Chinese eCrime Hackers Target 120+ Countries Banking Data using Smishing

Hoplon InfoSec
13 Apr, 2025
cybercrime has become increasingly sophisticated, with criminal groups continuously adapting their techniques to exploit vulnerabilities across the globe. One such group, known as the “Smishing Triad,” has been active since 2023 and has rapidly expanded its operations to target both organizations and individuals in over 121 countries. This blog post delves into the operations of this sophisticated Chinese eCrime group, examines their latest tactics, and provides guidance on how to protect yourself and your organization from similar threats.
The Smishing Triad has shifted its focus from traditional phishing techniques to more refined SMS phishing, commonly known as smishing. By using fraudulent text messages that mimic legitimate communications from postal services, government agencies, and even financial institutions, the group creates a sense of urgency that compels victims to click on malicious links. Over time, the group has evolved from targeting package delivery and government service lures to more insidious methods of stealing banking credentials.
The Rise of Smishing: How Chinese eCrime Hackers doing it

What Is Smishing?
Smishing is a form of phishing that uses SMS text messages to lure victims into divulging sensitive information or clicking on harmful links. Unlike traditional email phishing, smishing takes advantage of the trust people have in receiving text messages, often from sources they recognize or expect to hear from. Criminals craft messages that alert recipients to urgent issues, such as problems with a package delivery or unpaid tolls, thereby increasing the likelihood that the victim will act impulsively without verifying the authenticity of the message.
The Mechanism Behind the Attacks
The Smishing Triad employs a systematic approach to carry out their attacks. Their method involves sending out mass SMS messages that contain links to websites that have been designed to mimic legitimate portals. When users click on these links, they are redirected to convincing replicas of well-known websites, often complete with secure-looking interfaces and real-time updates that reinforce the illusion of legitimacy.
These websites are part of a vast network of malicious domains. Researchers have estimated that on any given day, there could be tens of thousands of these domains in operation. The sheer scale of this network is designed to evade detection and blocking by cybersecurity firms and regulatory authorities.
Detailed Analysis of the Smishing Triad’s Tactics
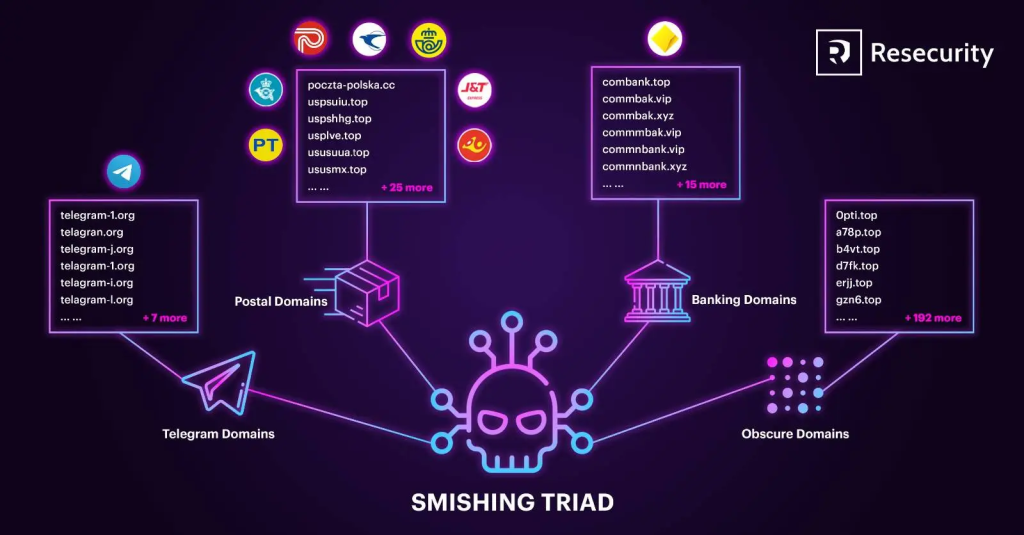
Rapid Domain Rotation
One of the most challenging aspects of combating the Smishing Triad is their rapid domain rotation strategy. It is estimated that the group maintains approximately 25,000 domains online over any given 8-day period. This high turnover rate allows them to bypass many traditional cybersecurity measures. Even if one domain is taken down or blacklisted, another is quickly put in its place, ensuring that the phishing campaign continues uninterrupted.
Shifting Targets: From Delivery and Government Services to Banking Credentials
Initially, the group focused on exploiting the vulnerabilities of individuals by targeting them with messages related to package delivery and government services. However, in a concerning development, the group has recently pivoted to stealing banking credentials. The stakes in this new focus are considerably higher, as compromising financial data can lead to substantial financial losses for both individuals and institutions.
The Introduction of the “Lighthouse” Phishing Kit
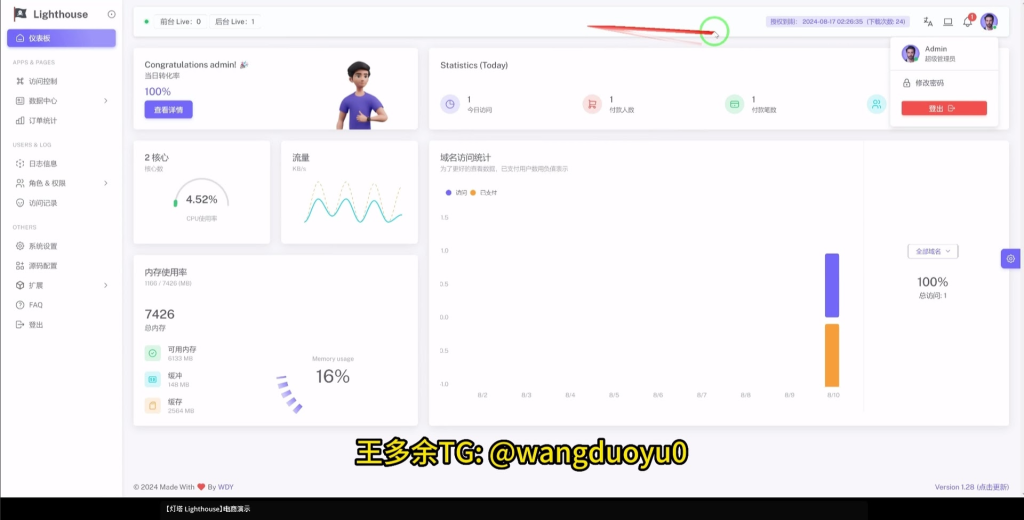
What Is the Lighthouse Phishing Kit?
In March 2025, Silent Push analysts observed a significant evolution in the Smishing Triad’s methodology with the introduction of a new phishing kit dubbed “Lighthouse.” This toolkit represents a notable leap in the sophistication and operational capabilities of the group. The Lighthouse kit has been designed primarily to target major financial institutions, with a particular focus on Australian banks and several major Western financial institutions.
Features and Capabilities
The Lighthouse phishing kit is packed with advanced features that enhance the efficiency and stealth of the phishing campaigns:
- Real-Time Synchronization: The kit enables real-time synchronization of data, which helps in maintaining the accuracy and immediacy of the replicated interfaces.
- One-Click Setup and Updates: With streamlined installation and update processes, the attackers can quickly deploy new phishing pages and modify existing ones without significant downtime.
- Automatic Diversion: This feature allows the kit to reroute traffic seamlessly, further complicating efforts to track and block the phishing activities.
- Multiple Verification Methods: To convincingly mimic legitimate banking procedures, the kit incorporates multiple layers of verification. These include OTP (One-Time Password) verification, app-based verification, PIN verification, and even 3DS (Three-Domain Secure) verification. These additional steps not only enhance the authenticity of the phishing pages but also help the attackers to extract more detailed data from the victims.
- Customizable Administration Panel: The phishing kit includes a sophisticated administrative panel that allows attackers to tailor the phishing pages. They can customize directory structures, implement country-based IP filtering to target specific regions, and adjust the demanded payment amounts to maximize financial gain.
- Mobile-Only Rendering Options: Recognizing the growing reliance on smartphones for online banking, the kit offers options for mobile-only rendering, ensuring that the phishing pages are optimized for smartphone users.
- Session Management Capabilities: The kit tracks the progress of victims as they move through the phishing process. For example, it displays Chinese-language status messages indicating the current stage of the phishing flow. These messages—ranging from indicating the user is on the home page to confirming that card details have been filled in—help the attackers manage the data collection process efficiently.
Technical Insights from the JavaScript Analysis
Technical analysts have examined a JavaScript file associated with the Lighthouse kit (identified as index-D76-mPwS.js). This file contains key parameters that indicate the kit’s capability to target a wide array of financial institutions. Among these are globally recognized entities such as PayPal, Mastercard, Visa, and HSBC, as well as several prominent Australian banks. The sophisticated design of the script is a testament to the technical expertise behind the Smishing Triad’s operations.
Infrastructure and Organizational Capabilities
The Scale of Operations
The Smishing Triad is not a loosely organized band of hackers. Rather, it is a well-structured criminal organization that reportedly employs over 300 front desk staff worldwide. This level of organization indicates significant resources and a high degree of operational efficiency. Such an enterprise is capable of mounting coordinated attacks across multiple industries and geographical regions simultaneously.
Hosting and Support from Major Chinese Companies
A critical aspect of the group’s infrastructure is its reliance on hosting services provided by major Chinese companies such as Tencent and Alibaba. More than half of their phishing infrastructure is hosted by these firms, which raises complex questions about cybersecurity oversight and the role of major technology companies in inadvertently facilitating cybercrime.
Global Impact and Industry-Specific Targeting
A Broad Spectrum of Targets
The group’s campaigns have not been limited to a single sector. Instead, they have systematically targeted a diverse range of industries, including:
- Postal Services: By leveraging the inherent trust that recipients have in delivery notifications, the group is able to capture sensitive data related to shipping and logistics.
- Logistics and Transportation: The continuous growth in e-commerce has made logistics a lucrative target, with criminals exploiting the reliance on timely deliveries.
- Telecommunications: By impersonating telecom companies, the attackers can gain access to personal and financial data.
- Retail: As retail transactions increasingly move online, phishing attacks targeting retail customers have become a profitable venture.
- Public Sectors: Government agencies and public institutions have also been under the scanner, as access to these systems can yield sensitive information.
Financial Sector: A New Focus Area
The recent pivot towards stealing banking credentials is particularly alarming. Financial institutions have always been prime targets for cybercriminals due to the direct access to monetary resources and personal financial data. With the introduction of the Lighthouse kit, the Smishing Triad has clearly elevated its ambitions. The toolkit’s advanced verification methods and real-time synchronization features make it one of the most potent phishing tools seen to date.
Defensive Measures: Protecting Yourself and Your Organization
Awareness and Education
One of the first lines of defense against smishing attacks is awareness. Both individuals and organizations must be educated on the tactics used by cybercriminals. Understanding that messages claiming urgent issues—whether related to package deliveries or financial discrepancies—might be fraudulent is crucial. Regular training sessions and updates on emerging cyber threats can help employees and the public remain vigilant.
Verifying Communications
A critical step in thwarting smishing attempts is verifying the legitimacy of the messages received. If you receive a text message that urges you to click a link or provide personal information, take the following steps:
- Do Not Click Immediately: Pause and verify the source of the message through official channels. For example, if the message appears to be from a postal service or bank, contact the institution directly using contact information from their official website.
- Look for Red Flags: Poor grammar, misspellings, and unusual email addresses or phone numbers are common indicators of a phishing attempt.
- Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enabling MFA on your accounts can provide an additional layer of security, making it more difficult for attackers to gain access even if some information is compromised.
Technical Solutions
Organizations can adopt several technical measures to mitigate the risk posed by smishing campaigns:
- Implement Advanced Email and SMS Filtering: Use systems that analyze incoming messages for known phishing indicators and block suspicious content before it reaches users.
- Regularly Update and Patch Systems: Cybercriminals often exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software. Keeping systems up-to-date minimizes the risk of successful attacks.
- Deploy Domain Monitoring Tools: Given the rapid domain rotation used by the Smishing Triad, it is beneficial to use tools that monitor and flag potentially malicious domains. This proactive approach can help in early detection and swift response.
- Establish Incident Response Protocols: Organizations should have clear, tested protocols in place for responding to a suspected phishing attack. This includes isolating affected systems, notifying stakeholders, and engaging cybersecurity experts for remediation.
Collaborative Efforts and Regulatory Oversight
The challenge posed by sophisticated cybercrime groups like the Smishing Triad calls for a collaborative approach. Governments, regulatory bodies, and private sector companies need to work together to share intelligence, strengthen cybersecurity standards, and develop more effective countermeasures. The fact that much of the phishing infrastructure is hosted by major companies highlights the need for enhanced oversight and collaboration between public and private entities to disrupt these criminal networks.
Best Practices for Financial Institutions
Strengthening Verification Methods
Financial institutions are at the forefront of the Smishing Triad’s target list. To protect against these advanced phishing kits, banks and other financial entities should consider implementing several additional measures:
- Enhanced Customer Verification: Adopt multi-factor authentication protocols and consider using biometric verification methods, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, to add extra layers of security.
- Customer Education Campaigns: Launch regular campaigns to educate customers about the risks of phishing and smishing. Clear guidelines on how to verify communications and what steps to take if suspicious messages are received can help reduce the number of successful attacks.
- Monitor for Unusual Activity: Implement systems that flag unusual account activity or login attempts. Quick detection of anomalies can help prevent or minimize damage from compromised accounts.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct frequent security audits and vulnerability assessments to identify potential weaknesses that could be exploited by attackers.
Leveraging Technology for Real-Time Threat Detection
The introduction of the Lighthouse kit underscores the importance of real-time monitoring and threat intelligence. Financial institutions should invest in advanced cybersecurity solutions that can:
- Track and Analyze User Behavior: Machine learning algorithms can detect deviations from normal behavior, alerting security teams to potential phishing attacks as they unfold.
- Integrate Threat Intelligence Feeds: By incorporating data from reputable threat intelligence sources, organizations can stay updated on the latest phishing tactics and quickly adapt their defenses.
- Deploy Automated Response Systems: Automation can be critical in mitigating threats as soon as they are detected. Automated systems that can isolate affected systems or block malicious domains can help limit the spread of an attack.
How Individuals Can Protect Themselves

Recognizing the Warning Signs
For individual users, being able to recognize the signs of a smishing attempt is paramount. Here are some common red flags to be aware of:
- Urgent Language: Messages that create a false sense of urgency—such as warnings about unpaid bills or delayed deliveries—should be treated with caution.
- Suspicious Links: Hover over any link before clicking to inspect the URL. Often, the actual URL will differ from what is claimed in the text message.
- Unsolicited Requests for Personal Information: Legitimate companies typically do not ask for sensitive information like passwords or PINs via text message.
Steps to Take if You Suspect a Smishing Attack
- Do Not Engage: Avoid clicking on any links or providing personal information. If in doubt, delete the message immediately.
- Report the Incident: Report any suspicious messages to your mobile service provider or the appropriate regulatory body. Many countries have dedicated agencies that track and combat phishing attempts.
- Enhance Personal Security: Consider installing security applications on your smartphone that provide real-time protection against malware and phishing attacks.
Keeping Your Data Secure
- Use Strong Passwords: Ensure that all accounts are protected with complex passwords. Using a password manager can help maintain strong, unique passwords across different accounts.
- Regularly Update Software: Whether it’s your mobile operating system or banking apps, keeping software updated is essential. Updates often include patches for newly discovered vulnerabilities.
- Enable Device-Level Security Features: Modern smartphones come with robust security features such as biometric authentication and remote wipe capabilities. Make sure these are activated to protect your data in case your device is lost or stolen.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Smishing and Cybercrime

Trends in Cybercrime Evolution
The activities of the Smishing Triad underscore a broader trend in cybercrime, where criminal groups continuously innovate to stay one step ahead of security measures. As technology evolves, so too do the tactics used by these groups. Some experts predict that in the coming years, we will see even more sophisticated phishing techniques that integrate artificial intelligence, further blurring the lines between legitimate and fraudulent communications.
The Importance of Ongoing Vigilance
In this rapidly evolving threat landscape, both organizations and individuals must remain vigilant. Cybersecurity is not a one-time effort but rather a continuous process that requires regular updates, training, and investment in the latest technology. The tactics used by groups like the Smishing Triad serve as a stark reminder that the battle against cybercrime is ongoing, and everyone has a role to play in maintaining a secure digital environment.
Collaboration Between Stakeholders
The fight against smishing and other forms of cybercrime will require unprecedented levels of collaboration between governments, private companies, and individuals. By sharing threat intelligence and best practices, stakeholders can collectively strengthen the defenses that protect sensitive data and financial assets. International cooperation is particularly important, given the global reach of these criminal networks.
Conclusion: Staying One Step Ahead
The Smishing Triad represents a formidable challenge in today’s cybersecurity landscape. Their ability to adapt quickly, rotate domains at a staggering pace, and deploy advanced phishing kits like Lighthouse makes them a persistent threat to both individuals and institutions worldwide. By understanding the mechanics of these attacks and implementing comprehensive defensive measures, organizations and individuals alike can reduce their risk of falling victim to these sophisticated scams.
In summary, staying informed about the latest trends in cybercrime, implementing robust security measures, and fostering a culture of vigilance are critical steps in defending against smishing and related attacks. Whether you are a financial institution, a small business, or an individual user, the onus is on all of us to take proactive steps to secure our digital lives.
The evolving tactics of groups like the Smishing Triad are a clear indication that the threat landscape is constantly changing. As cybercriminals refine their methods, our defensive strategies must evolve accordingly. Embracing a multi-layered approach to cybersecurity that includes education, technological innovation, and collaborative efforts will be essential in mitigating the risks posed by these sophisticated threats.
Share this :