Top 10 Most Common Cyber Attacks of 2024

Hoplon InfoSec
02 Jan, 2025
The year 2024 marked a pivotal moment in the ever-evolving realm of cybersecurity. Cyber Attacks of 2024 have become more frequent, sophisticated, and disruptive than ever before. With industries rapidly adopting digital transformation and the increasing interconnectedness of systems, attackers exploited vulnerabilities on an unprecedented scale. From crippling ransomware incidents targeting critical infrastructure to phishing campaigns powered by artificial intelligence, the threat landscape showcased both innovation and persistence on the part of cybercriminals.
This article explores the top 10 most common cyberattacks of 2024, shedding light on their mechanisms, real-world examples, and impacts. By understanding these threats, organizations can better prepare to combat evolving risks and protect critical assets in an increasingly hostile digital landscape. In today’s interconnected world, cybersecurity is no longer optional but necessary.
10 Cyber Attacks of 2024
Malware Attacks

Malware remained one of the most pervasive threats in 2024. Encompassing viruses, ransomware, spyware, and worms, malware infiltrates systems to disrupt operations, steal sensitive data, or cause damage.
Ransomware: The Dominant Malware Threat
Ransomware attacks surged globally in 2024, enabled by the rise of Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) platforms. These platforms made it easier for less-skilled attackers to execute sophisticated attacks. High-profile incidents included:
- German Food Processor VOSSKO: Operations were disrupted for weeks due to a ransomware attack.
- Japan’s Port of Nagoya: Millions of dollars in damages were incurred after ransomware paralyzed port operations.
Spyware and Trojans
Spyware and Trojan malware were widely used for data exfiltration and espionage, mainly targeting businesses and government entities.
Defense Strategies
- Deploy endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools.
- Regularly update software to patch vulnerabilities.
- Implement robust backup protocols to ensure data recovery during an attack.
Phishing Attacks

Phishing attacks experienced a dramatic spike in 2024, with a 202% increase in phishing messages and a staggering 703% surge in credential-based phishing attempts. Attackers leveraged email, SMS (smishing), and voice calls (vishing) to deceive users into revealing sensitive information.
Advanced Phishing Techniques
- Spear Phishing: Personalized emails targeted specific individuals or organizations, often impersonating trusted entities such as colleagues or service providers.
- Multichannel Phishing: Attackers expanded beyond email, exploiting platforms like LinkedIn, Microsoft Teams, and messaging apps.
High-Profile Incidents
- RockYou2024 Password Leak: Nearly 10 billion passwords were exposed, facilitating brute-force and credential phishing attacks.
- Paris Olympics Ticket Scam: A “Ticket Heist” campaign tricked individuals into purchasing fake tickets for significant events, leveraging over 700 fraudulent domains.
- Financial Sector Phishing Surge in India: Over 135,000 phishing attacks targeted India’s financial sector in the first half of the year, many using AI-generated phishing schemes.
Defense Strategies
- Train employees to recognize phishing attempts.
- Use email filtering systems with real-time threat detection.
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) to protect user accounts.
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks

DDoS attacks, which overwhelm networks with traffic to render services unavailable, increased by 20% in 2024. State-sponsored actors played a significant role in these attacks.
Notable Techniques
- Amplification Attacks: Exploiting protocols like DNS and NTP to magnify attack traffic.
- Motivations: Used as smokescreens for invasive breaches or as political statements by hacktivist groups.
High-Profile Attacks
- Global DDoS Surge: A record-breaking 4.2 Tbps attack targeted financial services and telecom sectors in October 2024.
- State-Sponsored Campaigns: China emerged as the most targeted country, with critical services disrupted globally.
Defense Strategies
- Deploy Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) for traffic distribution.
- Use DDoS mitigation services to absorb excess traffic.
- Monitor network traffic for anomalies.
Insider Threats

Insider threats surged in 2024, fivefold higher than in 2023. These threats stemmed from malicious employees or negligent staff actions.
Key Risks and Challenges
- Risks: Data theft, system sabotage, and unauthorized access using legitimate credentials.
- Challenges: Insider threats are difficult to detect due to their legitimate access privileges.
High-Profile Incident
- Hathway ISP Data Breach: Sensitive data of over 41.5 million customers was exposed, with insider vulnerabilities exploited to leak over 200 GB of data.
Defense Strategies
- Implement Zero Trust Architecture to limit access based on roles.
- Monitor user activity using behavioral analytics tools.
- Conduct regular audits and enforce strict access controls.
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)

APTs are stealthy, prolonged attacks aimed at stealing data or causing disruption without immediate detection. In 2024, state-sponsored groups like China’s Volt Typhoon targeted critical U.S. infrastructure.
Characteristics of APTs
- Exploiting software vulnerabilities and using social engineering tactics.
- Resource-intensive, highly targeted operations.
High-Profile Attack
- Volt Typhoon Campaign: This Chinese state-linked APT targeted U.S. critical infrastructure providers by hijacking small office/home office (SOHO) routers to form botnets capable of launching large-scale attacks.
Defense Strategies
- Intrusion detection systems (IDS) are used to monitor network activity.
- Regularly update software and conduct vulnerability assessments.
- Segment networks to limit lateral movement by attackers.
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks

MitM attacks intercept communications between two parties to steal or manipulate sensitive information. In 2024, attackers exploited flaws in SSL/TLS protocols and unsecured Wi-Fi networks.
Common Scenarios
- Stealing login credentials during online banking sessions.
- Redirecting users to malicious websites through URL manipulation.
Defense Strategies
- Enforce HTTPS connections using secure certificates.
- Avoid public Wi-Fi or use Virtual Private Networks (VPNs).
- Implement strong encryption protocols for sensitive communications.
Supply Chain Attacks
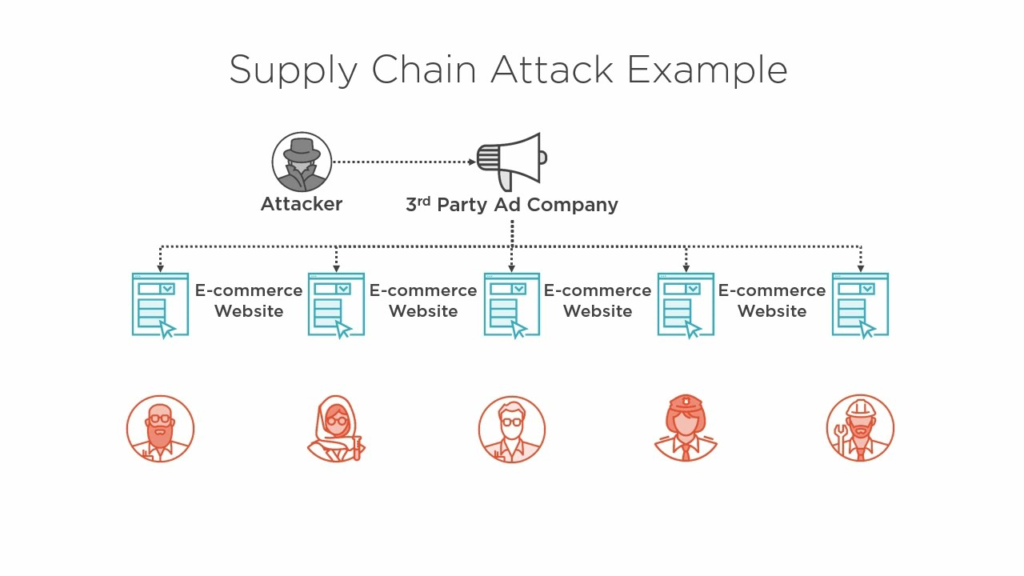
Supply chain attacks target third-party vendors or software providers to infiltrate larger organizations. These attacks grew more prevalent as businesses increasingly relied on interconnected systems.
Notable Trends
- Compromising software updates or hardware components before delivery.
- Exploiting trust relationships between vendors and clients.
Defense Strategies
- Vet third-party vendors rigorously before partnerships.
- Monitor supply chain activities for anomalies.
- Use endpoint protection solutions across all devices.
Code Injection Attacks

Code injection techniques, such as SQL Injection and Cross-Site Scripting (XSS), will remain common in 2024. These methods exploit poorly secured web applications to execute malicious scripts or queries.
Examples
- SQL Injection: Extracting sensitive database information by inserting malicious queries.
- XSS: Injecting scripts into web pages viewed by other users to steal session cookies or credentials.
Defense Strategies
- Validate all user inputs on web applications.
- Use web application firewalls (WAFs).
- Conduct regular penetration testing.
Brute Force Attacks

Brute force attacks involve systematically guessing login credentials until access is gained. Variants like password spraying and credential stuffing became more sophisticated in 2024.
Key Developments
- Attackers used leaked credentials from previous breaches to target accounts.
- Automated tools accelerated the guessing process.
Defense Strategies
- Enforce strong password policies with regular updates.
- Enable account lockout mechanisms after failed login attempts.
- Use MFA for an additional security layer.
DNS Tunneling
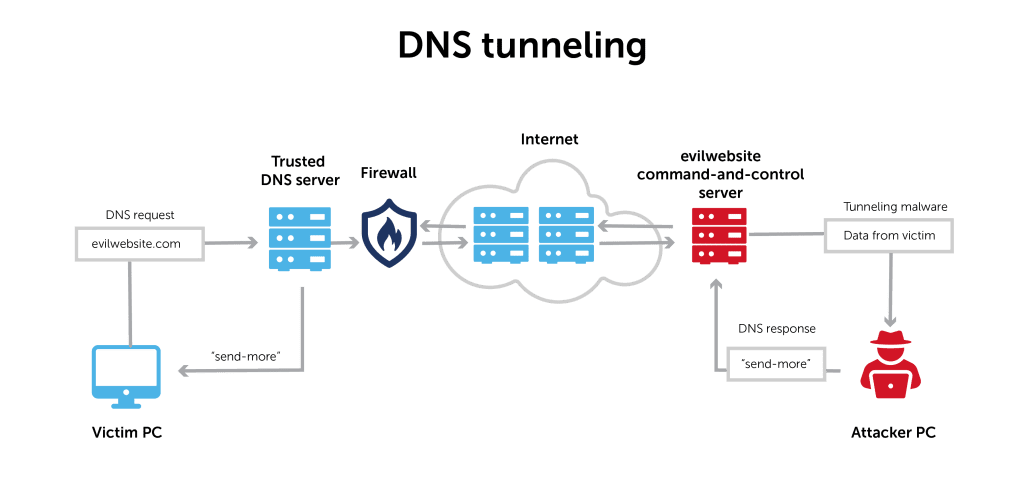
DNS tunneling emerged as an advanced method for bypassing network security measures. Attackers used DNS queries to exfiltrate data or establish command-and-control channels.
Mechanism
DNS tunneling embeds malicious payloads within DNS requests and responses, making them harder to detect than traditional methods.
Defense Strategies
- Monitor DNS traffic for unusual patterns.
- Restrict external DNS queries using firewalls.
- Deploy DNS security solutions capable of detecting tunneling activities.
Conclusion
The cybersecurity landscape in 2024 underscored the evolving sophistication of cyberattacks across industries worldwide. Organizations faced unprecedented challenges, from ransomware paralyzing operations to insider threats exploiting trusted access points. To combat these threats effectively:
- Adopt Multi-Layered Security: Incorporate advanced tools like AI-driven threat detection systems.
- Employee Training: Focus on recognizing social engineering tactics such as phishing.
- Global Collaboration: Governments and private sectors must work together to address state-sponsored threats like APTs.
As cybercriminals continue refining their methods, staying vigilant is essential for survival in an increasingly interconnected world.
For More:
Share this :