AI-Powered Cyberattacks: A Survival Guide for the Upcoming 12 Months

Hoplon InfoSec
30 Aug, 2025
AI-Powered Cyberattacks
A night when the network seemed to come to life
The message appeared to be typical. Keeping your system updated, staying away from untrusted apps, checking permissions carefully, and running monthly scans are small habits that protect you more effectively than any single app can. The voice note then came. The head of finance sounded just like it. The same rhythm, the same brief silence before the numbers. But it wasn’t him. The room became chilly at that point.
Such incidents are no longer uncommon. Cyberattacks powered by AI transform common signals into weapons that have a personal touch. The email seems to be correct. It sounds like a good call. The timing is ideal. Defenders continue to see hashes and IPs. Attackers can now see rhythm, people, and habits.
Why the latest round of attacks feels different
Conventional intrusions search for a gap in the wall. Operations for today involve watching the guard patrol the perimeter and then mimicking their movements. Criminals can test thousands of micro-variations, scale credible outreach, and persist until someone blinks thanks to automation and intelligent language models. The atmosphere in a security office is altered by this combination of speed, realism, and constant iteration.
Additionally, we observe a change from a single large exploit to numerous small nudges. An assistant tool begins working for the attacker after a small prompt is slipped there and a small piece of data is scraped here. The hallmark of AI-powered cyberattacks is that encroaching influence.
The stack that supports contemporary offensive tools
There’s a familiar stack under the hood. gathering information from vendor documents, meeting recordings, public posts, and compromised credentials. commercially available models for text generation and speech cloning. scripts that connect everything and communicate with cloud APIs, collaboration apps, and email services. It spreads because none of this is exotic.
Sometimes security teams overlook the fundamentals in their quest for the ideal detector. Open shares, permissive API keys, and inadequate identity checks are typically the foundations of model misuse. Because of this, cyberattacks powered by AI frequently succeed without the use of elite zero days. At machine speed, they merely choreograph common gaps.
Using a silicon sidekick for social engineering
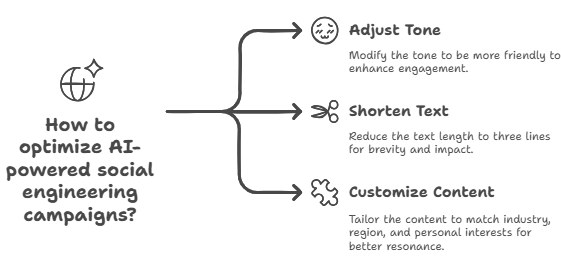
In the past, social engineering relied on talented manipulators. A novice scammer can now mimic the skills of an experienced con artist. The copy sounds customized. The wording changes depending on your industry, region, and even your favorite sports allusion. It mirrors you, so it lands better.
These campaigns learn from each response when run at scale. Incorrect tone? Change to “friendly.” Too much time? Trim to three lines. Because of this feedback loop, even when you have never met, AI-powered cyberattacks feel like you are speaking with a familiar person.
Deepfakes that persuade finance teams that money moves
Finance leaders are still uneasy about one case. Scammers impersonated multiple executives in a deepfake video call at the beginning of 2024 in order to fool an employee into sending about $25 million. Doubt was overcome by the convincing voices, images, and small talk. That one transfer turned into a worldwide warning.
The lesson is straightforward if you manage accounts payable or treasury. Video is not evidence. Speech is not evidence. AI-powered cyberattacks that rely more on performance than malware can be neutralized with a second channel, a shared code phrase, or a brief callback.
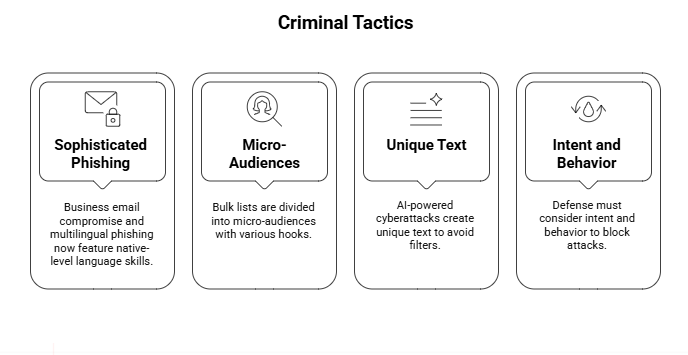
Large-scale phishing in any language
Words that slow down criminals. These days, business email compromise and multilingual phishing come with native-level spelling, grammar, and industry jargon. With various hooks for sales, legal, or operations, bulk lists are divided into micro-audiences. The wrapper is new, but the payload is as old as macros.
Your blocklists appear clean as engagement rises because of this. Because the text in targeted lures created by AI-powered cyberattacks is unique and not reused across campaigns, they avoid canned filters. A sentence that has never been used before cannot be reputation-blocked. The defense must consider intent and behavior.
Malware that changes during a campaign
Additionally, we are observing tooling that changes as it is being executed. Code that adapts to its surroundings, switches to more stealthy methods when EDR activates, and turns to data theft when encryption appears dangerous. Some strains now use small helper models in conjunction with automated recon to make real-time decisions about their next course of action.
Here, cyberattacks driven by AI blend into self-governing decision-making processes. The play doesn’t have to be flawless, but it isn’t always. Static detections that rely on fixed sequences can be outperformed by continuous small optimizations through a kill chain.
The supply chain for AI and model exposure
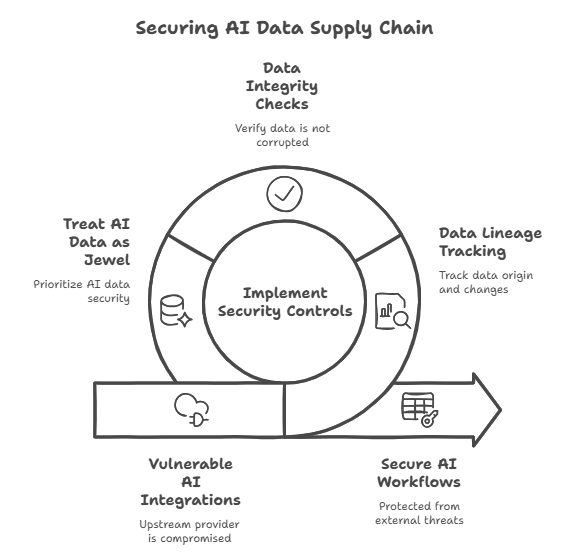
Even though your company doesn’t create models, you most likely use them in search, ticket triage, chat assistants, and code helpers. A new supply chain is created by those integrations. Your workflows are at risk if an upstream provider is compromised or improperly configured. External tools have the potential to retain, learn from, and resurface data.
For this reason, training data, fine-tuning sets, and prompt libraries are increasingly the targets of AI-powered cyberattacks. Lineage and data integrity are evolving from tedious documentation tasks to first-class security controls. On this point, CISA’s 2025 guidance is direct. Throughout its entire lifecycle, treat AI data like the jewel in the crown.
Quick injection and the silent rewrite
A prompt injection seems almost courteous. No loud exploit exists. In a document, ticket, or web page, an attacker conceals instructions. After reading it, your assistant gives the incorrect instructions. It could rewrite a task in the intruder’s favor, retrieve a booby-trapped file, or leak secrets. Indirect injection is a risky variation in which the poison resides in data that the system accesses later.
One of the most insidious routes for cyberattacks powered by AI is this one. There are social and technical components to the solution. Stop treating model responses as privileged truth, isolate browsing, and restrict tool access. These manipulations are classified by DHS and others as evasion, which, if unchecked, can compromise availability and confidentiality.
Real-world applications of adversarial machine learning
Adversarial machine learning lies beyond office tools. Consider manipulated inputs that cause a model to misclassify, extraction that clones it, or data poisoning that biases a model. Similar to ATT&CK for conventional threats, MITRE developed ATLAS to map these strategies. It provides teams with a common language for planning, simulating, and testing mitigations.
This is significant because cyberattacks powered by AI will not only use assistants to target you. Additionally, they will target the models you use for industrial control, content filtering, and fraud detection. The rest of your controls will inherit the error if those models have a faulty worldview.
Pressure on identity, cloud, and SaaS
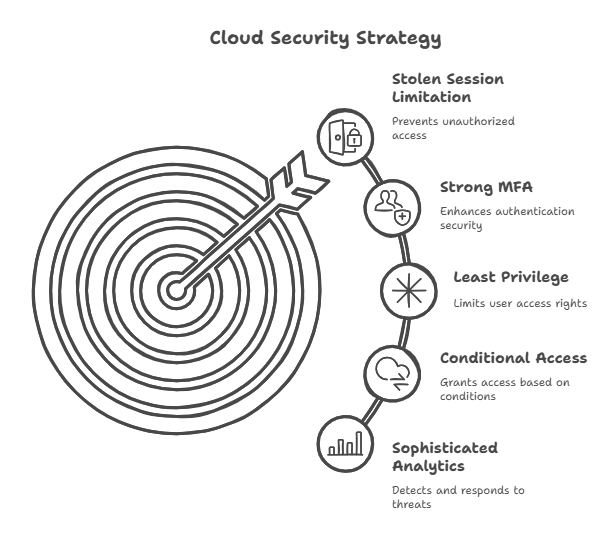
The cloud is where most modern businesses operate. Attackers use a combination of clever phishing, session hijacking, and API abuse to stealthily navigate developer platforms and collaboration suites. Machine accounts are frequently softer than human ones, and identity turns into the true perimeter.
To obtain tokens, replay sessions, and create convincing OAuth prompts automatically, attackers combine traditional methods with AI-powered cyberattacks. The antidote remains conditional access, least privilege, and strong MFA. Although sophisticated analytics are useful, nothing compares to limiting the potential of a stolen session.
Crucial infrastructure at risk
Models are now used in manufacturing, transportation, energy, and healthcare for safety, routing, and forecasting. National cyber agencies continue to warn that state-aligned groups and criminals are experimenting with AI to speed up reconnaissance, personalize operator lures, and probe OT-IT boundaries.
This is where being diligent becomes necessary and tedious. Divide networks into segments. Check for fail-safes. Practice falling back by hand. Trained humans must be able to check a gauge in the real world when AI-powered cyberattacks muddy the screen with plausible but fake readouts.
Keeping the plot intact while employing clever defense
Defenders can benefit from automation. Triage can be expedited. Threat hunting can identify trends that an exhausted analyst might overlook. However, your attack surface grows with each shiny tool. Prior to activating fancy detections, start with data governance, access controls, and clear logging.
Consider it akin to hiring a new intern who never sleeps. beneficial if observed. risky if left unattended. The objective is to prevent the development of new blind spots while thwarting AI-powered cyberattacks. That balance is given structure by the secure-by-design concepts and the NIST AI risk framework.
The line-holding people, playbooks, and policies
Every week, technology evolves. Processes and people don’t. Create a brief playbook that covers the use of assistant tools, media authenticity checks, and financial verification. Manage tabletops with communications and legal. Determine when automation should be stopped and when a human should be involved.
Here, culture is important. Shame is inferior to curiosity. Celebrate when a teammate halts a payment because they sensed something wasn’t right. That’s how you deny AI-powered cyberattacks what they most need, which is our haste.
A 90-day plan that you can truly adhere to
the first thirty days. Map the areas where generative tools interact with code, legal archives, finance workflows, and customer data. Disable anything you don’t understand. Include domain limitations in the browsing capabilities. To authorize payments over a predetermined threshold, a second channel must be used.
31–60 days. Implement identity hardening. MFA for administrators supported by hardware. conditional access that keeps dangerous sessions separate. Change the machine’s login credentials. Include detections for bulk share link creation, unexpected OAuth grants, and abrupt mailbox rules. Run a tabletop on prompt injection and align with ATLAS for model-specific risks.
Days 61 through 90. Teach executive assistants, finance, and human resources about deepfake tells and verification procedures. For urgent requests, include code phrases and watermarks. Discuss AI data retention with vendors in accordance with CISA’s lifecycle guidelines. To get new hires off to a good start, publish a two-page internal guide.
Important lessons you can apply this week
Avoid using a persuasive voice when arguing. Check a second channel. Consider assistant outputs, training sets, and model prompts as essential code. Don’t let your automation see or do too much. Additionally, encourage people to raise their hands when something seems nearly correct. A lot of trouble starts with “almost.”
Explore our main services:
Share this :