On April 29, 2025, the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) added a critical vulnerability in SAP NetWeaver to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog. Tracked as CVE-2025-31324, this zero-day flaw carries a maximum CVSS 3.1 score of 10.0 and has been exploited in the wild since at least March 2025. Organizations running SAP NetWeaver Application Server Java (AS Java) with the Visual Composer component must take immediate action to prevent full system compromise.
What Is SAP NetWeaver Visual Composer?
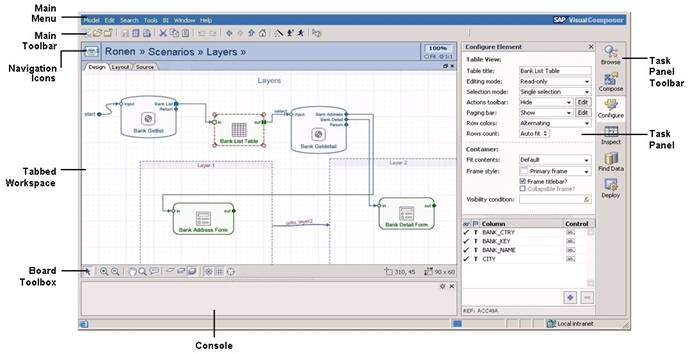
SAP NetWeaver Visual Composer is a graphical, model-driven tool that enables business users and process specialists to build applications without writing code manually. Although not installed by default, Visual Composer is estimated to be enabled on 50–70 percent of SAP Java systems because of its ease of use and popularity in rapid application development.
Timeline of Public Reporting and Exploitation
- March 2025: First evidence of exploitation appears in global threat-intelligence feeds.
- April 22, 2025: Security firm ReliaQuest publicly reports active attacks against the Visual Composer “development server/metadatauploader” endpoint.
- April 24, 2025: SAP issues an emergency patch via Security Note #3594142.
- April 29, 2025: CISA adds CVE-2025-31324 to its KEV catalog, mandating remediation by May 20, 2025, for U.S. federal agencies.
Technical Details of the Vulnerability
Nature of the Flaw (CWE-434)
CVE-2025-31324 is classified under CWE-434: Unrestricted Upload of File with Dangerous Type. The Metadata Uploader component does not enforce authentication or file-type restrictions, allowing unauthenticated attackers to submit arbitrary files, including executable binaries or JSP web shells, to the target server.
Vulnerable Endpoint and Component
- Component: Visual Composer (VCFRAMEWORK 7.50)
- Endpoint: /development server/metadatauploader
- Prerequisites: Network access only; no valid SAP credentials required.
Impact and Risk Assessment
Remote Code Execution and Full System Compromise
Once a malicious JSP web shell is uploaded, threat actors gain the ability to execute arbitrary code in the context of the Java application server. This effectively hands over complete control of the SAP system, enabling:
- Extraction of financial records and sensitive business data
- Manipulation of transactional processes
- Lateral movement into connected on-premises or cloud systems
According to Onapsis, exploitation can result in “immediate full compromise” of affected environments, making CVE-2025-31324 one of the most severe SAP vulnerabilities in recent years.
Exposure in Enterprise Environments
Enterprises often focus security investments on perimeter defenses and cloud workloads, leaving legacy SAP systems relatively under-hardened. Visual Composer endpoints may be inadvertently exposed to untrusted networks, increasing the likelihood of successful attacks.
Detection and Indicators of Compromise
Unusual Files in SAP Directories
SAP has published guidance on how to look for unfamiliar .jsp, .java, or .class files under Visual Composer directories. Key directories to audit include:
- <SAP_INSTALL_DIR>/vc/VC framework
- <SAP_WORK_DIR>/usr/sap/<SID>/JC<nr>/j2ee/cluster/server*/applications/VCFRAMEWORK
Log-Based Detection
Monitoring HTTP POST requests to /development server/metadatauploader—especially those returning 200 OK status codes with large payloads—can reveal file-upload attempts. Integrate these patterns into SIEM alerts to flag potential exploitation.
Mitigation and Remediation Strategies

Emergency Patch Deployment
SAP’s Security Note #3594142 provides a corrective update introducing authentication checks and file-type validation in the Metadata Uploader component. Organizations should:
- Download and apply the patch on all AS Java instances running Visual Composer.
- Validate that the uploaded file functionality now enforces user authentication and restricts extensions to safe types (e.g., .xml, .txt).
Temporary Workarounds (SAP Note #3593336)
For environments that cannot immediately install the emergency patch, SAP recommends:
- Blocking access to /development server/metadatauploader via network ACLs or web-dispatcher rules.
- You can turn off the Metadata Uploader component by renaming or removing the vcframework.jar file (note: this will suspend Visual Composer functionality).
- Implementing WAF rules to inspect and block multipart file uploads targeting Visual Composer endpoints.
Compliance Requirements
CISA KEV Catalog and Binding Operational Directive 22-01
Federal civilian agencies in the United States must remediate CVE-2025-31324 by May 20, 2025, per CISA’s Binding Operational Directive (BOD) 22-01. Non-compliance may trigger increased oversight and reporting mandates.
Industry Best Practices
Beyond federal requirements, all organizations handling sensitive data should treat this vulnerability as a top priority. Recommended actions:
- Align patching timelines with critical CVSS 9.0+ vulnerabilities (within 15 days).
- Conduct post-patch penetration testing on SAP landscapes.
- Review and tighten network segmentation to isolate management interfaces.
Long-Term Hardening Recommendations

Principle of Least Functionality
- Uninstall or turn off unused SAP components, including Visual Composer, on production systems.
- Regularly audit installed modules and remove development-oriented tools from live environments.
Continuous Monitoring and Threat Intelligence
- Subscribe to SAP security advisories and CISA alerts to stay informed of emerging threats.
- Integrate SAP-specific threat intelligence feeds (e.g., Onapsis, SAP Enterprise Threat Detection) into your SOC.
Secure Development Lifecycle for Low-Code Tools
- Apply the same code review and testing rigor to model-driven tools and custom code.
- Enforce strong authentication (e.g., SAML, MFA) on all development interfaces.
Conclusion
CVE-2025-31324 represents a critical risk to any organization using SAP NetWeaver Visual Composer. Its unrestricted file upload nature enables unauthenticated remote code execution, leading to full system takeover and data exfiltration. Immediate application of SAP’s emergency patch (Security Note #3594142) or implementation of temporary mitigations (SAP Note #3593336) is essential. Furthermore, enterprises must adopt long-term hardening measures, such as turning off unused components, strengthening network segmentation, and enhancing monitoring, to reduce the attack surface of their SAP landscapes. By treating low-code and graphical development tools with the same security scrutiny as custom code, organizations can better defend against advanced threat actors targeting mission-critical business systems.