Everything You Need to Know About the Apple CVE-2025-43300 Zero-Day Patch

Hoplon InfoSec
21 Aug, 2025
Apple CVE-2025-43300 zero-day patch
Imagine waking up and checking your iPhone only to find a security alert from Apple. In August 2025, Apple announced a major zero-day vulnerability, CVE-2025-43300, that was actively being exploited in the wild. Users were warned that attackers might have already targeted certain individuals and that immediate action was required.
Zero-day flaws are rare but can be extremely harmful. They appear suddenly, and both users and developers must act quickly to protect devices. This should serve as a caution to all Apple users to stay alert and respond promptly.
What Does CVE-2025-43300 Stand For?
CVE-2025-43300 is a vulnerability in Apple’s Image I/O framework, which enables devices to work with common photo formats.
At its core, it is an out-of-bounds write flaw, allowing data to be written outside allocated memory. This could let attackers run arbitrary code or even take control of a device. Apple noted that the zero-day had been used in “very advanced attacks” targeting certain individuals.
Although detailed technical information is scarce, it is clear that this flaw has been exploited in the real world, not just theorized.
Understanding Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
Zero-day vulnerabilities are hidden traps in software that remain unknown until discovered. There is no patch yet, making them extremely dangerous. Hackers can exploit these flaws before any security measures are implemented.
Historically, zero-days have caused significant problems. For example, the Heartbleed bug exposed millions of private records, and the Pegasus spyware used Apple zero-days to monitor devices covertly. CVE-2025-43300 reminds us that even trusted platforms can be vulnerable.
The Role of Apple’s Image I/O Framework
The Image I/O framework is a crucial component of Apple’s ecosystem. It allows apps to efficiently read, write, and process images. Many iOS, iPadOS, and macOS apps rely on this framework, so a flaw here can affect multiple applications simultaneously.
Think of it like a building’s foundation: a small weakness at the base can compromise the entire structure. Since users work across multiple devices to handle images, this is a widespread concern.
How the Vulnerability Works: Out-of-Bounds Write
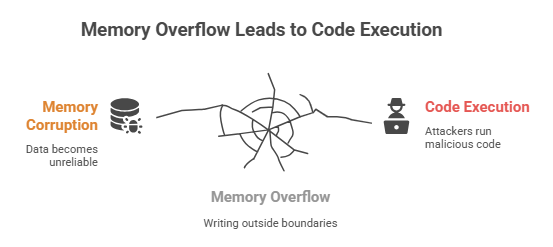
CVE-2025-43300 happens when a program writes outside the allocated memory boundaries. This can lead to memory corruption and allow attackers to execute malicious code.
For most users, this means that simply opening a malicious image, whether through email, chat apps, or downloads, could put a device at risk. The technical details may be complex, but the essence is simple: a small error in image processing can create serious security risks.
Real-World Risks: Memory Corruption and Arbitrary Code Execution
Memory corruption can let attackers manipulate your device, install spyware, or deploy ransomware. Arbitrary code execution allows commands to run without your knowledge.
A seemingly harmless image from a friend could secretly exploit this flaw. Within seconds, an attacker could access your phone, monitor your actions, or steal private data.
Targeted Exploitation in the Wild
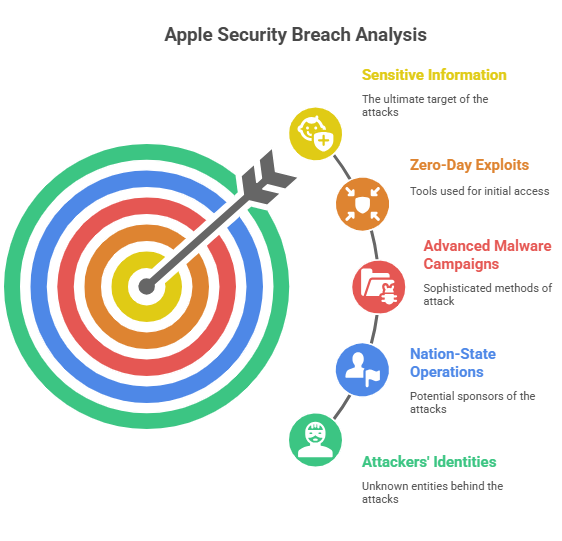
Apple confirmed that CVE-2025-43300 was used in highly targeted attacks. These were not random but aimed at specific individuals. Experts believe the likely goal was espionage or theft of sensitive information rather than widespread disruption.
Even users who consider themselves “low-risk” may be targeted if chosen by attackers.
Potential Threat Actors and Campaigns
Apple has not revealed the attackers’ identities. Cybersecurity experts speculate that the attacks may involve nation-state operations or advanced malware campaigns.
Zero-days are often used to gain long-term access to devices and collect sensitive information. The precision of these attacks suggests careful planning and technical expertise, not casual hacking.
Apple’s Response: The Security Patch
Apple acted quickly and released updates across all affected devices:
iOS 18.6.2 and iPadOS 18.6.2
iPadOS 17.7.10
macOS Sequoia 15.6.1
macOS Sonoma 14.7.8
macOS Ventura 13.7.8
The patch improves bounds checking, ensuring memory operations remain within safe regions and neutralizing the exploit.
Affected Devices and Software Versions
The vulnerability affects multiple Apple products:
iPhone XS and later
Various iPad Pro, Air, and Mini models
Macs running macOS Ventura, Sonoma, and Sequoia
This highlights how deeply integrated the Image I/O framework is across Apple’s ecosystem, emphasizing the need for urgent updates.
How the Patch Fixes the Problem
The patch improves the Image I/O framework by verifying memory boundaries more strictly. This prevents images from writing outside allocated memory. Once updated, devices are protected against active exploits.
The fix is straightforward but only effective if users install updates promptly.
What Users Should Do Right Away
To stay safe, Apple users should:
Update iOS, iPadOS, and macOS to the latest versions.
Avoid opening files or images from untrusted sources.
Enable automatic updates to minimize exposure.
Delaying updates leaves users vulnerable to an active zero-day, so immediate action is essential.
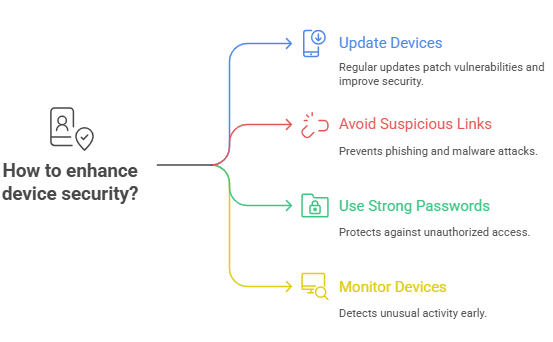
Best Ways to Lower Future Risks
CVE-2025-43300 reminds us to maintain ongoing cybersecurity:
Keep devices updated regularly.
Avoid suspicious links, downloads, or attachments.
Use strong, unique passwords and enable two-factor authentication.
Monitor devices for unusual behavior.
Security is like maintaining a home: locks are important, but vigilance is equally essential.
Lessons CVE-2025-43300 Teaches Apple Users
This incident highlights the importance of proactive cybersecurity. Hackers can exploit flaws in even the safest platforms. Users and developers need to:
Stay up to date with security updates.
Prioritize applying fixes immediately.
Be aware that advanced attackers can bypass standard protections.
Ultimately, everyone shares responsibility for security. Awareness and swift action can make the difference between safety and compromise.
Staying Safe in a Rapidly Changing Threat Landscape
CVE-2025-43300 demonstrates how fast new threats can appear. Users can reduce their risk by applying the Apple CVE-2025-43300 zero-day patch, handling files carefully, and following strong cybersecurity practices.
This zero-day serves as both a warning and a lesson. Staying updated, vigilant, and proactive is the best defense in the digital age. After applying the patch, users gain better control and peace of mind but must remain cautious.
Share this :