Cybersecurity Challenges in Cloud Computing: Threats, Risks, and Solutions

Hoplon InfoSec
08 Mar, 2025
Cloud computing has revolutionized how businesses and individuals store, manage, and process data. It offers scalability, cost-efficiency, and flexibility, making it an essential component of modern IT infrastructure. However, with these benefits come significant cybersecurity challenges. As more data migrates to the cloud, cyber threats evolve, making security a top concern for organizations and individuals alike.
This blog explores the key cybersecurity challenges in cloud computing, their associated risks, and strategies for effectively mitigating these threats.
Data Breaches and Data Loss

One of the most serious cybersecurity concerns in cloud computing is data breaches. Cybercriminals target cloud storage systems to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data, including personal information, intellectual property, and financial records. Data loss, on the other hand, can occur due to accidental deletions, hardware failures, or cyberattacks.
The risk of data breaches increases with inadequate encryption, weak access control mechanisms, and insider threats from employees or third-party vendors. Additionally, vulnerabilities in cloud service providers (CSPs) can expose critical data to unauthorized access.
To mitigate these risks, organizations should implement strong encryption for data at rest and in transit. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) should be enforced to add an extra layer of security. Regular backups of critical data to secure off-cloud locations can help prevent data loss incidents.
Insecure APIs and Interfaces
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) are crucial for cloud services but can also be a security vulnerability if not properly secured. Attackers exploit insecure APIs to manipulate cloud resources, gain unauthorized access, or execute data theft.
Weak authentication, exposure of sensitive information, and lack of API monitoring make APIs a prime target for cybercriminals. Organizations must secure APIs using gateways with strict authentication protocols and employing OAuth or token-based access mechanisms. Regular updates and security patches should be applied to prevent potential exploits.
Misconfigured Cloud Storage
Misconfiguration of cloud storage is a leading cause of data leaks and breaches. Many organizations fail to configure their cloud settings correctly, exposing storage repositories to unauthorized access. Default settings, lack of knowledge about security configurations, and insufficient security audits contribute to this issue.
Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments can help detect misconfigurations. Automated security tools should be used to identify and remediate risks. Implementing role-based access control (RBAC) ensures that only authorized personnel can access sensitive data, reducing the risk of accidental exposure.
Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks
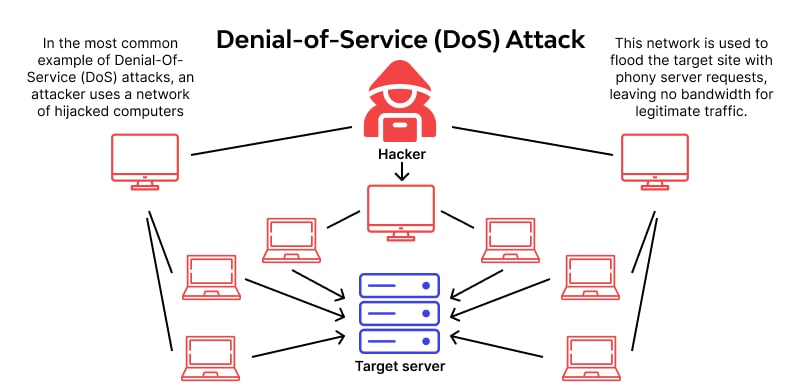
Cloud services are vulnerable to DoS attacks, where attackers flood cloud servers with excessive traffic, causing system downtime and service disruptions. This can severely impact businesses, leading to financial losses and operational inefficiencies.
A lack of rate-limiting controls and inadequate distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) mitigation solutions make cloud environments susceptible to such attacks. To counteract this, businesses should deploy cloud-based DDoS protection solutions and use content delivery networks (CDNs) to absorb malicious traffic. Traffic analysis tools should also be implemented to detect and mitigate threats proactively.
Insider Threats
Not all cybersecurity threats originate from external attackers. Employees, contractors, or even cloud service providers may intentionally or unintentionally compromise cloud security. Excessive access privileges, lack of monitoring for unusual user activity, and weak background checks contribute to the risks posed by insider threats.
To mitigate these risks, organizations should enforce the principle of least privilege (PoLP) for access control. User behavior analytics (UBA) can be employed to detect suspicious activities. Conducting regular security awareness training for employees helps reduce the likelihood of insider threats.
Lack of Cloud Security Compliance
Organizations using cloud computing must comply with regulatory requirements such as GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001. Non-compliance can lead to legal consequences, financial penalties, and reputational damage. However, inconsistent security policies, inadequate understanding of compliance requirements, and poor documentation pose challenges to achieving compliance.
Businesses should establish clear security policies aligned with regulatory standards. They must also conduct regular compliance audits and risk assessments. Choosing cloud service providers that adhere to recognized security frameworks can help organizations maintain compliance effectively.
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)

APTs are prolonged cyberattacks in which attackers infiltrate cloud environments and remain undetected for extended periods. They are highly sophisticated, making them difficult to detect and mitigate.
Weak identity and access management (IAM) controls, lack of threat intelligence, and delayed incident response contribute to the success of APTs. Organizations should implement advanced threat detection systems, conduct continuous monitoring using Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solutions, and strengthen IAM with adaptive authentication mechanisms.
Misunderstanding the Shared Responsibility Model
Cloud security is a shared responsibility between the cloud provider and the customer. Many organizations mistakenly assume that security is solely the provider’s responsibility, leading to gaps in protection. Over-reliance on cloud service providers and poorly defined security roles contribute to this issue.
Businesses must clearly define and understand the shared responsibility model to address this. Security measures should be implemented at both customer and provider levels. Organizations should review security responsibilities and compliance policies regularly to ensure adequate cloud security.
Conclusion
Cloud computing offers immense benefits, but it also introduces significant cybersecurity challenges. Understanding these threats, assessing associated risks, and implementing robust security measures can help businesses ensure a safer cloud environment.
A proactive approach to cloud security is essential. Regular security assessments, continuous monitoring, employee awareness training, and leveraging advanced security technologies are key to mitigating cyber threats. As cyber risks continue to evolve, staying vigilant and adopting a multi-layered security strategy is crucial for protecting valuable data in the cloud.
By taking the proper precautions and adhering to best security practices, businesses can fully leverage cloud computing without compromising cybersecurity.
References:
Share this :