The Importance of Cyber Security in Industrial Control System

Hoplon InfoSec
30 Jul, 2025
In the era of Industry 4.0, industrial systems are becoming more connected than ever before. While this improves efficiency, it also opens up serious cybersecurity risks. ICS cyber security refers to the practice of securing industrial control systems; including SCADA, DCS, and PLCs from cyber threats that can disrupt operations, damage infrastructure, or even endanger lives. As industrial networks become more integrated with IT systems, the need for robust ICS cybersecurity is more crucial than ever.
What Are Industrial Control Systems (ICS)?
Industrial Control Systems (ICS) are systems used in industrial environments to control and monitor machines, processes, and equipment. These systems are common in places like factories, power plants, water treatment facilities, oil and gas pipelines, and transportation networks. ICS can automatically manage complex tasks such as turning machines on and off, regulating temperatures, or controlling chemical mixtures.
ICS includes different technologies like Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA), Distributed Control Systems (DCS), and Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC). These systems help industrial operators manage and automate tasks that would be difficult or dangerous for people to do manually. For example, a water treatment plant might use ICS to monitor water levels, control pumps, and ensure safe chemical levels.
ICS plays a big role in keeping critical infrastructure working properly. They are designed for long-term operation, often running for years without updates. Because of this, many older ICS devices are still in use today and were not built with cybersecurity in mind. This creates a serious security risk.
Why ICS Cyber security Is Important
ICS cybersecurity is important because these systems control critical services that people use every day. If an attacker gains access to an ICS, they can cause serious damage. For example, they could shut down electricity in a city, contaminate drinking water, or stop transportation systems. These types of attacks can lead to financial loss, public safety risks, and even loss of life.
Unlike regular computers, ICS devices often control physical systems. If something goes wrong in an ICS environment, it’s not just about losing data. Real-world consequences can happen, like machines breaking, fires starting, or harmful chemicals leaking. This makes cybersecurity in ICS even more important.
As more industrial systems connect to the internet, they become easier targets for cyberattacks. Hackers, including cybercriminals and even government-supported attackers, are now focusing on ICS networks. Securing ICS means protecting not only computers but also human lives and national safety. Strong ICS cybersecurity is essential for a stable and safe society.
Common ICS Components at Risk
There are several components in ICS environments that are vulnerable to cyber threats. Each one plays a key role in controlling industrial processes, and if compromised, the entire system may fail.
One important component is the PLC (Programmable Logic Controller). These devices control specific tasks such as starting motors, turning valves, or regulating temperatures. Hackers can change how a PLC works, causing machines to malfunction.
Another key component is the SCADA system. It collects data from machines and allows operators to control them remotely. If a SCADA system is hacked, attackers might see everything the system does and even take control of it.
Human-Machine Interfaces (HMI) are also at risk. These are screens or devices that allow workers to control and monitor the system. If an attacker changes what the HMI shows, workers may make wrong decisions.
Communication networks in ICS environments are often weak and unencrypted. Attackers can spy on data or send fake messages to machines. In many ICS setups, devices use old software and have no password protection. All these weak points need to be secured to keep ICS safe from cyber threats.
Major ICS Cybersecurity Threats
ICS networks face many cyber threats, and some of them can cause massive damage. One common threat is ransomware. This is a type of malware that locks important systems and demands money to unlock them. If ransomware hits an ICS, it can stop machines or shut down operations.
Phishing attacks are also common. These attacks trick employees into clicking fake emails or links, which can install malware. Once inside the system, hackers can move through the network quietly. Another major threat is remote access attacks. Many ICS are now connected to the internet, making them easy targets if they have weak passwords or no firewalls.
Insider threats are also dangerous. Sometimes, employees or contractors misuse their access to harm the system. They may do this on purpose or by mistake. Supply chain attacks are when hackers attack third-party companies that provide software or devices to ICS environments. If the attacker puts malware into a software update, they can infect many systems at once.
ICS cybersecurity must deal with many different types of threats, and all of them can be harmful.
Notable ICS Cyber Attacks in History
Several big cyberattacks in the past have targeted ICS systems and caused real-world problems. One famous example is the Stuxnet worm in 2010. It was a powerful computer virus designed to attack Iran’s nuclear facilities. It targeted PLCs and caused machines to break down while showing normal readings to the operators. This showed the world how dangerous ICS cyberattacks can be.
Another example is the Ukraine power grid attack in 2015. Hackers used malware to shut down the power in parts of Ukraine, leaving hundreds of thousands of people without electricity. They gained access through phishing emails and then took control of the SCADA system.
In 2021, the Colonial Pipeline attack in the U.S. caused fuel shortages across several states. Although the attackers did not directly hit the ICS, they targeted the company’s business network. As a safety step, the company shut down the pipeline, which affected millions.
These examples show that ICS attacks are not just ideas they are real events with big impacts. They remind industries that they must take ICS cybersecurity seriously.
ICS vs. IT Cybersecurity: Key Differences
Cybersecurity in ICS is very different from cybersecurity in traditional IT (Information Technology) systems. Understanding these differences is important for creating good protection strategies.
In IT, the main goal is to protect data. In ICS, the goal is to protect physical processes like machines and safety systems. In an IT system, a cyberattack might steal private information. But in an ICS, it could cause machines to explode or systems to shut down.
ICS systems often use older technology and are not designed to be updated regularly. Many ICS devices cannot handle normal antivirus software or system scans because they could crash the machines.
Another key difference is downtime. In IT, systems can often be shut down for maintenance or updates. But in ICS, downtime can be dangerous or very expensive, especially in critical systems like power or water.
ICS networks also use special communication protocols that are different from regular IT systems. These protocols may not have security features like encryption. Because of these differences, ICS cybersecurity needs special tools, strategies, and skills.
Best Practices for ICS Cybersecurity
To protect Industrial Control Systems (ICS) from cyber threats, companies should follow best practices that strengthen their security. First, segment networks by separating the operational technology (OT) network from the IT network. This helps to contain threats and stop attackers from moving easily between systems.
Next, implement strong access control. Only authorized personnel should have access to ICS systems. Use strong passwords, two-factor authentication, and role-based access to limit exposure. It’s also a good idea to regularly check who has access and remove unused accounts.
Regular updates and patches are important. Even though many ICS systems are older and sensitive, applying security patches is necessary. If real-time patching is not possible, create a plan to patch during maintenance times.
Continuous monitoring is another key step. Use intrusion detection systems to spot unusual activity. Logs and alerts can help identify issues before they become serious.
Security training is also vital. All staff including engineers and IT staff should know how to recognize phishing attacks, follow security procedures, and respond to incidents.
Finally, always have a disaster recovery and incident response plan. This plan should include how to quickly stop attacks, restore systems, and report the incident.
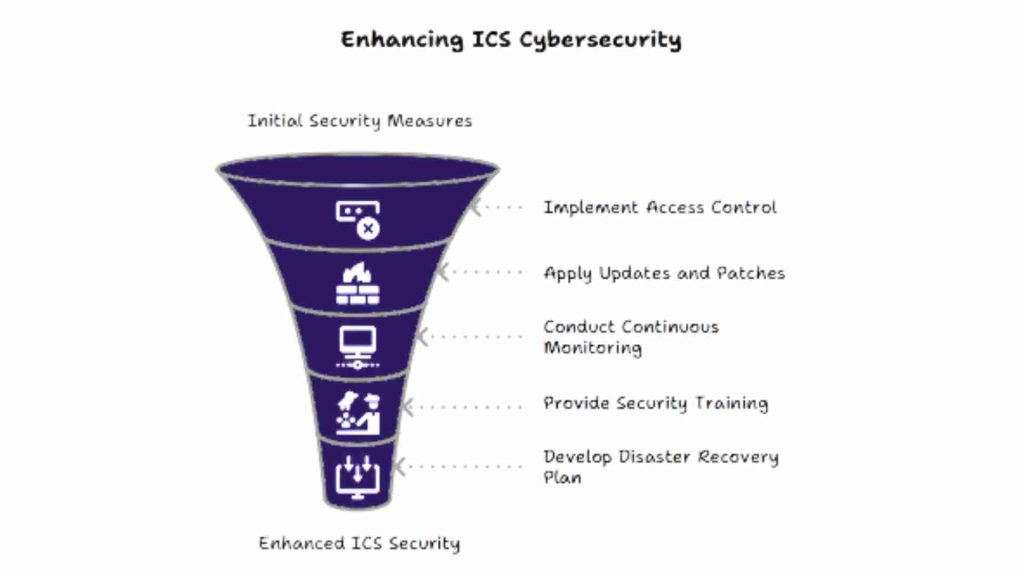
By following these best practices, companies can reduce their risks and make ICS networks more secure.
ICS Cybersecurity Frameworks & Standards
To help organizations protect their ICS, many global standards and frameworks are available. These provide guidance on how to manage cyber risks and secure systems.
One widely used framework is the NIST Cybersecurity Framework. It includes five main steps: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. It is not specific to ICS but can be adapted to fit industrial systems.
Another important standard is IEC 62443, developed by the International Electrotechnical Commission. It focuses on ICS and provides detailed guidance for securing automation and control systems. It covers topics like system design, secure communication, and user roles.
The ISA/IEC 99 standard is another well-known guideline for industrial cybersecurity. It helps organizations build strong security programs for ICS networks. In the United States, the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) provides tools and resources for ICS security, such as the CISA (Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency) guidelines.
Following these frameworks can help organizations create a safer environment, ensure compliance with regulations, and be ready for any future audits or assessments.
Future Trends in ICS Cybersecurity
As technology grows, the future of ICS cybersecurity will continue to change. One major trend is the increase in connected devices. More machines are using the Internet of Things (IoT), which means more entry points for cyber attackers. This requires better monitoring and security at all levels.
Another trend is the use of cloud technology in industrial systems. While cloud tools bring efficiency, they also bring new risks. Cloud security for ICS will need special tools and protections.
Regulations and laws will likely become stricter. Governments around the world are realizing the risk to critical infrastructure and are introducing stronger cybersecurity rules. Automation of security tasks is also growing. As networks get more complex, companies will use automated tools to detect and respond to threats faster.
Lastly, the future will see more collaboration between IT and OT teams. In the past, these teams worked separately. Now, they need to work together to protect the entire organization. These trends will shape how companies defend their ICS and prepare for new cyber challenges.
Role of AI and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are becoming useful tools in ICS cybersecurity. They can help detect threats faster and respond more effectively. AI can analyze large amounts of data from machines, sensors, and networks. It can find patterns and detect unusual activity that may signal a cyberattack. This is helpful in ICS environments, where early warning is critical.
Machine learning systems can learn from past incidents. Over time, they get better at spotting risks and predicting threats. For example, if a system always works in a certain way and suddenly behaves differently, AI can raise an alert.
AI can also automate routine tasks like monitoring, log analysis, and even some responses. This saves time and allows human operators to focus on more important issues. However, AI is not perfect. Attackers can try to trick AI systems by feeding them false data. So, it’s important to use AI as a support tool, not the only defense. With proper use, AI and ML can greatly improve ICS cybersecurity and help stay ahead of modern threats.
Challenges in Implementing ICS Security
Securing ICS is not easy. One big challenge is that many systems are very old. These systems were not built with security in mind and may not support modern protections.
- Another issue is downtime. Many ICS networks must run 24/7, and it is hard to stop them for updates or security checks. This makes patching and maintenance very difficult.
- There is also a lack of skilled workers. Cybersecurity experts who understand both IT and ICS are rare. This skill gap makes it hard for companies to build strong defenses.
- Budget limits are another challenge. Some organizations do not invest enough in ICS security because they do not see the immediate risk. However, an attack can cost much more than prevention.
- Finally, ICS often involves many vendors and systems, making it complex to manage. Each system may have different rules, passwords, and vulnerabilities.
Despite these problems, it is important to take steps now. Even small improvements in ICS security can protect against big losses in the future.
Case Study: The Stuxnet Attack on Iran’s Nuclear Facility
One of the most well-known ICS cyberattacks in history is the Stuxnet attack, which took place around 2010. It targeted Iran’s Natanz nuclear facility. Stuxnet was a computer worm believed to have been developed by state-sponsored actors.
The worm was designed to specifically target Siemens PLCs used to control centrifuges in the facility. Stuxnet caused the centrifuges to spin at speeds that eventually damaged them, while at the same time giving operators false information that everything was normal. What made Stuxnet unique was that it did not rely on internet access. It was spread through infected USB drives. This showed that even isolated or “air-gapped” systems can be attacked.
The attack delayed Iran’s nuclear program and shocked the cybersecurity world. It was the first major example of a cyberattack causing real-world physical damage. This case study teaches the world that ICS systems are vulnerable and must be secured no matter how safe they may seem.
Final Thoughts
As industrial systems become more connected and complex, cybersecurity is no longer optional, it is essential. ICS cybersecurity helps protect not only machines and operations but also national infrastructure, public safety, and human lives. The threats are growing, but so are the tools and strategies to defend against them.
Every organization that depends on ICS must take action. Begin by assessing risks, training teams, and updating outdated systems. Prevention is always better than recovery.
If you’re looking for a reliable partner to enhance your ICS protection, Hoplon Infosec offers a wide range of cybersecurity services tailored to meet the unique needs of industrial environments. Among these, the most effective and relevant for ICS cybersecurity is:
- Endpoint Security: This service protects your industrial control devices like PLCs, SCADA systems, and HMIs from unauthorized access, malware, and other threats. Since ICS devices often lack modern security features, securing endpoints is a critical step in defending your infrastructure.
Other valuable services include:
- Web Application Security and Penetration Testing to protect SCADA interfaces and backend systems.
- Artificial Intelligence solutions to detect threats early.
- Mobile Security Services for remote ICS control platforms.
- Deep and Dark Web Monitoring to watch for threats before they strike.
Take Action Today
Cyber threats don’t wait and neither should your defense strategy. With Hoplon Infosec by your side, you gain more than protection; you gain peace of mind. Whether you operate in energy, manufacturing, water, or transportation, your ICS deserves world-class security.
Contact Hoplon Infosec now to schedule a consultation or security audit tailored to your systems. Let’s secure your industrial future before someone else tries to control it.
Share this :