Defend Against Hellcat Ransomware - RaaS Model Threat Analysis

Hoplon InfoSec
29 Jan, 2025
In the ever-evolving world of cybersecurity, a new threat group has emerged, causing concern across critical sectors such as government, education, and energy. Dubbed Hellcat, this ransomware group is leveraging advanced tactics and a Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) model to orchestrate devastating attacks on high-value entities. This blog delves into the rise of Hellcat Ransomware, its methods, and steps organizations can take to protect themselves.
The Emergence of Hellcat Ransomware
First identified in mid-2024, Hellcat Ransomware operates on a decentralized RaaS model. This structure enables the group to provide ransomware tools and infrastructure to affiliates in exchange for a share of the ransom profits. By decentralizing its operations, Hellcat has scaled its attacks quickly, becoming a significant player in the ransomware landscape.
The RaaS model allows even relatively inexperienced cybercriminals to launch sophisticated ransomware attacks. Affiliates are equipped with ready-to-use tools, which include advanced payloads and detailed instructions for executing the attacks. In return, Hellcat receives ransom payments, creating a profitable partnership between the group and its affiliates.
Advanced Double-Extortion Tactics
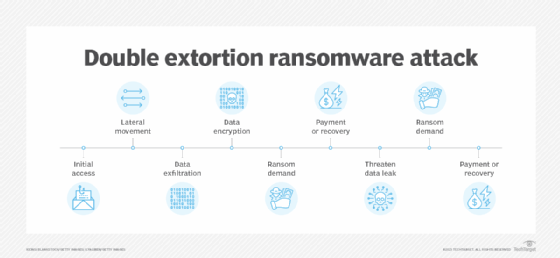
Photo Credit: https://www.techtarget.com/
Hellcat is known for employing double-extortion tactics, amplifying the pressure on victims. This involves:
Data Exfiltration: Affiliates steal sensitive data before encrypting the victim’s systems, creating a backup.
Encryption: The stolen data is encrypted using the Windows Cryptographic API, which ensures file contents are locked without altering file extensions or metadata.
The stolen data is then used as leverage. If victims refuse to pay the ransom, their sensitive information could be leaked. By employing this tactic, Hellcat maximizes its chances of receiving a ransom while ensuring minimal system disruption for the victim, which could hinder negotiation.
Exploiting Vulnerabilities for Initial Access
A hallmark of Hellcat’s operations is its exploitation of vulnerabilities in widely used enterprise tools. The group actively scans for weaknesses in software to gain initial access to target systems. One of the most notable incidents occurred in November 2024, when Hellcat infiltrated Schneider Electric’s Atlassian Jira system by exploiting a zero-day vulnerability.
This breach was particularly damaging, leading to the theft of over 40GB of sensitive data, including project files and user information spanning over 400,000 rows. The group demanded a ransom of $125,000 in Monero cryptocurrency but mockingly referred to the payment as “baguettes” about Schneider Electric’s French origins.
Shared Infrastructure with Other RaaS Groups
Researchers have found striking similarities between Hellcat’s payloads and those used by another RaaS group, Morpheus. The overlap in codebases and infrastructure suggests that these groups may share resources or have affiliates operating across both platforms.
Key similarities include:
Excluding critical system files from encryption to ensure operational continuity.
Using nearly identical ransom note templates that guide victims to .onion portals for payment negotiations.
The resemblance between the two groups highlights the interconnected nature of the RaaS ecosystem, making it harder for cybersecurity professionals to attribute attacks accurately.
Notable Incidents
Hellcat’s activities have made headlines worldwide, targeting organizations across diverse sectors. Here are some of the most significant incidents:
1. Schneider Electric
The ransomware group infiltrated Schneider Electric’s systems, exposing operational data and employee details. Despite Hellcat’s public humiliation tactics, Schneider Electric refused to pay the ransom, prioritizing recovery efforts over negotiation.
2. Tanzania’s College of Business Education
In another attack, Hellcat Ransomware leaked over 500,000 records containing personal and billing information of students and staff. The incident highlighted the vulnerabilities in educational institutions, which often lack robust cybersecurity measures.
3. U.S. University
Hellcat Ransomware took a more audacious approach by offering root access to a U.S. university’s server for just $1,500 on dark web forums. This exposed the institution’s student records and financial systems to potential buyers.
4. Iraq City Government
Hellcat Ransomware targeted a city government in Iraq, advertising root access to municipal servers for $300. This low ransom demand reflects the group’s willingness to disrupt public services for profit.
Mitigating the Threat of Hellcat
The rise of Hellcat Ransomware underscores the importance of proactive cybersecurity measures. Organizations must adopt a multi-layered approach to defend against such sophisticated threats. Here are some actionable steps:
1. Implement Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
Zero Trust frameworks enhance security by limiting access to only authenticated and authorized users. This approach minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and lateral movement within a network.
2. Regularly Patch Vulnerabilities
Keeping enterprise tools like Atlassian Jira up to date is crucial. Vulnerabilities often serve as the entry point for ransomware attacks. Regular patch management ensures these loopholes are closed before attackers can exploit them.
3. Deploy Advanced Threat Detection Systems
Investing in advanced threat detection systems can help identify ransomware behaviors in real-time. These systems analyze unusual activity patterns, such as large-scale data exfiltration or unauthorized encryption, enabling a quicker response to threats.
4. Train Employees on Cyber Hygiene
Human error remains one of the weakest links in cybersecurity. Regular training programs on recognizing phishing attempts, using strong passwords, and reporting suspicious activity can significantly reduce the risk of ransomware attacks.
The Growing Challenge for Cybersecurity Professionals
Hellcat Ransomware’s reliance on the RaaS model has made high-profile attacks more accessible to affiliates, posing a significant challenge for cybersecurity professionals. The decentralized nature of RaaS operations means that even small-scale cybercriminals can execute large-scale attacks, overwhelming existing defense mechanisms.
Additionally, the group’s ability to exploit vulnerabilities, leverage double-extortion tactics, and share resources with other RaaS groups has made it a formidable adversary. As ransomware groups continue to innovate, organizations must stay one step ahead by investing in robust cybersecurity solutions and fostering a culture of security awareness.
Conclusion
Hellcat Ransomware represents a growing threat in the cybersecurity landscape, targeting critical sectors with sophisticated tactics. By leveraging the RaaS model, the group has democratized access to advanced ransomware tools, enabling a wider pool of cybercriminals to launch attacks.
Organizations must adopt a proactive approach to cybersecurity to mitigate the risks posed by groups like Hellcat Ransomware. This includes implementing advanced detection systems, regularly patching vulnerabilities, and educating employees on best practices. As the battle against ransomware continues, staying vigilant and prepared will be the key to protecting sensitive data and systems.
Share this :