How AkiraBot OpenAI Spam Targets 420,000 Sites Effortlessly

Hoplon InfoSec
10 Apr, 2025
The rapid evolution of artificial intelligence has not only revolutionized the way we work, communicate, and innovate but has also introduced new challenges in cybersecurity. One of the most alarming recent developments is the emergence of an AI-powered platform known as AkiraBot. This blog post provides an in-depth examination of AkiraBot, outlining how it operates, its technical underpinnings, and the broader implications for website security. Additionally, we will discuss emerging cybercrime tools and present mitigation strategies that website owners and cybersecurity professionals can adopt to defend against such threats.
Understanding kiraBot OpenAI Spam
What is AkiraBot?
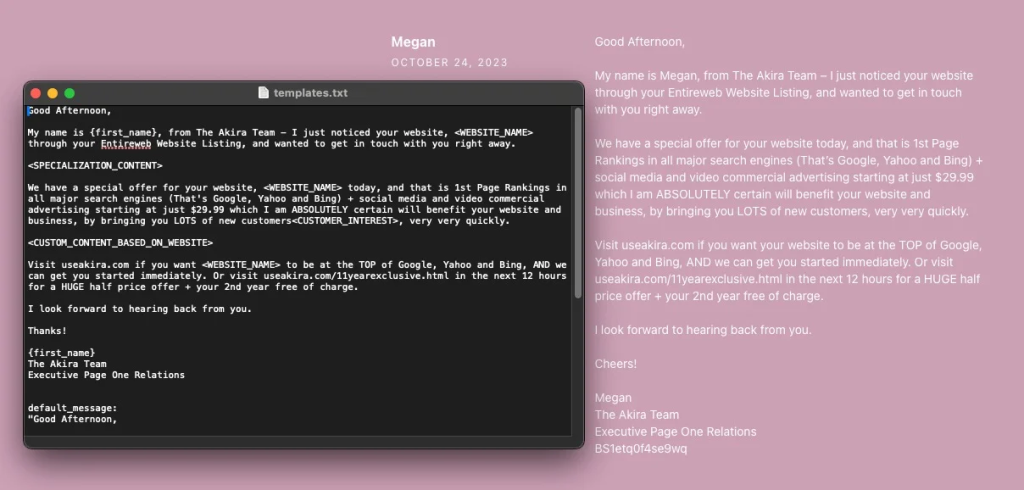
AkiraBot is an automated tool that leverages artificial intelligence to generate and distribute spam messages across website chat interfaces, comment sections, and contact forms. According to cybersecurity researchers, AkiraBot has been used to promote dubious search engine optimization (SEO) services, including brands such as Akira and ServicewrapGO. The tool has already targeted over 400,000 websites and successfully spammed more than 80,000 websites since its operations began in September 2024.
At its core, AkiraBot harnesses the capabilities of OpenAI’s large language models (LLMs) to create tailored outreach messages. By analyzing the content and purpose of a website, the bot can craft messages that appear relevant and context-specific, thereby increasing the likelihood of bypassing spam filters and evading detection by website administrators.
How Does AkiraBot Operate?
AkiraBot’s operation is a blend of sophisticated programming and the strategic use of AI-generated content. The developers behind the tool have integrated it with OpenAI’s API, which allows the bot to generate custom messages. Here’s a closer look at its modus operandi:
- Template-Based Message Generation: The bot starts with a generic template that outlines the structure and intent of the message it intends to send. This template is then processed via a prompt sent to the OpenAI chat API. The AI customizes the message according to the specific content and context of each targeted website, ensuring that the outreach message seems natural and purposeful.
- Python-Based Framework: AkiraBot is built using Python, a programming language known for its versatility and efficiency in handling automated tasks. This choice of language facilitates rapid development and allows the bot to be easily updated as new tactics are required to bypass evolving security measures.
- Graphical User Interface (GUI): The tool includes a GUI that simplifies the process of selecting target websites and setting parameters such as the number of concurrent spam attempts. This user-friendly design lowers the barrier to entry, enabling even less technically proficient individuals to exploit the tool for malicious purposes.
Technical Aspects of the AkiraBot Platform
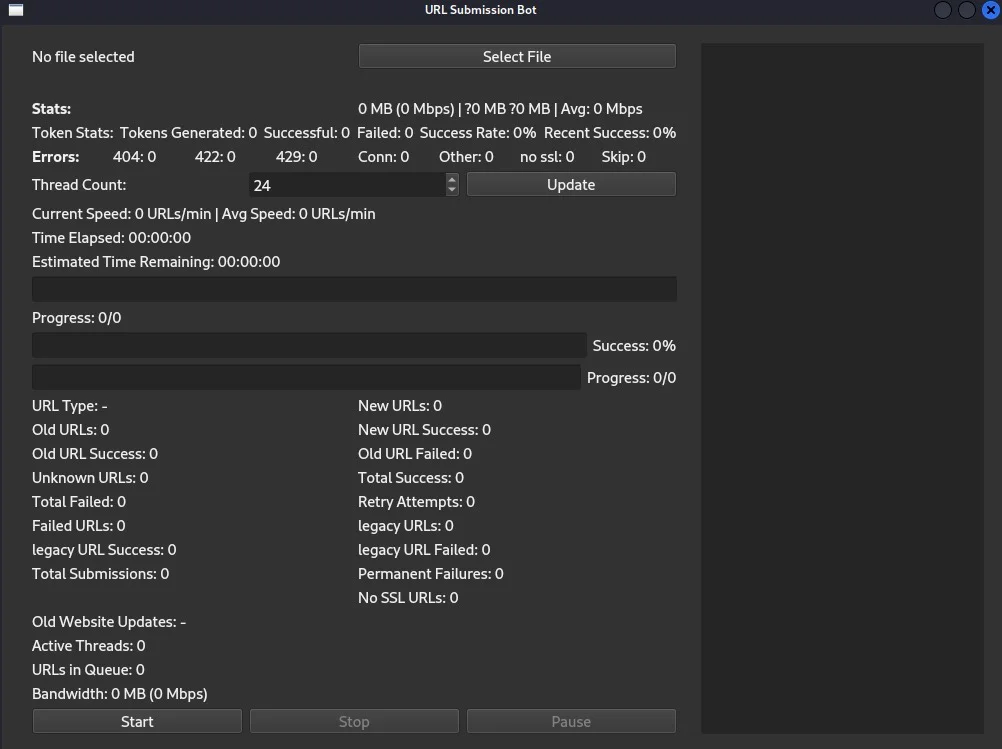
AI-Powered Customization and the OpenAI API
A standout feature of AkiraBot is its integration with OpenAI’s API. By utilizing models such as the GPT-4o-mini, the bot is able to act as a “helpful assistant” that crafts marketing messages tailored to each website’s specific context. This dynamic approach to spam message creation not only increases the effectiveness of the outreach but also makes it much harder for standard spam filters to flag the messages as generic or automated.
The use of AI in this manner demonstrates how advanced language models can be repurposed for cybercriminal activities. What was once considered a tool for benign or constructive applications is now being harnessed to facilitate widespread spam and potentially fraudulent activities.
Bypassing Security Measures
One of the most sophisticated aspects of AkiraBot is its ability to bypass common security measures:
- CAPTCHA Evasion: Many websites rely on CAPTCHA systems such as hCAPTCHA, reCAPTCHA, and Cloudflare Turnstile to verify that interactions on their sites are legitimate. AkiraBot, however, has been engineered to overcome these barriers. By mimicking legitimate user behaviour and employing advanced techniques, the bot can bypass CAPTCHA challenges, allowing it to infiltrate websites en masse.
- Use of Proxy Services: To mask its activities further, AkiraBot uses proxy services like SmartProxy. This strategy obscures the origin of the bot’s web traffic, making it difficult for network-based defences to identify and block malicious activity. By rotating between different proxy hosts, the tool effectively minimizes the chances of being detected and blocked by security systems.
- Activity Logging and Metrics: The bot keeps a detailed log of its activities in a file named “submissions.csv,” recording both successful and unsuccessful spam attempts. This blog is not just for record-keeping; it also helps the operators analyze the bot’s effectiveness and adjust their tactics accordingly. Furthermore, the success metrics related to CAPTCHA bypass and proxy rotation are sent to a Telegram channel via an API, allowing real-time monitoring of the bot’s performance.
Security Implications and Industry Response
Analysis by Cybersecurity Researchers
SentinelOne researchers, including Alex Delamotte and Jim Walter, have provided detailed insights into AkiraBot’s operations. Their analysis reveals that the bot’s effectiveness in bypassing CAPTCHA systems and evading network detections is a testament to the significant effort invested by its developers. Such advancements in bot design underscore the evolving challenges in defending websites against AI-powered spam attacks.
The researchers noted that the bot’s ability to generate customized spam messages using OpenAI’s API marks a new phase in the ongoing battle between cybercriminals and cybersecurity professionals. The complexity and sophistication of AkiraBot are clear indicators that cyber threat actors are increasingly leveraging advanced AI to enhance their operational capabilities.
Response from Service Providers
In response to the threat posed by AkiraBot, OpenAI has taken decisive action by turning off the API key and associated assets that the threat actors were using. This move highlights a critical aspect of cybersecurity in the AI era: the need for technology providers to monitor and, when necessary, intervene when their platforms are misused for malicious purposes.
The quick response from OpenAI also sets a precedent for how companies can and should react when their services are exploited. By disabling access to their API, OpenAI not only mitigates the immediate threat but also signals to other providers that there is a collective responsibility to safeguard against the misuse of AI technologies.
The Broader Landscape of AI-Powered Cybercrime Tools
Emergence of New Threats: Xanthorox AI
The rise of AkiraBot is part of a larger trend where cybercriminals are increasingly employing AI-powered tools to enhance their operations. One notable example is a tool known as Xanthorox AI. Marketed as an all-in-one chatbot, Xanthorox AI is designed for a variety of nefarious purposes, including code generation, malware development, vulnerability exploitation, and data analysis.
What sets Xanthorox AI apart is its unique operational framework:
- Local-First Deployment: Unlike many other tools that rely on public cloud infrastructure, Xanthorox AI operates on local servers controlled by the seller. This approach drastically reduces the risk of detection, shutdown, or traceability, making it an attractive option for cybercriminals looking to maintain a low profile.
- Multi-Model Architecture: Five distinct models power Xanthorox AI, each optimized for specific tasks. This specialization allows the tool to handle a wide range of activities effectively, from generating code to exploiting vulnerabilities. The versatility of Xanthorox AI illustrates the expanding toolkit available to cyber threat actors, further complicating efforts to defend against such attacks.
Challenges in Combating AI-Driven Cybercrime
The advent of AI-powered cybercrime tools like AkiraBot and Xanthorox AI poses significant challenges for the cybersecurity community. Traditional security measures are often inadequate in the face of dynamic, adaptive threats that leverage machine learning to evolve and circumvent defences. As these tools become more prevalent, organizations must rethink their strategies and invest in more robust, AI-driven defences.
Mitigation Strategies for Website Owners and Cybersecurity Professionals
Enhancing CAPTCHA and Bot Detection
One of the first lines of defence against automated spam and cyber attacks is the implementation of robust CAPTCHA systems. However, as evidenced by AkiraBot’s capabilities, traditional CAPTCHA solutions may no longer suffice. Website owners are encouraged to consider the following enhancements:
- Dynamic CAPTCHA Systems: Utilize CAPTCHA systems that continuously evolve based on the latest threat intelligence. Dynamic CAPTCHAs can adapt to new patterns of automated behaviour, making it more challenging for bots to bypass them.
- Behavioural Analysis: Incorporate behavioural analysis tools that monitor user interactions for signs of automation. By analyzing patterns such as mouse movements, keystroke dynamics, and interaction timings, these tools can help differentiate between legitimate users and bots.
Leveraging Advanced Network Defenses
In addition to improving CAPTCHA systems, website owners should bolster their network defences:
- Proxy and Traffic Analysis: Implement solutions that analyze web traffic to identify anomalies associated with proxy use and unusual access patterns. By flagging and scrutinizing traffic from known proxy sources, organizations can reduce the risk of automated attacks.
- Rate Limiting and Throttling: Apply rate limiting on forms and chat interfaces to restrict the number of submissions from a single source. This can help prevent bulk spam attacks by limiting the volume of messages that can be sent in a given period.
- Comprehensive Logging and Monitoring: Maintain detailed logs of user activity and monitor these logs for suspicious behaviour. Automated analysis of these logs can alert administrators to unusual patterns that may indicate the presence of a bot like AkiraBot.
Collaborative Cyber Threat Intelligence
Given the rapidly evolving nature of AI-driven cybercrime, collaboration between organizations and cybersecurity professionals is more important than ever. Sharing threat intelligence can help identify emerging patterns and develop countermeasures more effectively:
- Information Sharing Networks: Participate in information-sharing networks and cybersecurity forums where professionals can exchange insights on new threats and effective defence strategies. These networks are invaluable in keeping pace with the latest developments in cybercrime.
- Industry Collaboration: Work with technology providers such as OpenAI and CAPTCHA vendors to ensure that their systems are updated to counteract new threats. Proactive collaboration can help prevent tools like AkiraBot from exploiting vulnerabilities in widely used platforms.
Future Trends in AI-Powered Cybersecurity Threats
The Evolving Role of AI in Cybercrime
As artificial intelligence continues to advance, its dual-use nature becomes increasingly evident. While AI has the potential to transform industries and improve security measures, it also equips cybercriminals with tools that are more adaptive and efficient. Future threats may include even more sophisticated bots that are capable of learning from their interactions and continuously refining their tactics.
The cybersecurity landscape is likely to witness a surge in AI-driven attacks that leverage a combination of natural language processing, machine learning, and advanced automation. These attacks could range from targeted phishing campaigns to large-scale spam operations that disrupt online services and compromise user data.
Preparing for the Next Wave of Cyber Threats
In light of these challenges, organizations must take proactive steps to safeguard their digital assets:
- Invest in AI-Enhanced Security Solutions: Embrace security solutions that themselves use AI to detect and respond to threats in real time. These solutions can analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns indicative of an attack, and deploy countermeasures much faster than traditional systems.
- Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing: Conduct regular audits and penetration tests to identify vulnerabilities in your digital infrastructure. By simulating potential attack scenarios, organizations can better prepare for and defend against real-world threats.
- Ongoing Education and Training: Educate staff and stakeholders about the latest cybersecurity trends and best practices. Continuous training ensures that everyone, from IT professionals to end-users, is aware of the risks and knows how to respond to potential threats.
The Broader Impact on Digital Ecosystems
Economic and Reputational Risks
The use of AI-powered spam tools like AkiraBot is not just a technical challenge—it also poses significant economic and reputational risks for businesses. For small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), a successful spam attack can lead to loss of customer trust, damage to brand reputation, and even financial losses due to decreased website functionality or downtime.
Moreover, as these tools become more advanced, even larger organizations are at risk. The cost of mitigating such attacks can be substantial, and the indirect impact on customer relationships can have long-lasting consequences. It is, therefore, critical for companies to invest in robust cybersecurity infrastructure and maintain vigilance against evolving threats.
The Role of Regulatory and Policy Measures
Regulatory bodies and policymakers are increasingly recognizing the need for frameworks that address the misuse of AI. Future regulations may focus on the ethical deployment of AI technologies, establishing clear guidelines for usage, and imposing penalties for misuse. Companies that fail to adhere to these standards could face significant legal and financial repercussions.
Businesses need to stay informed about emerging regulations and adapt their practices accordingly. Proactive compliance with cybersecurity standards not only protects against threats like AkiraBot but also builds a foundation of trust with customers and partners.
Conclusion
The emergence of AkiraBot underscores a critical turning point in the cybersecurity landscape. As AI-powered tools become more accessible and sophisticated, they are increasingly being exploited for malicious purposes such as mass spamming and fraudulent outreach. The detailed analysis provided by cybersecurity researchers highlights the significant technical advancements that have enabled these tools to bypass traditional security measures, such as CAPTCHAs and network-based detections.
The rapid response from companies like OpenAI, which have disabled compromised API keys, illustrates that the cybersecurity community is actively working to mitigate these threats. However, as demonstrated by the parallel emergence of tools like Xanthorox AI, cybercriminals are continuously developing new methods to exploit AI for their gain.
For website owners and cybersecurity professionals, the key to staying ahead of these threats lies in a multi-layered approach that includes improved CAPTCHA technologies, advanced network defences, and robust monitoring systems. Furthermore, collaboration and information sharing within the cybersecurity community are essential to counteract the evolving tactics of AI-driven attacks.
Sources: The Hacker News, Cybersecurity News
Share this :