Understanding Protocols: What They Are and Why They Matter

Hoplon InfoSec
01 Apr, 2025
In our daily lives, we follow common rules for communication—such as speaking the same language or taking turns in conversation. In the digital world, protocols serve a similar purpose. They are sets of rules or an agreed-upon language that devices use to exchange information. Just as a common language prevents misunderstandings among people, protocols ensure that different gadgets like your phone, laptop, or smart TV can share information without confusion. This guide explores what protocols are, reviews various types with real-world examples, and explains why they are essential in today’s digital age.
What Exactly is a Protocol?
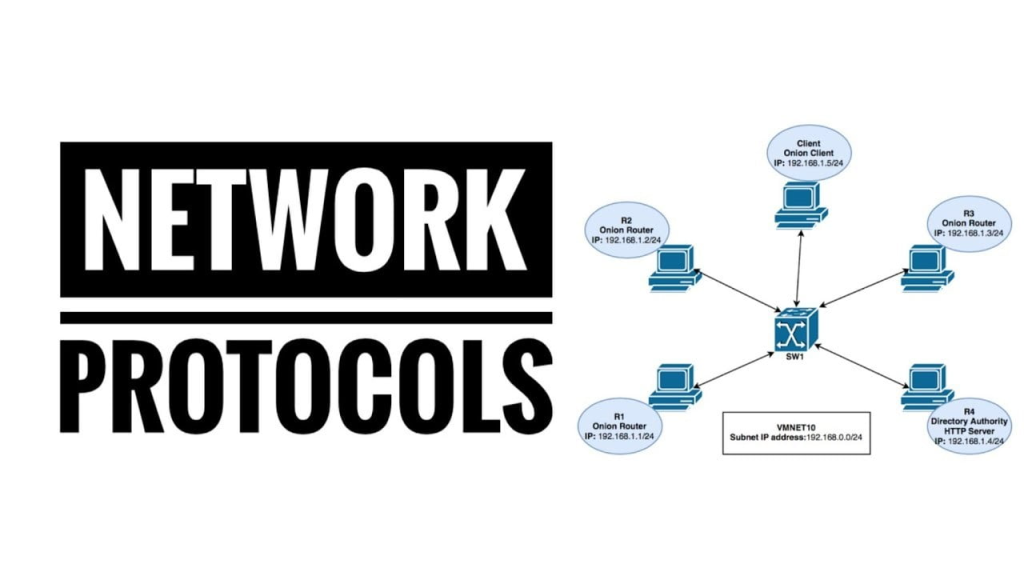
A protocol is a shared set of rules that defines how information should be formatted and exchanged. It acts as a digital rulebook or language that all devices must follow for successful communication. When you send a text or browse a website, both your device and the receiving server adhere to the same protocol, much like two people speaking the same language. Without a common protocol, the data would be garbled, and the communication would fail—similar to how people speaking different languages might not understand each other.
Consider mailing a letter: there are rules about where to place the address, using a stamp, and following size or weight guidelines. If you ignore these rules, the postal service won’t deliver your letter. Similarly, protocols ensure that data is packaged and handled correctly so that it reaches the intended destination reliably.
Types of Protocols

Network Protocols: Rules of the Internet
Network protocols are the foundational communication rules that enable the Internet and local networks to function. They determine how data is transmitted across networks and ensure that devices connect and share information seamlessly. For example, the HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) defines how web browsers fetch resources like web pages from servers. Every time you click a link or type a URL, your browser sends an HTTP request, and the server responds with the appropriate content. Without HTTP, the modern web would not exist. Equally important is TCP/IP, which serves as the core language of the Internet.
IP functions as the addressing system, directing data packets to their correct destinations, while TCP guarantees that these packets are delivered reliably and in order. This combination is crucial for everyday tasks such as sending emails or downloading files. Additionally, the File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is used to move files between computers in a client-server model. For instance, web developers often use FTP to update website files, ensuring that the data exchange is performed accurately and efficiently.
Communication Protocols: Connecting Our Devices
Communication protocols allow devices to interact in specific contexts beyond traditional Internet use, from wireless gadgets to smart appliances. Bluetooth is one example; it is designed for short-range wireless communication, typically within 10 meters or 30 feet. This technology enables your smartphone to connect with wireless headphones, speakers, or even your car’s audio system, facilitating the exchange of data without the need for wires.
In the realm of the Internet of Things (IoT), MQTT offers a lightweight messaging solution. It uses a publish/subscribe model to transfer small amounts of data efficiently, making it ideal for applications such as remote sensors and smart home devices. Similarly, Zigbee is tailored for low-power, short-range wireless networks and is commonly found in smart home devices like light bulbs, motion sensors, and smart plugs. Zigbee creates a mesh network that not only extends the network’s range but also conserves battery life, ensuring that devices remain connected reliably over long periods.
Security Protocols: Keeping Data Safe
Security protocols play a crucial role in protecting data as it travels between computers, especially over the Internet. They focus on encrypting information, verifying identities, and ensuring data integrity so that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable and unaltered. For example, SSL/TLS protocols secure communications between devices by encrypting the data exchanged between your browser and a website. This is why websites starting with “https://” display a padlock icon. This encryption process ensures that sensitive information, such as passwords and credit card numbers, is kept confidential.
Similarly, IPsec is used to secure data at the network layer by encrypting and authenticating IP packets. This is especially useful in Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), where IPsec creates secure tunnels between remote devices and networks. HTTPS is another important protocol, HTTP layered on top of SSL/TLS encryption, which protects data during web transactions and ensures that communication remains private and secure.
Industrial Protocols: Machines Talking to Machines
Industrial protocols are designed for environments where specialized devices such as sensors, controllers, and robots must communicate reliably and in real-time. Modbus is one of the oldest and most widely used industrial protocols, originally developed in the late 1970s to allow programmable logic controllers (PLCs) to exchange data with other devices. This protocol remains prevalent in manufacturing and industrial control systems, ensuring that data is transferred efficiently on the factory floor. Another protocol, Profibus, which stands for Process Field Bus, was developed in Germany during the late 1980s and is used extensively in automated factories to connect sensors, actuators, and controllers. It standardizes communication between various instruments on the assembly line, enabling coordinated operations.
Additionally, the Controller Area Network (CAN Bus) was initially designed for automobiles. In modern vehicles, the CAN Bus allows multiple electronic components to share information over a limited number of wires, ensuring that critical functions such as engine control and dashboard updates operate seamlessly. Its reliability also makes it suitable for other industries, including aviation and industrial machinery.
Other Common Protocols: Everyday Digital Rules
Beyond specialized categories, several protocols are integral to everyday digital activities. The Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) governs the sending of emails, ensuring that your email client communicates effectively with mail servers. This protocol acts much like the postal service for electronic mail, directing messages to their intended recipients. The Domain Name System (DNS) is often described as the phonebook of the Internet, translating human-friendly domain names into numerical IP addresses that computers use for communication.
Without DNS, users would have to remember complex strings of numbers instead of simple website names. Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) is another example; it enables voice and video calls over the Internet by converting analogue signals into digital data packets that travel across the network and are reassembled at the destination. This technology underpins services like Skype, Zoom, and WhatsApp, making global communication accessible and cost-effective.
Why Understanding Protocols is Essential

Protocols are the unsung heroes of our digital world, forming the backbone of every online interaction. Every digital transaction—from sending an email to streaming a video—relies on protocols to ensure that data flows smoothly and securely. This understanding not only provides insight into how complex digital processes operate but also fosters an appreciation for the intricate systems that make modern technology possible. The standardization of protocols enables interoperability, allowing devices from different manufacturers and eras to communicate seamlessly, which in turn fuels innovation.
Moreover, having a basic knowledge of protocols can help with troubleshooting network issues and configuring devices more effectively. In today’s age, where security and privacy are paramount, understanding how protocols protect sensitive data empowers users to make informed decisions about their online activities. Protocols are also fundamental to the digital economy, ensuring that services such as online banking, cloud computing, and industrial automation operate reliably and securely.
Conclusion
Protocols might seem technical, but at their core, they are simply agreements on how to communicate. Much like traffic lights and road rules maintain order and safety on the roads, protocols ensure that data flows smoothly and securely across the global network of computers and devices. Understanding these digital rules demystifies the functioning of your favourite apps and devices and highlights the importance of collaboration and standardization in technology. In an increasingly connected world, being informed about protocols transforms you from a passive user into an empowered participant in the digital society, where every webpage load and message sent is supported by countless protocols working silently behind the scenes.
Share this :