Win-DDoS Vulnerabilities: Understanding and Defending Against the Rising Threat

Hoplon InfoSec
11 Aug, 2025
In our interconnected world, cyber threats are growing more advanced every day. Among these threats, Win-DDoS vulnerabilities have become a serious issue for Windows-based networks globally. These vulnerabilities allow cybercriminals to take control of devices and launch large-scale distributed denial-of-service attacks. Such attacks can disrupt critical systems and prevent users from accessing important online services. Whether you manage a business or use Windows at home, knowing what Win-DDoS vulnerabilities are and how to protect yourself against them is vital.
This article will guide you through the essentials of Win-DDoS vulnerabilities, explaining how the malware operates, what makes these vulnerabilities dangerous, and practical steps you can take to defend your systems.
What is Win-DDoS Malware? An Overview of the Threat
Win-DDoS vulnerabilities are weaknesses in Windows systems that are exploited by a specific malware family called Win-DDoS. This malware infects machines and turns them into part of a botnet, a large group of compromised devices remotely controlled by attackers. The attackers then use these botnets to flood targeted servers with overwhelming traffic, causing service outages.
Unlike other generic DDoS malware, Win-DDoS targets particular flaws in Windows, especially those related to remote procedure call (RPC) and lightweight directory access protocol (LDAP) services. These specific Win-DDoS vulnerabilities make it harder to detect and stop the malware once it gains access.
Understanding the Core Vulnerabilities Exploited by Win-DDoS
The primary weaknesses that make Windows vulnerable to Win-DDoS attacks lie in key protocols and services:
- RPC (Remote Procedure Call) enables programs to communicate over networks.
- LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) manages directory services like user information.
Attackers exploit these Win-DDoS vulnerabilities by sending malicious requests that let them run harmful code remotely or flood the network with bogus traffic. Many of these vulnerabilities exist because systems are outdated, improperly configured, or have exposed services accessible from the internet.
How Win-DDoS Leverages Windows RPC and LDAP Protocols
Win-DDoS malware uses RPC and LDAP to increase its spread and attack power. It works like this:
- The malware sends specially crafted RPC requests to vulnerable Windows machines. This lets it execute malicious commands without any user action.
- It abuses LDAP servers to collect network device information, allowing it to infect more systems or amplify the attack traffic.
These two protocols together help exploit Win-DDoS vulnerabilities, enabling rapid infection growth and powerful attacks that overwhelm targets.
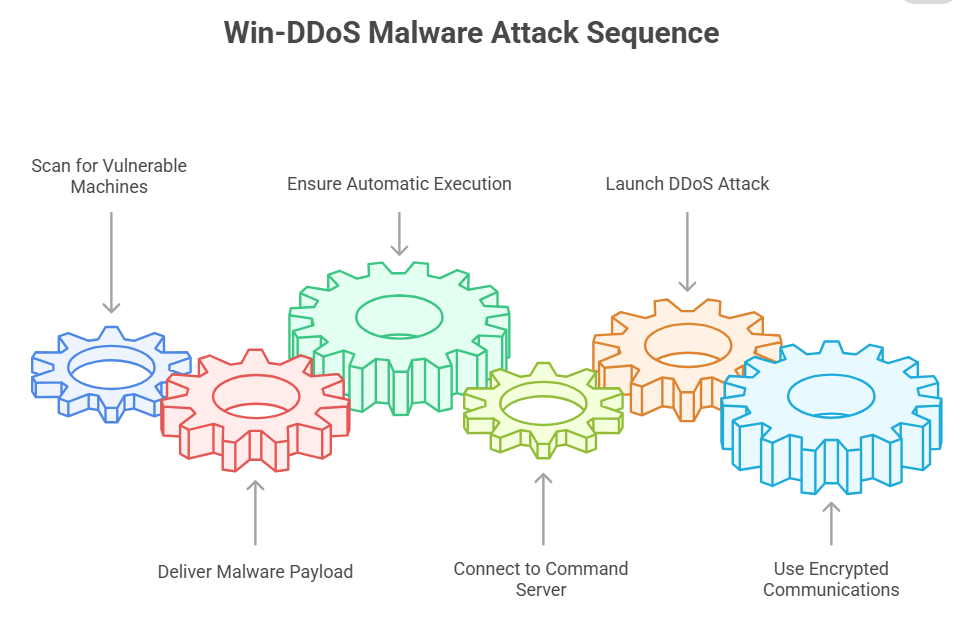
Anatomy of a Win-DDoS Botnet Attack: Step-by-Step Breakdown
To understand the threat fully, here is how a typical Win-DDoS botnet attack happens:
- The attacker scans the internet for Windows machines exposing RPC or LDAP services vulnerable to exploitation.
- Using those weaknesses, the attacker delivers the Win-DDoS malware payload, taking advantage of Win-DDoS vulnerabilities.
- Once infected, the malware ensures it runs automatically and hides by mimicking legitimate Windows processes.
- The infected machine connects to a command-and-control server, ready to receive instructions.
- When activated, all infected machines in the botnet send overwhelming traffic to the target, causing denial of service.
- The malware uses tricks like encrypted communications to avoid detection and continues spreading.
Recent Win-DDoS Attacks and Their Impact on Global Networks
The frequency of Win-DDoS attacks exploiting Win-DDoS vulnerabilities has increased in recent years. For instance:
- In early 2025, a financial institution suffered hours of downtime after a massive Win-DDoS attack exploited RPC vulnerabilities. The losses ran into millions.
- Several cloud service providers reported service interruptions caused by LDAP query amplification using Win-DDoS malware.
These examples show how dangerous Win-DDoS vulnerabilities can be for large organizations and the internet infrastructure they rely on.
The Economic and Operational Consequences of Win-DDoS Attacks
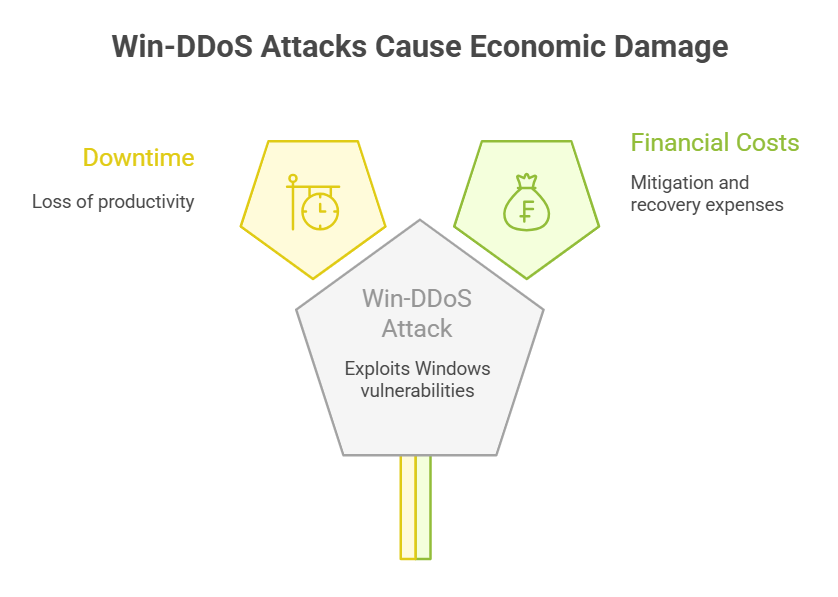
Win-DDoS attacks that exploit Win-DDoS vulnerabilities cause more than just technical headaches; they lead to serious economic and operational damage for affected organizations. When a company’s Windows network is compromised through these vulnerabilities, the immediate result is often significant downtime. This downtime means lost productivity and, for customer-facing businesses, lost revenue as services become unavailable. For example, a retailer hit by a Win-DDoS attack may face hours or even days where customers cannot make purchases, directly impacting sales.
Beyond lost revenue, organizations face costs associated with detecting and mitigating attacks that leverage Win-DDoS vulnerabilities. Emergency response teams must be mobilized, forensic investigations conducted, and system restorations performed. These activities often require hiring external cybersecurity experts or paying overtime to internal teams, driving up expenses.
There is also reputational damage when customers or partners lose trust due to repeated or prolonged service interruptions caused by exploitation of Win-DDoS vulnerabilities. In some industries, regulatory fines and legal consequences may follow if businesses fail to protect sensitive data during these attacks.
In short, the fallout from Win-DDoS attacks exploiting Win-DDoS vulnerabilities can ripple across every aspect of an organization. Understanding these consequences underscores the importance of investing in strong defenses and incident response capabilities.
Identifying Signs of a Win-DDoS Infection on Your Windows Devices
Spotting a Win-DDoS infection early is key to stopping damage. Watch for these signs:
- Unexpected spikes in network traffic coming from Windows devices.
- Devices slowing down or crashing for no clear reason.
- Outbound connections to unknown or suspicious IP addresses.
- Processes using high CPU or memory without explanation.
- Security software failing to update or being disabled unexpectedly.
If you notice these, it could mean your system is suffering from Win-DDoS vulnerability exploitation.
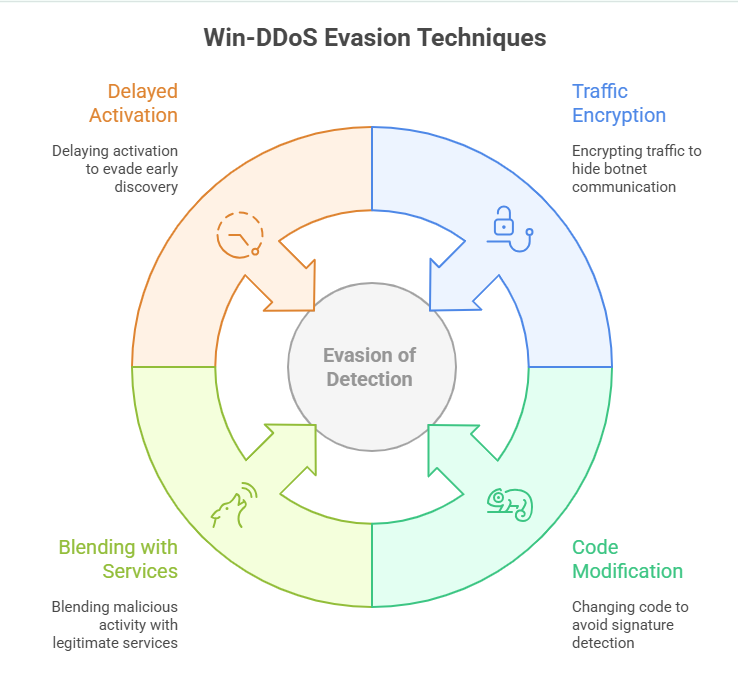
Techniques Used by Win-DDoS to Evade Detection and Analysis
Win-DDoS malware uses several methods to hide from security tools:
- It encrypts traffic to hide botnet communication.
- It changes its code to avoid signature detection.
- It blends malicious activity with legitimate Windows services.
- It delays activation to evade early discovery.
These tactics make defending against Win-DDoS vulnerabilities more challenging for security teams.
How Win-DDoS Propagates: Infection Vectors and Spread Mechanisms
Win-DDoS primarily spreads by exploiting RPC and LDAP, but other methods include:
- Brute force attacks on weak Windows passwords.
- Being dropped by other malware such as trojans or worms.
- Phishing campaigns that trick users into running malicious files.
Its self-propagation abilities make Win-DDoS vulnerabilities a serious risk in unpatched or poorly secured environments.
Mitigation Strategies: Patching Windows RPC and LDAP Vulnerabilities
The best way to defend against Win-DDoS vulnerabilities is through timely patching and system security:
- Apply all Microsoft security updates, especially for RPC and LDAP.
- Disable RPC and LDAP on internet-facing systems if not necessary.
- Use firewalls and network segmentation to limit access.
- Enforce strong passwords and multi-factor authentication.
- Deploy intrusion detection and prevention tools to catch abnormal traffic.
Best Practices for Securing Windows Environments Against DDoS
Beyond patching, follow these steps to protect your environment:
- Perform regular vulnerability assessments and penetration tests.
- Continuously monitor logs for suspicious activity.
- Train users on phishing risks and safe computing.
- Use endpoint detection and response solutions.
- Maintain backups and a recovery plan in case of infection.
Detecting Win-DDoS Traffic: Network Monitoring and Analysis Tools
Detecting attacks leveraging Win-DDoS vulnerabilities requires strong monitoring:
- Use flow analysis tools to identify traffic spikes.
- Deploy SIEM platforms for centralized alerting.
- Apply behavioral analytics to spot anomalies.
- Use packet inspection to detect malicious RPC or LDAP requests.
Early detection reduces the impact and helps stop further damage.
Case Study: A Deep Dive Into a Recent Win-DDoS Incident
In March 2025, a global e-commerce company experienced a prolonged outage after a Win-DDoS attack targeted its RPC services. Thousands of Windows servers worldwide became part of a botnet, flooding the company’s servers.
The attack caused revenue loss and harmed customer trust. The incident team traced the problem to unpatched Windows machines and quickly applied emergency fixes and network controls. This case highlights the importance of regular updates and constant vigilance against Win-DDoS vulnerabilities.
The Role of Botnets in Win-DDoS Campaigns: How Attackers Control Networks
Botnets are the foundation of Win-DDoS attacks. Attackers use command-and-control servers to manage thousands of infected machines. These networks can be rented or used for criminal purposes such as extortion or data theft.
Each infected device adds to the attack power, making even small botnets able to exploit Win-DDoS vulnerabilities and cause significant disruption.
Win-DDoS and Its Connection to Other Malware Families
Win-DDoS malware often appears alongside other malware like trojans, worms, or ransomware. Some variants also steal credentials or install backdoors.
Knowing these connections helps build a complete defense strategy against Win-DDoS vulnerabilities and related threats.
Future Trends: How Win-DDoS Vulnerabilities Might Evolve
As cybersecurity defenses improve, attackers continually adapt their tactics, and the landscape of Win-DDoS vulnerabilities is no exception. One emerging trend is the increasing use of artificial intelligence and machine learning by attackers to identify new vulnerabilities in Windows systems more quickly and launch smarter, more adaptive Win-DDoS campaigns.
Additionally, future Win-DDoS malware may target a broader range of Windows services beyond RPC and LDAP, taking advantage of other undersecured protocols. Attackers could also develop more advanced evasion techniques that blend malicious traffic seamlessly into legitimate network activity, making detection harder.
Another anticipated evolution is the rise of multi-vector attacks combining Win-DDoS with ransomware or data exfiltration malware. Such combined threats increase the stakes for defenders, as they must address multiple risks simultaneously.
Finally, with more devices connected to the internet through the Internet of Things (IoT), new attack surfaces may emerge where Win-DDoS vulnerabilities in embedded Windows systems or related devices could be exploited.
Staying ahead of these future trends in Win-DDoS vulnerabilities requires continuous investment in research, threat intelligence, and adaptive security measures.
Preparing Your Incident Response Plan for Win-DDoS Attacks
Preparation is critical for handling attacks using Win-DDoS vulnerabilities. Your response plan should include:
- Steps to detect and isolate infected machines.
- Communication protocols for internal teams and customers.
- Backup and recovery procedures.
- Coordination with ISPs and law enforcement.
- Post-attack analysis to improve security.
Regular testing of your plan ensures effective response when attacks occur.
Final Thoughts
Win-DDoS vulnerabilities remain a dangerous threat to Windows networks by exploiting RPC and LDAP weaknesses. Protecting against them demands awareness, regular patching, continuous monitoring, and a strong response plan. Understanding Win-DDoS malware behavior helps you secure your systems.
Hoplon Infosec’s advanced threat detection and vulnerability assessment services can identify and address Win-DDoS vulnerabilities before they cause damage. Their expert incident response team also provides rapid containment and recovery during attacks. Combining these services with your security efforts greatly reduces the risk from Win-DDoS vulnerabilities and strengthens your overall defense.
Share this :