In today’s digital landscape, cybersecurity threats evolve with alarming sophistication. One of the latest examples is the emergence of a remote access trojan (RAT) known as ResolverRAT, which was recently identified in targeted attacks against the healthcare and pharmaceutical sectors. This article provides an in-depth look into ResolverRAT, its techniques, and its potential impact on organizations. Additionally, we will compare it with other notable threats, such as Neptune RAT, offering insights into how these sophisticated malware families operate and what measures can be taken to defend against them.
Overview of ResolverRAT

ResolverRAT is a highly advanced remote access trojan that cybersecurity researchers have recently uncovered. It has been designed to infiltrate systems, establish persistent access, and execute commands from remote command-and-control (C2) servers. The primary initial infection method appears to be phishing emails that employ fear-based tactics to lure victims into clicking malicious links. These emails use a range of persuasive themes, including legal investigations and copyright violations, to create a false sense of urgency.
Sophisticated Phishing Techniques
The phishing emails associated with ResolverRAT are particularly notable for their use of localized language and culturally relevant content. This strategic approach involves crafting messages in several languages—including Hindi, Italian, Czech, Turkish, Portuguese, and Indonesian—to maximize the likelihood of engagement across diverse regions. By tailoring the phishing content to the linguistic and cultural nuances of the target audience, the attackers significantly increase the success rate of their campaigns.
The Infection Process
Once a victim clicks on the malicious link, they are directed to download a file that triggers the execution chain of ResolverRAT. The infection process employs a complex technique known as DLL side-loading. This method uses a seemingly legitimate dynamic-link library (DLL) to load and execute the malicious payload. During the initial stage, an in-memory loader decrypts and executes the primary payload while implementing multiple strategies to evade detection. These strategies include encryption, compression, and the fact that the payload resides only in memory once decoded, leaving minimal traces on the infected system.
Technical Deep Dive into ResolverRAT
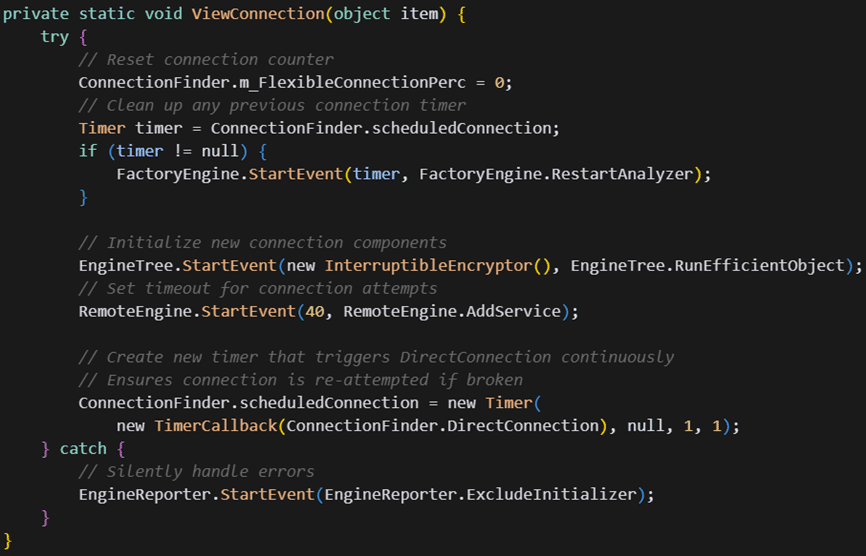
Understanding the technical aspects of ResolverRAT reveals the depth of planning behind its design. The malware incorporates several advanced mechanisms that ensure both stealth and resilience.
Multi-Stage Bootstrapping Process
The initialization sequence of ResolverRAT is particularly sophisticated. It begins with a multi-stage bootstrapping process engineered to operate covertly within the infected system. Initially, an in-memory loader is deployed, which performs the critical function of decrypting the primary payload. This method avoids leaving detectable artifacts on the system’s hard drive, complicating forensic analysis and malware detection efforts.
Redundant Persistence Mechanisms
Once the payload is active, ResolverRAT implements multiple redundant persistence methods. These include modifications to the Windows Registry and installing copies of the malware in various locations within the file system. The redundancy ensures that if security software detects and removes one persistence method, other mechanisms will maintain the malware’s foothold on the system.
Command-and-Control Communication
A standout feature of ResolverRAT is its robust command-and-control (C2) communication system. Before initiating contact with a C2 server, the malware performs a bespoke certificate-based authentication process. This ensures the malware bypasses the usual security checks the host system’s root authorities perform. Furthermore, ResolverRAT employs an IP rotation mechanism, allowing it to seamlessly connect to alternate C2 servers if the primary one is taken down or unreachable. This design significantly complicates defenders’ efforts to block the malware’s communications.
Evasion Techniques
To further complicate detection, ResolverRAT utilizes several evasion techniques. Certificate pinning, for instance, helps prevent interception and analysis of the malware’s communication channels. Additionally, the malware’s source code is heavily obfuscated, making it difficult for cybersecurity professionals to reverse-engineer its functions. Its irregular beaconing patterns—unpredictable intervals at which it communicates with the C2 server—further hinder detection by conventional network monitoring systems.
Regional and Cultural Adaptation in Attack Strategies
An interesting aspect of the ResolverRAT campaign is the attackers’ use of region-specific phishing lures. By crafting emails in languages predominant in the target regions, the threat actors increase the likelihood of engagement and reduce suspicion. This localized approach demonstrates a high level of planning and suggests that the threat actors have invested significant resources in understanding the target demographics.
The Role of Fear and Urgency
The thematic content of phishing emails plays a critical role in the success of these campaigns. The emails invoke themes such as legal investigations and copyright violations to create a sense of urgency and fear. This psychological manipulation often compels recipients to take immediate action, such as clicking on the malicious link or downloading the infected file without proper scrutiny. Exploiting human emotions is a well-known tactic in social engineering; in this case, it is used to devastating effect.
Comparing ResolverRAT with Neptune RAT
In parallel with the discovery of ResolverRAT, another dangerous remote access trojan—Neptune RAT — has come to light. While both malware families share similarities in using sophisticated evasion and persistence techniques, they differ in key operational methodologies and objectives.
Introduction to Neptune RAT

Neptune RAT is a modular, plugin-based remote access trojan designed to perform various malicious activities. Unlike ResolverRAT, which has been primarily observed in the healthcare and pharmaceutical sectors, Neptune RAT has a broader target range and is disseminated more freely via public platforms such as GitHub, Telegram, and YouTube.
Modular Design and Capabilities
Neptune RAT’s modular architecture extends it easily and provides additional functionality. This design enables the malware to incorporate features such as crypto clipping, password stealing, ransomware capabilities, and even live desktop monitoring. With the ability to exfiltrate credentials from over 270 different applications, Neptune RAT poses a significant threat by potentially compromising a wide array of sensitive data.
Anti-Analysis and Persistence Techniques
Like ResolverRAT, Neptune RAT incorporates advanced anti-analysis measures and multiple methods for maintaining persistence on infected systems. Its use of obfuscation and anti-debugging techniques makes it challenging for security professionals to analyze and counteract its functions. Moreover, Neptune RAT employs persistence mechanisms that ensure its continued presence on the system even if one method is compromised, reflecting a level of operational sophistication that is concerning for cybersecurity teams.
Impact and Threat Landscape
ResolverRAT and Neptune RAT represent a growing trend of increasingly complex and evasive malware. The similarity in their design, particularly in terms of DLL side-loading and redundant persistence methods, suggests that there may be an overlap in the threat actor infrastructure or a shared set of tactics among related cybercriminal groups. This coordinated approach highlights the evolution of cyber threats, where attackers continuously refine their methods to bypass traditional security measures.
How the Malware Operates in Real-World Scenarios

Understanding the operational mechanics of these trojans in real-world settings is crucial for developing effective defensive strategies. ResolverRAT and Neptune RAT are designed to infiltrate systems, maintain long-term access, exfiltrate data, and potentially disrupt system operations.
Data Exfiltration Strategies
Once established on a system, ResolverRAT begins processing commands from its C2 server. One of the more technical aspects of its design is its method for exfiltrating data. The malware breaks data over 1 MB in size into 16 KB chunks, a technique likely implemented to avoid triggering alarms on network monitoring systems that look for large, unusual data transfers. This granular approach to data exfiltration minimizes the detection risk and ensures that the malware can operate continuously without drawing undue attention.
Command Processing and Execution
The primary goal of ResolverRAT is to act as a remote access tool that can execute commands issued by the attacker. Once a connection with a C2 server is established, the malware processes these commands and returns the results. This capability enables threat actors to perform a wide range of actions on infected systems—from stealing sensitive information to installing additional malicious software, thereby expanding the scope of the attack.
Defensive Measures and Best Practices
Given the advanced techniques that ResolverRAT and Neptune RAT employ, organizations must adopt a multi-layered cybersecurity strategy to protect against these threats. Below are some recommended defensive measures and best practices:
Strengthening Email Security
Since phishing emails are the primary vector for these attacks, enhancing email security is crucial. Organizations should deploy advanced email filtering solutions to detect and block suspicious messages based on content, language, and embedded links. Training employees to recognize phishing attempts is equally important, as human error remains one of the leading causes of successful cyberattacks.
Endpoint Protection and Monitoring
Another critical step is investing in robust endpoint protection solutions that monitor real-time system behavior. These solutions should be capable of detecting anomalous processes, such as unauthorized DLL side-loading or unusual memory usage, indicative of malware activity. Additionally, continuous network traffic monitoring can help identify irregular beaconing patterns associated with C2 communications.
Regular System Updates and Patching
Keeping software and operating systems up to date with the latest security patches is an essential defense against many forms of malware. Attackers often exploit known vulnerabilities that have already been patched in the latest software versions. Regular updates reduce the attack surface and limit the opportunities for threat actors to infiltrate systems.
Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds a layer of security by requiring multiple verification forms before granting access to sensitive systems or data. Even if malware like ResolverRAT manages to compromise credentials, MFA can serve as a critical barrier that prevents unauthorized access.
Incident Response and Recovery Planning
Organizations must also develop robust incident response plans to address and contain any security breaches quickly. This involves detecting and neutralizing the malware and ensuring that backups are regularly maintained. In the event of a successful attack, having a recovery plan in place can significantly reduce downtime and minimize data loss.
The Future of Malware Threats

The emergence of ResolverRAT and Neptune RAT is a stark reminder that cyber threats are continually evolving. Cybercriminals constantly refine their techniques to bypass security measures and exploit vulnerabilities in modern IT infrastructures. Cybersecurity professionals must remain vigilant and proactive as these threats become more sophisticated.
Evolving Tactics and Techniques
The trends observed in ResolverRAT—such as using in-memory loaders, multiple persistence mechanisms, and advanced C2 communication strategies—will likely become more common in future malware. Attackers are increasingly leveraging automation and machine learning to refine these techniques further, making it more challenging for traditional security measures to keep pace.
Collaboration and Information Sharing
In the face of these evolving threats, collaboration among cybersecurity professionals, organizations, and government agencies is more important than ever. Sharing information about new malware strains, attack vectors, and defensive strategies can help create a more resilient security ecosystem. Initiatives like threat intelligence sharing platforms and industry-wide cybersecurity standards are critical in this ongoing battle.
Preparing for a Proactive Defense
Organizations must shift from a reactive security posture to a proactive and anticipatory one. This includes investing in the latest cybersecurity technologies and fostering a culture of security awareness across all levels of the organization. By anticipating potential threats and preparing in advance, companies can significantly reduce the likelihood of a successful attack and mitigate the damage if one does occur.
Conclusion
The discovery of ResolverRAT, alongside threats like Neptune RAT, highlights a concerning trend in the cybersecurity landscape. These remote access trojans are designed with advanced techniques that allow them to bypass traditional security measures, persist on systems, and execute commands with high stealth. The implications are particularly severe for organizations in high-risk sectors such as healthcare and pharmaceuticals.
By understanding the technical intricacies of these malware families—from the initial phishing attack to the sophisticated persistence and communication mechanisms—security professionals can better prepare to defend against them. Implementing robust email security, endpoint protection, regular patching, multi-factor authentication, and a comprehensive incident response plan are essential steps in mitigating the risks posed by these threats.
The evolution of malware like ResolverRAT and Neptune RAT is a potent reminder that cybersecurity is not a static field. Threat actors are continuously adapting, and the defenses must evolve in parallel. Staying informed about the latest trends, collaborating across industries, and proactively strengthening cybersecurity defenses are the best ways to safeguard critical systems and sensitive data in an increasingly hostile digital environment.
As cyber threats continue to advance, the importance of a resilient and adaptive cybersecurity strategy cannot be overstated. Organizations must invest in technology and human capital to ensure they are prepared to counter these sophisticated attacks. By fostering a culture of continuous improvement and vigilance, companies can defend against current threats and be ready to meet the challenges of tomorrow’s cyber landscape.
Sources: Security Affairs, Cybersecurity News, The Hacker News