The Importance of Regular Security Audits in a Digital World

Hoplon InfoSec
02 Apr, 2025
In today’s digital landscape, the significance of safeguarding sensitive information has grown exponentially. As organizations and individuals increasingly rely on digital systems to store, process, and transmit data, the risks associated with cyber threats continue to evolve. Regular security audits are no longer a luxury—they are an essential part of any robust cybersecurity strategy. In this blog, we will explore the importance of regular security audits, how they can protect your assets, and the strategies for implementing an effective audit process.
Cybersecurity is not simply about installing firewalls or antivirus software; it involves a continuous effort to identify, assess, and mitigate risks. Regular security audits play a crucial role in this process by ensuring that any vulnerabilities in the system are promptly discovered and addressed before malicious actors can exploit them.
Understanding The Importance of Regular Security Audits in a Digital World

Security audits are comprehensive evaluations of an organization’s information systems and security policies. These assessments can range from automated scans to in-depth manual reviews, with the goal of identifying potential security risks. By examining configurations, policies, user access controls, and even the behaviour of the IT infrastructure, auditors are able to pinpoint vulnerabilities that could lead to data breaches or unauthorized access.
The process of auditing involves not only checking the technical controls in place but also assessing the organizational procedures that support cybersecurity. Regular audits help organizations keep up with the fast-paced changes in technology, regulatory environments, and threat landscapes. By doing so, businesses can remain compliant with industry standards and regulatory requirements, thereby avoiding potentially hefty fines and reputational damage.
Why Regular Security Audits are Crucial
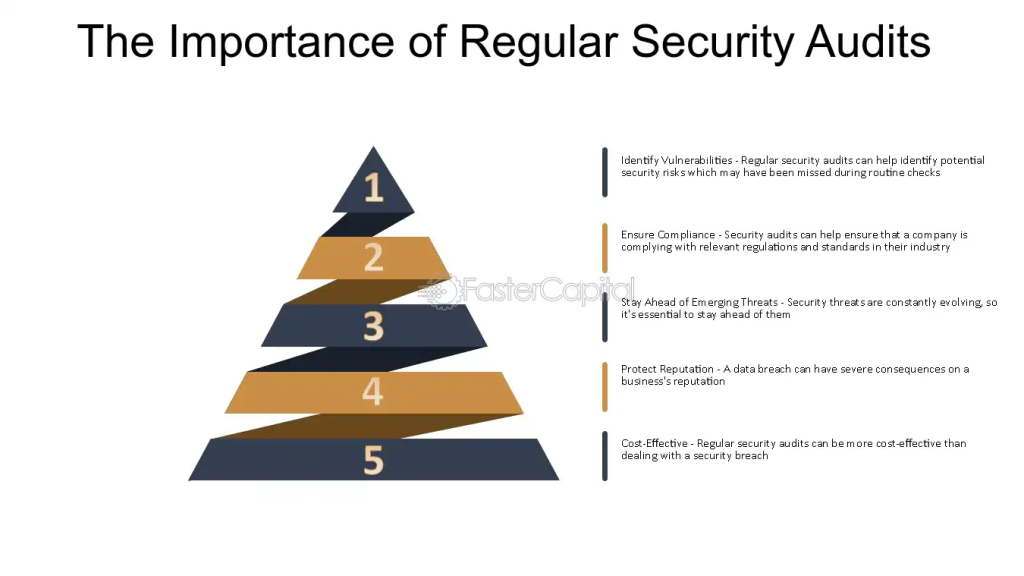
Identification of Vulnerabilities
One of the primary benefits of conducting regular security audits is the identification of vulnerabilities before cybercriminals can exploit them. In a digital world where threats are constantly evolving, what may have been secure yesterday could be at risk today. Regular audits help organizations stay ahead of the curve by continually identifying gaps in security protocols. This proactive approach enables the organization to implement corrective measures, reducing the risk of data breaches and financial losses.
Compliance with Regulations
Many industries are subject to strict regulatory standards that require regular security assessments. Compliance with these standards is not only a legal obligation but also a best practice that enhances the overall security posture of an organization. Regular audits ensure that security policies and practices align with current regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in significant fines, legal actions, and a loss of customer trust.
Maintaining Trust and Reputation
A single security breach can tarnish an organization’s reputation irreversibly. Customers, partners, and stakeholders place their trust in an organization’s ability to protect their data. Regular security audits serve as a testament to an organization’s commitment to cybersecurity, thereby enhancing its credibility and trustworthiness. A robust audit process demonstrates that the organization is taking proactive steps to protect sensitive information and maintain high standards of security.
Components of a Comprehensive Security Audit
A comprehensive security audit should cover both technical and administrative aspects of an organization’s cybersecurity framework. While there are various methodologies and tools available for conducting audits, there are several core components that should always be included.
Network Security Analysis
One of the first steps in any security audit is to analyze the organization’s network infrastructure. This includes reviewing firewall configurations, intrusion detection systems, and network segmentation practices. A thorough analysis can reveal potential entry points that attackers could exploit. Regularly assessing network security helps ensure that any changes in the infrastructure do not inadvertently introduce new vulnerabilities.
Application Security Testing
Applications are often the target of cyberattacks, making it imperative to test for vulnerabilities regularly. Security audits should include both static and dynamic analysis of software applications to detect issues such as code injection, cross-site scripting, and other common vulnerabilities. By simulating real-world attacks in a controlled environment, organizations can identify and fix weaknesses before they are exploited in a live scenario.
Access Control Reviews
Managing user access is a critical aspect of cybersecurity. Regular security audits should review user access rights, ensuring that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive information. This includes auditing user roles, permissions, and the processes in place for onboarding and offboarding employees. Strong access control measures minimize the risk of insider threats and accidental data exposure.
Policy and Procedure Evaluation
Technical controls are only as effective as the policies that govern them. Auditors must evaluate the organization’s security policies, incident response plans, and disaster recovery procedures to ensure they are up-to-date and effective. Policies should be regularly reviewed and revised to address emerging threats and to reflect changes in the organizational structure or technology landscape. A comprehensive audit ensures that every layer of security is robust and capable of protecting critical assets.
Benefits of Regular Security Audits

Regular security audits offer a wide range of benefits that extend beyond the identification of vulnerabilities. When implemented correctly, they serve as a foundation for a proactive and resilient cybersecurity strategy.
Improved Risk Management
Risk management is a continuous process that involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential threats. Regular security audits provide an ongoing snapshot of an organization’s security posture. This allows security teams to prioritize risks and allocate resources effectively. By understanding the current risk landscape, organizations can develop strategies to mitigate potential threats before they escalate into serious incidents.
Enhanced Incident Response
In the event of a security incident, the effectiveness of an organization’s response can mean the difference between a minor disruption and a catastrophic breach. Regular audits help organizations refine their incident response plans by identifying areas where the plan may be lacking. By incorporating the latest threat intelligence and lessons learned from previous incidents, organizations can develop a more robust response strategy that minimizes downtime and reduces damage.
Cost Savings
Investing in regular security audits can result in significant cost savings over time. The financial implications of a data breach, including legal fees, regulatory fines, and reputational damage, can be astronomical. By proactively identifying and addressing vulnerabilities, organizations can avoid these costs. Furthermore, regular audits can uncover inefficiencies in the current security setup, leading to more optimized resource allocation and reduced operational expenses.
Continuous Improvement
Security is not a one-time effort but a continuous process of improvement. Regular audits provide valuable feedback that can be used to refine and enhance security practices. This iterative process ensures that an organization’s security measures evolve in line with emerging threats and technological advancements. Continuous improvement not only strengthens the security framework but also fosters a culture of vigilance and resilience throughout the organization.
Challenges in Conducting Regular Security Audits
While the benefits of regular security audits are clear, there are several challenges that organizations may face when trying to implement them effectively.
Resource Allocation
Conducting a comprehensive security audit requires significant resources, including time, skilled personnel, and financial investment. For many organizations, especially small and medium-sized enterprises, allocating these resources can be challenging. Balancing the need for regular audits with day-to-day operational demands often requires strategic planning and prioritization. Outsourcing audits to specialized security firms can sometimes provide a cost-effective solution, though this option must be weighed against the benefits of maintaining internal expertise.
Keeping Up with Rapid Technological Change
The rapid pace of technological innovation means that security measures can quickly become outdated. New vulnerabilities are discovered on a regular basis, and the methods used by attackers are constantly evolving. Staying ahead of these changes requires not only regular audits but also continuous education and adaptation by security teams. Organizations must invest in training and development to ensure that their staff remains knowledgeable about the latest threats and security practices.
Integration with Business Processes
Security audits are often viewed as a disruptive process that interferes with normal business operations. Integrating regular audits into the everyday workflow of an organization requires careful planning and coordination. It is essential to communicate the importance of these audits to all stakeholders, ensuring that they understand the long-term benefits. By aligning the audit process with the organization’s strategic goals, companies can minimize disruptions while maximizing the effectiveness of their security measures.
Addressing False Positives and Negatives
No audit process is perfect. One of the ongoing challenges is managing false positives—instances where a non-existent vulnerability is flagged—and false negatives, where real vulnerabilities go undetected. Both issues can undermine the effectiveness of an audit and lead to a misplaced sense of security. Continuous refinement of auditing tools and techniques, coupled with expert analysis, is necessary to minimize these inaccuracies and ensure that the audit results are both accurate and actionable.
Best Practices for Conducting Effective Security Audits

To maximize the benefits of security audits, organizations should adhere to several best practices that ensure a thorough and effective evaluation of their security posture.
Establish Clear Objectives
Before initiating an audit, it is essential to define clear objectives. What are the specific areas of concern? What regulatory requirements need to be met? By establishing clear goals, organizations can focus their efforts on the most critical aspects of their security infrastructure. Clear objectives help to ensure that the audit is not only comprehensive but also relevant to the organization’s unique risk profile.
Involve All Stakeholders
Effective security audits require collaboration across multiple departments. From IT and security teams to legal and human resources, everyone has a role to play in maintaining a secure environment. Involving all relevant stakeholders ensures that the audit covers both technical and organizational aspects of security. Regular communication and collaboration can also lead to more comprehensive security policies and better incident response plans.
Leverage Automated Tools and Manual Reviews
A hybrid approach that combines automated tools with manual reviews is often the most effective way to conduct a security audit. Automated tools can quickly scan systems for known vulnerabilities and configuration issues, while manual reviews offer the nuanced analysis required to understand complex risks. This combined approach ensures that audits are both efficient and thorough, providing a detailed picture of the organization’s security posture.
Prioritize Remediation and Follow-Up
Identifying vulnerabilities is only half the battle. The next step is to remediate these issues promptly and effectively. It is essential to prioritize vulnerabilities based on their potential impact and likelihood of exploitation. Follow-up audits are also critical to verify that remediation efforts have been successful and that no new vulnerabilities have been introduced. Establishing a feedback loop between auditing, remediation, and subsequent audits ensures continuous improvement in security practices.
The Role of Regulatory Compliance in Security Audits
In many sectors, security audits are not only a best practice but a regulatory requirement. Compliance with standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and others necessitates regular audits to ensure that data is handled securely and that privacy protections are in place. Organizations that fail to comply with these standards face severe penalties, which can include financial fines, legal actions, and lasting reputational damage.
Regulatory bodies often update their requirements to reflect new threats and technological changes. As a result, organizations must stay informed about these changes and adjust their audit practices accordingly. Regular audits help organizations remain compliant by providing a structured framework for assessing adherence to regulatory standards. This not only reduces the risk of non-compliance but also builds trust with customers and partners who expect their data to be handled securely.
Embracing a Culture of Security
Regular security audits are most effective when they are part of a broader culture of security within an organization. Cybersecurity should be viewed as an integral part of the organization’s operations rather than a separate function. By fostering a culture that prioritizes security at every level, companies can ensure that all employees—from executives to entry-level staff—are aware of the risks and understand their role in maintaining a secure environment.
This cultural shift can be achieved through regular training sessions, clear communication of policies, and a commitment to continuous improvement. When employees are educated about the importance of cybersecurity and the role of regular audits, they are more likely to take proactive measures to protect sensitive information. A culture of security not only supports the audit process but also enhances the overall resilience of the organization against cyber threats.
Future Trends in Security Audits
As technology continues to evolve, so too will the nature of security audits. Emerging trends such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and blockchain technology are poised to transform the way organizations approach cybersecurity.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into security audits is already showing promising results. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data quickly, identifying patterns and anomalies that may indicate a security breach. By leveraging AI-driven tools, organizations can enhance the efficiency of their audits and detect vulnerabilities that traditional methods might miss. As these technologies continue to develop, they will undoubtedly become a cornerstone of modern security audit practices.
Blockchain for Enhanced Transparency
Blockchain technology offers the potential to revolutionize the audit process by providing a transparent and immutable record of all transactions. This level of transparency can help verify the integrity of data and ensure that any modifications or breaches are easily traceable. As blockchain technology matures, more organizations will likely adopt it as part of their security audit processes, particularly in sectors where data integrity is paramount.
Increased Integration with DevOps
The trend toward integrating security within the DevOps process—often referred to as DevSecOps—is changing the way audits are conducted. By incorporating security measures into every stage of the development lifecycle, organizations can identify and remediate vulnerabilities much earlier in the process. This proactive approach not only enhances security but also streamlines the audit process by embedding security considerations into routine operations.
Conclusion
Regular security audits are a critical component of any comprehensive cybersecurity strategy in today’s digital world. They offer a proactive approach to identifying vulnerabilities, ensuring regulatory compliance, and maintaining the trust of customers and stakeholders. While the process of auditing can be resource-intensive and challenging, the benefits far outweigh the costs. By investing in regular audits, organizations can mitigate risks, improve incident response, and foster a culture of security that is essential for long-term success.
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the importance of regular security audits will only grow. With the emergence of new technologies and increasing regulatory pressures, organizations must remain vigilant and adaptable. Embracing a comprehensive, proactive approach to security auditing not only protects sensitive data but also contributes to the overall resilience and sustainability of the organization.
Share this :