firm. In response, the government suspended Paragon deployments pending further investigation. This move has been interpreted as a step toward greater accountability and oversight in using surveillance technology.
The Broader Implications for Privacy and Digital Security
The Paragon Solutions case is a stark reminder of the vulnerabilities that persist even in the digital age. For years, cybersecurity experts have warned that zero-day exploits represent one of the most significant risks to modern communication systems. The recent attack on WhatsApp, exploiting a previously unknown vulnerability, highlights the potential for such exploits to be used as tools of surveillance against vulnerable populations.
Challenges Posed by Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
One of the most troubling aspects of this incident is that it illustrates how even well-established companies like WhatsApp can fall prey to sophisticated cyberattacks. The fact that the vulnerability was patched server-side without requiring users to update their devices suggests that attackers had managed to leverage an exploit deeply embedded in the system’s architecture. This not only underscores the technical prowess of the perpetrators but also raises critical questions about the readiness of global digital infrastructures to handle emerging threats.
The Ethics of Commercial Spyware
Furthermore, the incident calls into question the ethics of selling and deploying commercial spyware. Paragon Solutions has long maintained that its products are only sold to governments that adhere to international norms and respect civil liberties. However, the evidence now suggests that, in practice, deploying such tools can lead to abuses against legitimate civil society actors. The targeting of journalists and human rights activists, groups that are essential to a functioning democracy, is particularly concerning. It is a cautionary tale about the dangers of allowing surveillance technologies to proliferate without sufficient regulatory safeguards.
Legal and Regulatory Challenges
The evolving landscape of digital surveillance has brought significant legal and regulatory challenges. The Paragon case is emblematic of the difficulties governments and international bodies face in attempting to regulate the use of spyware. Unlike traditional weapons, spyware operates in a highly technical realm and is deeply intertwined with national security, privacy, and human rights issues.
Cross-Border Cyber Operations
One major hurdle in regulating spyware is the global nature of cyber operations. With suspected deployments in countries as varied as Australia, Canada, Cyprus, Denmark, Israel, and Singapore, it is clear that the reach of these tools extends far beyond national borders. This cross-border characteristic complicates efforts to create unified legal frameworks or international treaties that could govern the sale and use of surveillance technologies.
The Rapid Pace of Technological Advancement
Moreover, the rapid pace of technological advancement means that legal systems often struggle to keep up. When new regulations are enacted, the technology may have already evolved to a point where the old rules no longer apply. This dynamic creates a constantly shifting legal landscape where governments and private entities must continuously adapt their practices to remain compliant and ethical.
Therefore, The Paragon investigation serves as a call to action for policymakers worldwide. It underscores the urgent need for a collaborative international approach that addresses not only the technical aspects of cybersecurity but also the ethical and human rights implications of digital surveillance. By engaging a broad range of stakeholders—from government agencies to private companies and civil society organizations—there is hope for developing more robust mechanisms to oversee and regulate the use of spyware.
The Role of Collaboration in Combating Cyber Threats
A notable takeaway from the recent investigation is the importance of collaboration among various stakeholders in combating cyber threats. The partnership between independent cybersecurity researchers and major technology companies like Meta was critical in detecting and mitigating the zero-click exploit that targeted WhatsApp users.
The Value of a Unified Approach
This cooperative approach is increasingly vital in today’s interconnected world. Cyberattacks do not respect national boundaries, and perpetrators often operate in complex networks that span multiple jurisdictions. As a result, no single entity—be it a government agency or a private corporation—can effectively address these threats in isolation. Instead, a collaborative model that leverages the expertise of various actors is essential for mounting a comprehensive defense against digital espionage.
Enhancing Forensic Capabilities
Furthermore, this case highlights the role of forensic analysis in modern cybersecurity efforts. The discovery of the BIGPRETZEL artifact provided a crucial link between the compromised devices and the spyware operation. This level of detailed forensic work not only aids in attribution but also enhances the overall understanding of how advanced spyware operates, paving the way for improved defensive measures in the future.
Conclusion: Lessons Learned and the Road Ahead
The investigation into Paragon Solutions and its Graphite spyware has laid bare the complex interplay between technology, ethics, and governance in the modern digital landscape. It has demonstrated that even companies with claims of ethical restraint can become embroiled in controversies that threaten civil liberties and undermine public trust. The incident is a stark reminder of the need for robust security practices, greater transparency, and comprehensive oversight of surveillance technologies.
Key Takeaways
In light of these events, several lessons emerge. First, exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities remains one of the most potent threats to digital communication platforms. This underscores the cybersecurity community’s need for constant vigilance and rapid response mechanisms. Second, the case illustrates the importance of international collaboration—not only between tech companies and cybersecurity researchers but also among governments and regulatory bodies—to address the cross-border nature of cyber threats. Finally, the ethical use of surveillance tools must be a central consideration. Targeting journalists and civil society members, groups that play a crucial role in holding power to account represents a significant breach of public trust and highlights the potential dangers of unregulated spyware deployment.
The Road Ahead
The digital world must adapt to meet these challenges head-on as we move forward. By fostering a culture of collaboration, investing in advanced forensic capabilities, and developing clear, enforceable regulatory frameworks, the global community can work towards a safer, more transparent digital future. The case of Paragon Solutions is not just a story of technological innovation and cyber espionage—it is a call to action for all stakeholders to prioritize protecting human rights and the integrity of digital communications.
In conclusion, while the rapid evolution of technology offers unprecedented opportunities, it also brings equally unprecedented risks. The recent revelations about Paragon Solutions underscore the importance of maintaining robust defenses against cyber threats, ensuring ethical oversight of surveillance tools, and promoting accountability at every level. The lessons learned from this investigation will undoubtedly shape the future of cybersecurity and surveillance regulation, guiding efforts to safeguard the freedoms and privacy of individuals in an increasingly interconnected world.