Volkswagen Data Breach Exposes 800,000 Electric Car Owners

Hoplon InfoSec
27 Dec, 2024
Do you heard about the recent Volkswagen Data Breach Exposes 800,000 Electric Car Owners Data? In a significant cybersecurity lapse, Volkswagen inadvertently exposed the personal information of approximately 800,000 electric vehicle owners. The compromised data included sensitive details such as contact information and precise GPS location data, raising critical concerns about privacy in the era of connected vehicles. This breach highlights the urgent need for robust security measures as the automotive industry becomes increasingly data-driven.
The Nature of the Data Breach
The breach originated from a misconfiguration within the systems of Cariad, Volkswagen’s software subsidiary. Sensitive data was stored on Amazon Cloud servers but was left publicly accessible for an extended period. This oversight allowed unauthorized access to critical personal information, including:
- Precise GPS data: This data could be used to create detailed movement profiles of vehicles and their owners.
- Contact details: Personal information such as phone numbers and email addresses was also exposed.
Notably, this breach didn’t just compromise the privacy of everyday users; it also affected high-profile individuals, including politicians, business leaders, and law enforcement officers. Such widespread exposure underscores the far-reaching implications of cybersecurity failures.
Discovery by Ethical Hackers
The vulnerability was uncovered by the Chaos Computer Club (CCC), a German hacker collective renowned for its ethical hacking practices. Upon discovering the flaw, the CCC promptly informed Volkswagen, enabling the company to address the issue before malicious actors could exploit it. This proactive approach by the CCC potentially prevented more severe consequences but highlighted the automotive industry’s pressing cybersecurity challenges.
The Bigger Picture: Data Privacy in Connected Cars
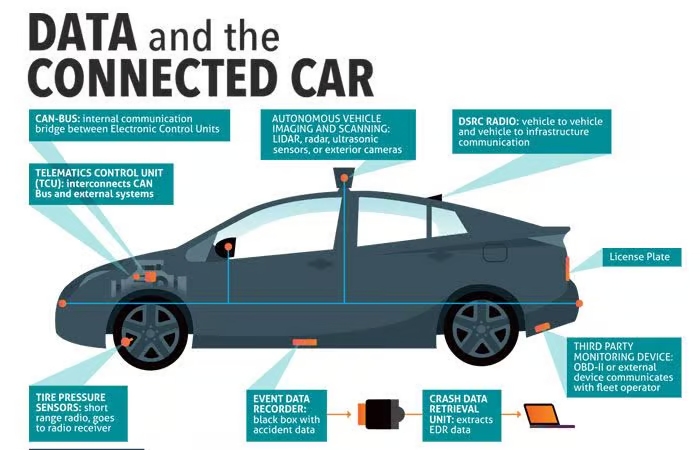
Volkswagen’s data breach is far from an isolated incident. It is part of a broader trend of privacy and security concerns within the automotive sector. As vehicles become more connected, they collect and store vast amounts of data—from driving patterns to personal information. A 2023 study by the Mozilla Foundation found alarming trends in this regard:
- Excessive Data Collection: Modern cars collect more data than is necessary for their functionality.
- Data Resale: Over 76% of car brands surveyed admitted they could potentially sell collected data to third parties.
- Frequent Incidents: Approximately 68% of these brands had experienced hacks, security incidents, or data leaks in the past three years.
Such findings paint a grim picture of the automotive industry’s approach to data privacy and emphasize the urgent need for comprehensive reforms.
Historical Data Breaches in the Automotive Industry

Volkswagen’s breach is the latest in a series of cybersecurity failures in the automotive world. Below are some notable examples that highlight the industry’s vulnerabilities:
- BMW Breach (2023): A Team led by ethical hacker Sam Curry demonstrated how they accessed BMW Employee and dealer accounts, enabling them to view confidential sales documents.
- Mercedes-Benz Chat System Hack: Hackers compromised the company’s internal chat system, exposing sensitive internal communications.
- Kia Vulnerabilities: Security flaws in Kia vehicles were found to allow remote unlocking and starting of cars.
- The Jeep Hack (2015): This incident remains one of the most infamous examples of automotive cybersecurity weaknesses. Two IT specialists remotely accessed a Jeep’s electronic systems via its cellular module, gaining control over its brakes, speed, and radio. This high-profile hack led to the recall of 1.4 million vehicles for a software update.
These incidents collectively demonstrate the high stakes of cybersecurity in the automotive sector and the potential risks posed by inadequate protection measures.
Lessons from the Volkswagen Data Breach

Volkswagen’s response to the breach has been relatively muted so far. The company has not yet provided detailed plans for mitigating the damage or preventing future incidents. However, this breach serves as a critical reminder of the importance of robust cybersecurity practices. Key lessons from this incident include:
- Proactive Security Measures: Automakers must adopt a proactive approach to cybersecurity, including regular system audits and vulnerability assessments.
- Employee Training: Employees at all levels should be trained in cybersecurity best practices to reduce the risk of human error leading to breaches.
- Transparent Communication: Companies must communicate openly with affected users during and after a breach, outlining steps to resolve the issue and prevent recurrence.
- Collaboration with Ethical Hackers: As demonstrated by the CCC, ethical hackers can play a vital role in identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities before they are exploited maliciously.
The Way Forward
The Volkswagen incident underscores a broader need for systemic changes in how the automotive industry approaches cybersecurity. As connected cars become the norm, automakers must prioritize data privacy and security through the following measures:
- Regulatory Compliance: Governments should enforce stringent data privacy laws tailored to the automotive sector.
- Secure Software Development: Automakers should integrate security features into the software development lifecycle, adopting practices such as encryption, two-factor authentication, and secure cloud storage.
- Independent Audits: Regular cybersecurity audits can help identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with best practices.
- User Awareness: Educating vehicle owners about potential privacy risks and providing them with tools to manage their data can reduce exposure.
Conclusion
The Volkswagen data breach is a stark reminder of the vulnerabilities inherent in connected vehicles and the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures. As cars become more intelligent and interconnected, protecting user data must become a top priority for automakers. By learning from incidents like this and implementing comprehensive security protocols, the industry can pave the way for a safer, more privacy-conscious future.
For More:
Share this :