Cybercriminals Exploit URL Shorteners & QR Codes in Tax Phishing Campaigns

Hoplon InfoSec
06 Apr, 2025
Cybercriminals have become more sophisticated than ever in their efforts to exploit taxpayers, especially during the tax season. In recent months, attackers have refined their methods, using a blend of social engineering and technical tricks to target both individual taxpayers and professionals in the accounting and tax preparation fields. In this blog post, we delve into the tactics used by these malicious actors, explain how these attacks work, and provide actionable recommendations on how to protect yourself and your organization from these emerging threats.
The Rise of Tax Phishing Campaigns
During tax season, there is an inherent sense of urgency and sensitivity among taxpayers. Cybercriminals exploit this environment by masquerading as legitimate authorities, such as the Internal Revenue Service (IRS), and sending emails that appear to be official notifications. These messages often include claims of tax refund information, audit warnings, or updates on tax-related policies. The attackers’ aim is to create a sense of trust and urgency, leading recipients to click on embedded links or scan QR codes without second thoughts.
Exploiting Human Psychology
Phishing campaigns are designed to exploit human psychology. Attackers leverage authority and urgency to bypass critical thinking and prompt immediate action. For example, an email that appears to come from the IRS might warn of a pending audit or an issue with a tax refund. Faced with the fear of missing out on a refund or incurring penalties, many users are inclined to click on the provided link or scan a QR code, inadvertently exposing themselves to credential theft or malware infection.
How the Attack Process Unfolds
Phishing attacks in the tax domain typically follow a multi-stage process. This strategy is aimed at bypassing modern security systems and exploiting gaps in user vigilance. The process can be broken down into several key stages:
Initial Contact Through Deceptive Emails
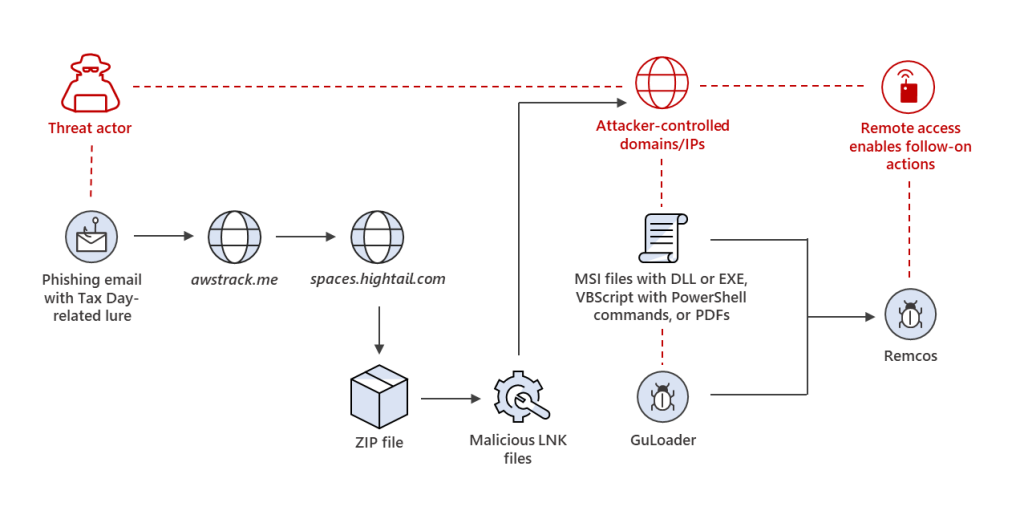
The attack usually begins with an email that appears to be a routine tax notification. These emails are carefully crafted to mimic official communications, complete with familiar logos and language. Attackers often employ redirection techniques such as URL shorteners and QR codes to obscure the true destination of any links or attachments. This redirection is a calculated move designed to evade security filters and traditional anti-phishing mechanisms.
Advanced Redirection Tactics
One of the more innovative tactics in this year’s campaigns is the use of URL shorteners and QR codes. These techniques allow threat actors to hide the malicious destination behind a seemingly innocuous link or image. When a recipient clicks on the link or scans the QR code, they are redirected to a malicious website that may host a replica of a legitimate tax or Microsoft 365 login page. This deception is designed to steal credentials, which can then be used for business email compromise, data exfiltration, or further malware deployments.
Multi-Stage Infection Chains
After the initial contact, many phishing campaigns proceed in a multi-stage fashion. The first email may establish a relationship with the recipient by being seemingly harmless. Only in follow-up communications is the malicious content delivered. This technique significantly increases the chance that the recipient will interact with the content because the attacker has already built a level of trust. Once the malicious payload is executed—whether through the download of malware or the theft of login credentials—the attackers gain a foothold within the victim’s system or network.
Case Study: QR Code Phishing with RaccoonO365 Payloads

Between February 12 and 28, 2025, a particularly concerning phishing campaign emerged that specifically targeted over 2,300 organizations. This campaign focused on sectors like engineering, IT, and consulting, and it used a clever blend of technology and personalization to increase its success rate.
How the RaccoonO365 Campaign Operated
The attackers behind this campaign sent emails that contained PDF attachments with a unique twist. Instead of including traditional clickable links or executable attachments, these PDFs featured embedded QR codes. The QR codes were the key to the attackers’ strategy, as they provided an alternative pathway to deliver the malicious payload.
Each QR code was uniquely generated for the individual recipient, incorporating their email address as a parameter. This not only allowed for personalized tracking but also gave the phishing campaign an air of legitimacy. When scanned, these QR codes redirected users to a domain that closely mimicked legitimate Microsoft services. The targeted domain, “shareddocumentso365cloudauthstorage[.]com”, was designed to look familiar and trustworthy, fooling many recipients into believing they were accessing a secure Microsoft 365 page.
The Role of the RaccoonO365 Platform
The RaccoonO365 phishing-as-a-service platform plays a central role in these campaigns. It provides attackers with pre-built phishing kits that replicate the look and feel of authentic Microsoft 365 sign-in pages. Once a victim enters their credentials on these fake pages, the information is captured by the attackers. With these credentials in hand, threat actors can infiltrate email accounts, potentially leading to business email compromise and further lateral movement within an organization’s network.
The success of this campaign was amplified by the use of familiar display names, such as “EMPLOYEE TAX REFUND REPORT” or “Tax Strategy Update Campaign Goals”. These names resonated strongly during the tax season, a period when individuals and businesses are already on high alert for tax-related communications.
The Technical Sophistication Behind Modern Phishing
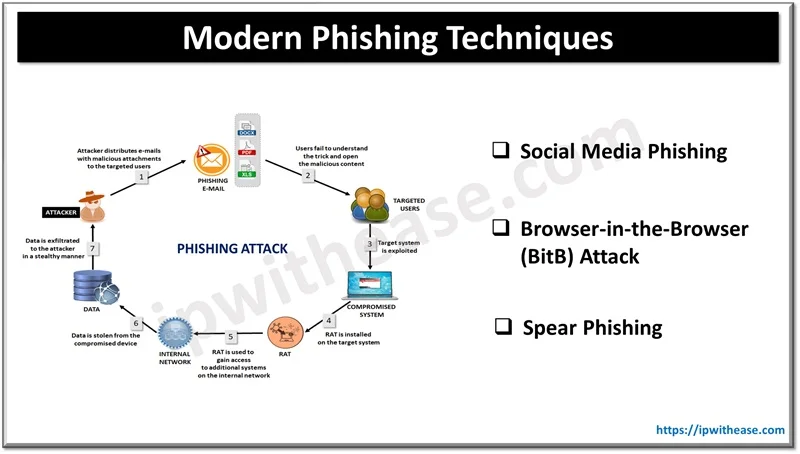
Modern phishing campaigns are not just about tricking users—they are highly technical operations designed to evade multiple layers of security. This sophistication includes the use of legitimate services to mask malicious activities, as well as advanced methods to bypass detection.
Abusing Legitimate Platforms
One method involves leveraging reputable platforms like file-hosting services and business profile pages. By hosting malicious payloads on well-known and trusted platforms, attackers reduce the likelihood that their activities will trigger security alerts. These platforms often have robust reputations, and their involvement gives the phishing campaign an added layer of credibility. The malicious payloads—ranging from remote access trojans (RATs) to information stealers and complex post-exploitation frameworks such as BruteRatel C4—are hidden behind this veneer of legitimacy.
Multi-Stage Evasion Techniques
The multi-stage nature of these attacks is designed to continuously outsmart security solutions. At each stage, attackers implement techniques that help them avoid detection. Whether it’s the initial benign email, the use of URL redirection to mask true destinations, or the deployment of unique QR codes for personalized tracking, each layer adds complexity to the attack. This careful orchestration ensures that even if one security measure fails, subsequent measures might still be bypassed, ultimately allowing the attack to succeed.
The Human Factor: Educating and Protecting Users
While technology plays a crucial role in defending against phishing attacks, human behavior remains one of the most vulnerable aspects of cybersecurity. Phishing campaigns succeed primarily because they exploit common behavioral tendencies, such as the urgency to act on time-sensitive information.
The Importance of Awareness Training
For both individual taxpayers and professionals in the accounting and IT sectors, awareness training is a vital line of defense. Organizations must invest in regular cybersecurity training that emphasizes the risks associated with unsolicited emails and unfamiliar attachments or links. Employees should be educated on the warning signs of phishing, including unusual sender addresses, unexpected requests for personal information, and the presence of URL shorteners or QR codes in suspicious emails.
Implementing Phishing-Resistant Technologies
In addition to training, organizations should adopt advanced authentication methods that are resistant to phishing. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is one of the most effective measures, as it adds an additional layer of security even if credentials are compromised. Some organizations are now exploring phishing-resistant authentication protocols that go beyond traditional MFA to offer even more robust protection.
Mitigation Strategies for Businesses and Individuals
To combat the rising threat of tax-related phishing attacks, both businesses and individual taxpayers should implement a range of technical and procedural safeguards.
Strengthening Email Security
Email remains the primary vector for phishing attacks. To mitigate this risk, organizations should deploy advanced email security solutions that include features such as Zero-hour auto purge (ZAP). ZAP is designed to identify and quarantine malicious emails in real time, minimizing the window of opportunity for attackers. By incorporating these tools, businesses can significantly reduce the likelihood that malicious emails will reach end users.
Adopting Zero Trust Architecture
The concept of Zero Trust has gained significant traction in cybersecurity circles. Rather than assuming that internal network traffic is safe, Zero Trust architectures require continuous verification of every request. This approach is especially effective against multi-stage phishing campaigns, as it forces every interaction to be authenticated and authorized, reducing the attacker’s ability to move laterally within a network once a breach occurs.
Routine Security Assessments and Updates
Regular security assessments and timely software updates are essential to maintaining a strong defense against phishing attacks. Vulnerabilities in outdated systems can be exploited by attackers to bypass even the most sophisticated security measures. Organizations should conduct periodic vulnerability assessments and invest in patch management solutions to ensure that their software and hardware are up to date with the latest security patches.
Addressing the Threat Through Industry Collaboration
Cybersecurity is not a challenge that can be tackled by any single organization or individual. It requires a coordinated effort across industries, government agencies, and international partners. Sharing threat intelligence and best practices is key to staying ahead of rapidly evolving phishing tactics.
The Role of Cybersecurity Communities
Many cybersecurity communities and forums play a crucial role in disseminating information about new threats. By actively participating in these communities, professionals can stay informed about the latest phishing techniques and the corresponding defensive strategies. Collaboration between different sectors, such as financial institutions, technology companies, and government bodies, fosters an environment where information is shared rapidly, allowing for quicker responses to emerging threats.
Government and Regulatory Involvement
Government agencies and regulatory bodies have also become more involved in addressing the challenges posed by phishing attacks. In recent years, there have been concerted efforts to educate the public about the dangers of phishing, particularly during high-risk periods like tax season. Regulatory mandates often require organizations to adhere to strict cybersecurity protocols, further reinforcing the importance of robust security measures.
Practical Steps for Taxpayers and Professionals
Given the sophistication of modern phishing campaigns, what practical steps can you take to protect yourself or your organization? Here are several recommendations that can make a significant difference.
Verify the Source of Communications
One of the simplest yet most effective steps is to verify the legitimacy of any email that claims to be from a tax authority or a well-known company. Check the sender’s email address closely for any discrepancies or unusual domains. If an email appears suspicious, contact the organization directly using a phone number or email address obtained from an official source rather than relying on the information provided in the email itself.
Be Cautious with QR Codes and Attachments
Phishing emails today often include QR codes that can bypass many traditional security measures. When you receive an email with an attached PDF containing a QR code, consider the context before scanning it. If the message seems out of place or the attachment is unexpected, refrain from scanning the code and report the email to your IT security team or email provider.
Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Implementing multi-factor authentication can provide a critical layer of defense. Even if an attacker manages to capture your credentials, MFA makes it significantly more difficult for them to access your accounts without the additional authentication factor, such as a security token or a biometric identifier.
Regularly Update and Back Up Data
Regular updates to your operating system and applications are essential in defending against new vulnerabilities that attackers may exploit. In addition to updates, maintaining regular backups of your data ensures that you can recover quickly in the event of a successful attack. This practice minimizes downtime and reduces the overall impact of an incident.
Future Trends in Phishing and Cybersecurity
As technology evolves, so too do the tactics employed by cybercriminals. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into both attack strategies and defense mechanisms is reshaping the cybersecurity landscape.
AI-Driven Phishing Campaigns
Looking ahead, it is likely that we will see an increase in AI-driven phishing campaigns. These campaigns can tailor their messages more effectively based on vast amounts of data about individual targets. By analyzing online behavior, social media activity, and previous interactions, attackers can craft highly personalized messages that are much more likely to succeed.
Advances in Defensive Technologies
In response to the increasing sophistication of phishing attacks, cybersecurity companies are also leveraging AI and machine learning to improve threat detection and response. These technologies can help identify anomalous behavior and flag potential phishing attempts before they can do any harm. The development of behavioral analytics and real-time threat intelligence systems is a promising trend that could significantly reduce the success rate of phishing attacks in the future.
The Importance of Ongoing Research and Development
Both attackers and defenders are engaged in an ongoing arms race. It is essential for organizations and cybersecurity professionals to invest in research and development to stay ahead of new tactics. By continually refining security protocols and adopting cutting-edge technologies, businesses can better protect themselves against emerging threats.
Conclusion: Staying Vigilant in an Uncertain Digital World
The tactics employed by cybercriminals in recent phishing campaigns, particularly those exploiting tax season, demonstrate that no organization or individual is completely immune to digital threats. The use of advanced techniques like URL shorteners, QR codes, and personalized PDF attachments underscores the need for both robust technological defenses and informed, vigilant users.
As we have discussed, understanding the threat landscape is the first step toward building a comprehensive defense strategy. By educating yourself and your team, implementing strong security measures such as MFA and Zero Trust architectures, and staying informed about the latest trends in cybersecurity, you can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to these sophisticated phishing campaigns.
The importance of collaboration cannot be overstated. Whether you are an individual taxpayer, a CPA, or an IT professional, staying connected with the broader cybersecurity community and sharing best practices is essential. As cyber threats continue to evolve, our collective efforts to share knowledge and strengthen defenses will be the key to safeguarding sensitive information in an increasingly digital world.
Remember, while technology can provide robust defenses, the human element remains critical. Vigilance, awareness, and prompt action in response to suspicious activities are as important as any technological solution. Together, these strategies can help mitigate the risks posed by phishing attacks and protect both personal and organizational data from the prying hands of cybercriminals.
Sources: Cybersecurity News, Microsoft
Share this :