AI in Cybersecurity Protects The Cloud-Learn About its Importance

Hoplon InfoSec
24 Jun, 2025
The rise of cloud computing has revolutionized how organizations store, access, and manage their data. As workloads increasingly shift to platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP), security becomes a critical concern. Traditional cybersecurity approaches, which rely on static rules and manual processes, are proving insufficient against sophisticated threats. This is where artificial intelligence (AI) steps in to reshape the cybersecurity landscape.
AI-powered cybersecurity in the cloud represents a new frontier in threat detection, prevention, and response. It uses machine learning models, big data analysis, and intelligent automation to continuously monitor cloud environments, adapt to evolving risks, and act swiftly to mitigate potential damage. This article explores the concept of AI cybersecurity in cloud computing, its benefits, its significance, core features, and how it functions (using AI in cybersecurity protects the cloud).

How does AI help cyber security?
AI plays a vital role in enhancing cybersecurity by making it faster, smarter, and more proactive. It can quickly analyze large amounts of data to detect unusual behavior or signs of malware, helping to identify threats early. AI systems can also prevent attacks in real time by blocking malicious activities before they cause damage. Additionally, it automates responses such as isolating infected systems or sending alerts to security teams. Over time, AI continues to learn from new threats, improving its ability to defend against future attacks. It also supports security experts by uncovering hidden threats that might go unnoticed by humans.
What Is AI Cybersecurity in the Cloud?

The Convergence of Two Critical Technologies
AI cybersecurity in the cloud combines artificial intelligence and cloud security to protect digital assets, workloads, and users from cyber threats. Unlike traditional systems that rely on predefined rules, AI-based solutions learn from vast amounts of data and adapt over time. This makes them well-suited for cloud environments, which are dynamic, scalable, and inherently complex.
Cloud security must deal with varied workloads, distributed resources, and frequent configuration changes. Human analysts cannot feasibly monitor the scale and speed at which these changes occur. AI bridges this gap by offering continuous, automated oversight. It ingests logs, detects anomalies, and proactively mitigates threats across cloud services.
Intelligent Security at Scale
AI cybersecurity is not a single product but a collection of intelligent processes embedded into cloud-native tools or third-party platforms. It includes services that detect threats, assess vulnerabilities, enforce policies, and respond to incidents, all in real-time. These systems leverage deep learning, neural networks, and natural language processing to understand behavior patterns and environmental contexts.
Examples of AI-driven tools include Microsoft Defender for Cloud, AWS GuardDuty, and Google Chronicle. These services integrate with cloud infrastructure to provide comprehensive, intelligent protection tailored to the organization’s risk profile and compliance needs.
What Are the Benefits of AI Cybersecurity in the Cloud?
Real-Time Detection and Response
One of the most transformative benefits of AI cybersecurity is its ability to provide real-time threat detection and response. Traditional systems often rely on signature-based detection, which can miss new or unknown threats. AI can identify zero-day attacks, abnormal behavior, or policy violations by learning from patterns in data rather than relying on pre-set rules.
This continuous analysis reduces the time between detection and action. In critical environments, where every second counts, AI can isolate threats or restrict access before an attacker causes serious damage.
Improved Accuracy and Reduced False Positives
AI systems are trained to differentiate between legitimate activity and suspicious behavior. This helps reduce the number of false positives and alerts, which waste time and resources. Security teams can focus on genuine threats instead of being overwhelmed by noise. As AI models refine over time, their accuracy improves, making detection more reliable.
Scalability and adaptability.
Cloud environments grow and shrink based on demand. AI security solutions scale alongside them. Whether an organization operates hundreds or thousands of virtual machines or containers, AI systems can adapt without sacrificing performance. This flexibility allows consistent protection even during spikes in traffic or resource changes.
Cost Efficiency and Resource Optimization
AI cybersecurity reduces the need for manual intervention, enabling smaller teams to manage larger environments. Automated detection and response reduce overhead, while predictive analytics help organizations avoid costly breaches. Over time, these systems lower the total cost of ownership by minimizing damage, downtime, and compliance failures.
Strengthened Compliance and Governance
Cloud service providers operate under strict regulations, and their customers must also comply with frameworks like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS. AI tools help monitor for misconfigurations, risky permissions, and data flows that could violate these rules. With AI-generated audit logs and reports, companies can prove compliance and identify gaps before they escalate into violations.
Why Is AI Cybersecurity Important in the Cloud?

The Rise of Cloud Adoption and Complexity
Cloud adoption has soared across industries, with organizations hosting everything from databases to application backends in virtualized environments. This shift introduces a level of complexity that is difficult to manage using conventional tools. Cloud environments are not static; they involve continuous provisioning, de-provisioning, and integration with third-party services. This dynamism presents a moving target for attackers.
Evolving Threats in Cloud Ecosystems
Attackers are increasingly targeting cloud environments through novel techniques, including API exploits, privilege escalations, and container escapes. They often use AI for themselves to evade detection. Manual systems are too slow to detect and react to these modern attack vectors. AI cybersecurity is crucial for staying ahead of adversaries who operate at machine speed.
Insider threats are another pressing concern. Cloud environments are accessed by multiple users from various locations. A compromised credential can go undetected unless systems are monitoring behavioral patterns. AI excels in identifying such anomalies by analyzing user access, device usage, and contextual clues.
Shared Responsibility and the Need for Visibility
In cloud computing, security is a shared responsibility. While providers manage the physical infrastructure and core services, customers must secure their data, identities, and applications. Unfortunately, many organizations struggle with visibility across their cloud assets. AI provides this visibility by offering centralized monitoring and analytics across services and providers.
Data Protection and Reputation Management
Data breaches in the cloud are not just technical failures; they can have serious legal and reputational consequences. Lost customer trust, regulatory fines, and public backlash can cripple a company. AI minimizes this risk by proactively identifying vulnerabilities and securing data in motion and at rest.
In a world where every organization is a potential target, AI cybersecurity is no longer optional; it is essential for digital survival.
How AI in Cybersecurity Protects the Cloud?

Behavioral and User Analytics
One of the core features of AI cybersecurity is its ability to analyze user and system behavior. Instead of relying solely on predefined rules, AI models establish baselines for normal activity. Deviations from this norm, such as accessing files at odd hours or downloading large datasets, are flagged as potential threats.
Behavioral analytics helps detect insider threats and account takeovers, which are notoriously hard to catch using traditional techniques. The AI adapts its understanding of “normal” over time, improving its detection capabilities.
Threat Intelligence and Risk Scoring
AI systems ingest global threat intelligence feeds to stay informed about new attack methods, malicious IP addresses, and indicators of compromise. This information helps prioritize threats based on severity. Risk scoring mechanisms assess the potential impact of an event, allowing security teams to focus on the most dangerous threats first.
Automated Response and Remediation
AI enables automated responses that are swift, consistent, and effective. These may include disabling user accounts, blocking IP addresses, isolating virtual machines, or triggering alert workflows. This feature reduces the time to containment and lessens the impact of breaches.
Automation also supports playbook execution in Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) platforms. AI determines the appropriate course of action based on context and executes predefined protocols without human intervention.
Compliance Monitoring and Configuration Audits
Misconfigured cloud resources such as publicly exposed storage buckets are one of the leading causes of data breaches. AI tools continuously audit these configurations and compare them against compliance frameworks. They provide alerts and recommendations to bring environments back into compliance.
These systems can also generate reports for regulators, making audits smoother and more accurate. Some even provide real-time dashboards showing the compliance status of various cloud components.
Identity and Access Anomaly Detection
AI tracks identity and access patterns across cloud services. It looks for anomalies such as multiple failed login attempts, impossible travel scenarios (logging in from two distant locations simultaneously), and use of outdated or unverified credentials. This helps in detecting account compromises early.
How is AI used in cloud security?
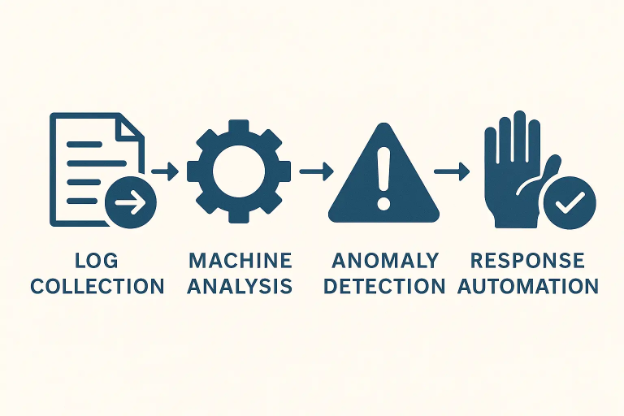
Data Collection and Ingestion
The process starts with collecting data from across the cloud ecosystem. This includes logs from virtual machines, containers, databases, network traffic, APIs, user activity, and third-party services. This raw data provides the foundation for analysis.
Cloud-native services like AWS CloudTrail, Azure Monitor, and Google Cloud Audit Logs offer rich telemetry. AI tools integrate with these services to gather insights in near real-time.
Data Normalization and Preprocessing
Once collected, the data is cleaned and transformed into standardized formats suitable for analysis. This includes organizing logs, removing redundancies, and extracting metadata such as IP addresses, device IDs, and timestamps. Preprocessing ensures consistency and accuracy, allowing AI models to detect subtle patterns.
Machine Learning Model Execution
AI tools apply machine learning models to identify threats and anomalies. Supervised learning models compare new activity to known examples of malicious and benign behavior. Unsupervised learning models cluster data and highlight outliers without prior labeling. Deep learning and reinforcement learning may also be used to improve detection and response over time.
These models evolve with each new data input, becoming more accurate and context-aware. They continuously refine their algorithms based on feedback, human validation, and incident outcomes.
Threat Classification and Prioritization
Once a threat is identified, AI systems classify it as phishing, malware infection, lateral movement, or privilege abuse and assign it a risk score. This helps security teams understand the urgency of the issue and act accordingly. High-risk events may trigger immediate containment measures, while low-risk activities are monitored for escalation.
Automated Action and Feedback Loop
After classification, AI systems can automatically execute mitigation actions. These might include terminating sessions, resetting credentials, or applying stricter firewall rules. All actions are logged, and the system receives feedback from human analysts or predefined results, which it uses to fine-tune its accuracy.
The learning process is continuous. AI cybersecurity systems evolve by consuming more data and adjusting their parameters, ensuring that they remain effective even as threat landscapes change.
Conclusion
AI cybersecurity has become an essential component of cloud defense. With the complexity and scale of modern cloud environments, traditional security methods can no longer keep pace. AI brings intelligence, automation, and adaptability, enabling organizations to defend against sophisticated threats in real time.
From behavioral analytics and threat classification to automated response and compliance monitoring, AI reshapes how we approach cloud security. It not only enhances protection but also streamlines operations, improves visibility, and ensures resilience.
As cloud adoption continues to grow, the integration of AI into cybersecurity is not just an advantage; it’s a necessity for organizations seeking to secure their data, operations, and reputation in an increasingly hostile digital world.
Resources:
Fortinet
Safari Solutions
Share this :