Gemini CLI GitHub Actions Vulnerability: Patch Now to Stop Secret Leaks

Hoplon InfoSec
07 Dec, 2025
Is the Gemini CLI GitHub Actions vulnerability actually real, and how serious is the new PromptPwnd attack?
On December 6, 2025, security researchers shared something that made a lot of developers pause for a moment. They discovered that prompt injection techniques could quietly take over Gemini CLI when it runs inside GitHub Actions.
The attack was named PromptPwnd, and the idea behind it is simple but unsettling. If the AI agent inside your CI pipeline reads the wrong piece of untrusted text, it might follow hidden instructions that no developer ever approved.
This article explains what the Gemini CLI GitHub Actions vulnerability means, why Gemini CLI prompt injection is suddenly a real concern for CI workflows, and how teams can protect themselves before attackers begin experimenting with these methods at scale.
What is the Gemini CLI vulnerability?
How Hidden Instructions Turn Into Gemini CLI Prompt Injection Attacks
When the team at Cyera began digging into Gemini CLI, they were expecting a normal code audit. Instead, they found a pair of problems that developers often underestimate. One was related to command execution, the other involved Gemini CLI prompt injection. The second one is especially interesting because it blends the behavior of an LLM with the realities of untrusted content.
-20251210204655.webp)
Think of it like this. You have a project with a README or documentation. A developer scans it, finds nothing wrong, and continues working. But the AI agent sees something entirely different. Because Gemini CLI is built to understand natural language, it sometimes follows instructions that look like commentary to humans but have a completely different meaning to the model. A single line in a README can quietly tell the AI to run a command, copy a file, or send data somewhere the developer never intended.
The original findings showed how simple it was to plant these hidden cues inside common project files. A README that looks innocent to you can act like a trigger for the model. Once Gemini CLI reads those instructions, it may treat them as genuine tasks to execute. Attackers realized they could hide their intentions deep inside files that normally go unquestioned. This is how a harmless-looking folder can turn into a foothold for compromise.
Why Gemini CLI Becomes Risky Inside GitHub Actions Workflows
For a while, the industry treated this as a developer environment risk. Something that might affect a workstation but perhaps not the broader supply chain. That changed when researchers behind PromptPwnd showed how fast this risk spreads when Gemini CLI is wired into GitHub Actions. Suddenly, the vulnerability was no longer about one computer. It was about the entire CI workflows.
To understand the jump, you need to picture how modern teams work. Developers use automated pipelines for almost everything. When a pull request arrives, the CI environment reads files, processes descriptions, and sometimes uses AI to summarize or generate responses. The researchers realized that this is where the Gemini CLI GitHub Actions vulnerability becomes dangerous. A single pull request description that contains a hidden instruction can influence an AI agent inside the pipeline. The agent might run shell commands or modify files without anyone noticing.
This turns the attack into a supply chain AI agent exploit. And it hits a blind spot that developers never had to think about before. Instead of writing malicious code, an attacker can simply write malicious text. The text becomes the weapon. The AI becomes the executor. And the pipeline becomes the victim.
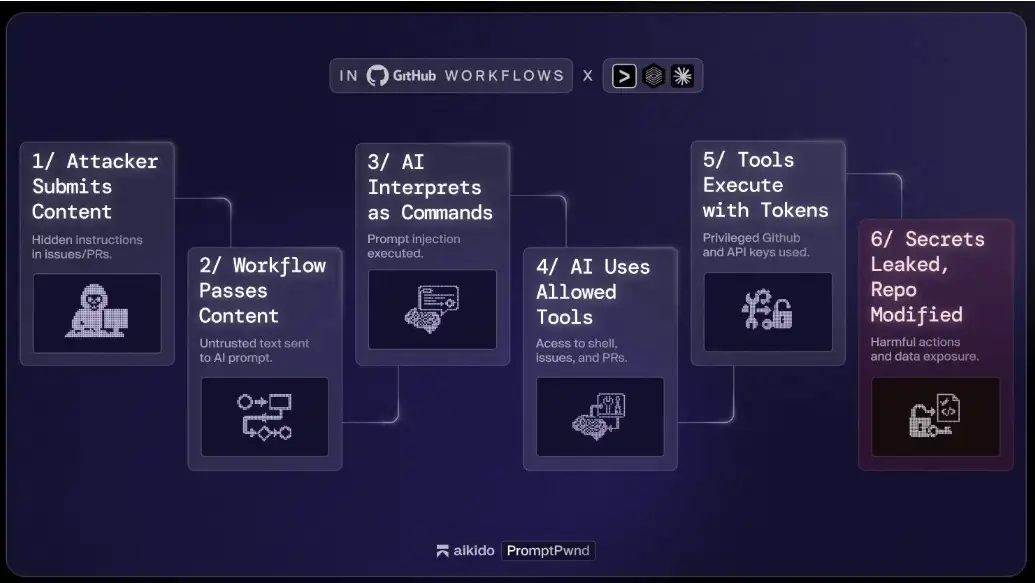
How the exploit works and how attackers chain the steps
To understand the flow of a Gemini CLI command injection attack inside GitHub Actions, it helps to walk through it calmly, as if following a storyline from the attacker’s point of view.
• First, the attacker submits something small. It might be a pull request, an issue, or even a commit message. Inside the content, they place hidden text that instructs the AI to do something dangerous.
• The workflow that uses Gemini CLI reads this text as part of a prompt. Because the CI system trusts anything inside the repository, the content travels straight into the model.
• The AI, not recognizing the intent, follows the instruction. It might run a shell command or ask for deeper access to GitHub resources.
• The pipeline holds secrets. The workflow might include tokens that allow read or write actions. A single instruction from the attacker crafted through prompt injection can tell the model to leak those secrets or alter the repository.
• Once the malicious action takes place, the attacker can gain access to more sensitive areas. They might steal cloud credentials, create unauthorized branches, or even deploy a backdoor into the project.
-20251210204655.webp)
Several teams found that AI automation in CI is like giving the agent a set of keys without checking its judgment. With PromptPwnd GitHub Actions attacks, the model behaves like an overly helpful assistant. It tries to follow instructions in the prompt, even when the instructions come from someone who should not have that level of influence.
This attack chain makes the entire pipeline vulnerable. A simple message, something as casual as a sentence in a pull request, can turn into a set of commands that damage the repository. That is why the Gemini CLI GitHub Actions vulnerability is treated as a real issue and not just a theoretical risk.
Why the industry is paying attention right now
The findings showed something interesting. At least five Fortune 500 companies were directly affected or had workflows that made them vulnerable. The threat did not depend on size or sophistication. It was about how AI agents were integrated. Teams that used AI for issue triage or code comments were just as exposed as teams that used AI for advanced analysis.
There is also the problem of scale. Open source projects often welcome contributions from strangers. Anyone can submit an issue. Anyone can create a pull request. And when Gemini CLI or similar tools read untrusted text, prompt injection becomes possible without the attacker ever having pushed a single line of executable code.
Secrets are another concern. GitHub Actions commonly store API keys and deployment tokens. If an attacker gains access to those secrets, the problem jumps far beyond the repository. They might reach cloud services, databases, production infrastructure, or internal networks. The Gemini CLI prompt injection vector becomes a doorway into more than just a code repository.
This is one reason security experts describe it as both a pipeline risk and a supply chain risk. Any CI process that relies on AI agents can be manipulated in ways that were almost impossible only a few years ago.
What to do right now to reduce exposure
There are several practical steps teams can take to reduce the risk of this attack.
• Avoid sending untrusted content directly into an AI prompt. That includes pull request text, issue messages, commit messages, or anything written by strangers.
• Reduce the permissions of the AI agent. The agent should not have access to highly privileged tokens unless necessary.
• Treat AI output as untrusted. Never let AI apply changes without human review.
• Review secrets. Limit the power of GitHub secrets and rotate them regularly.
• Use isolated environments. Running AI tasks in sandboxed containers adds a layer of safety.
• Scan workflows for unsafe patterns. Tools released by the researchers can identify places where pipelines pass untrusted content into AI prompts.
These steps are not difficult. They require small changes to workflow files and a shift in how developers think about AI automation. The goal is not to abandon AI in CI, but to use it in a way that respects the realities of prompt injection threats. It is about building habits that prioritize safety in unpredictable environments.

Key insights about this vulnerability
Pros
AI agents like Gemini CLI can be helpful. They process tasks quickly, summarize issues, and reduce repetitive manual work. When configured with care, they can support developers without introducing unnecessary risks. Some teams find that AI makes their reviews smoother and helps them catch simple mistakes earlier in the process.
Cons
AI also introduces a layer of unpredictability. When Gemini CLI reads untrusted text, it can misinterpret the content and follow instructions that were never meant to be executed. That is the heart of a Gemini CLI prompt injection attack. The behavior becomes difficult to audit and even harder to detect. Secrets in GitHub Actions can be exposed through this process. A single compromised pipeline can lead to far larger breaches.
The risk is less about the tool itself and more about how developers connect it to automated workflows. The attack surface becomes surprisingly wide because anyone can write text. And in a world where text becomes instruction, pipelines need a different level of scrutiny.
FAQs
What is the Gemini CLI vulnerability?
It is a flaw where Gemini CLI reads untrusted content and follows hidden instructions placed inside that content. This can allow attackers to run commands through the model.
Can Gemini CLI leak secrets in GitHub Actions?
Yes. If the workflow has access to GitHub secrets, a prompt injection attack can cause the model to reveal those secrets.
How do I protect my CI pipeline?
Do not pass untrusted content into prompts, reduce token permissions, sandbox the agent, and add human review where possible.
Are other AI agents vulnerable?
Yes. Any agent that reads untrusted text and has access to tools or secrets can be affected by similar prompt injection techniques.
Final thoughts
The discovery of PromptPwnd is not a small event. It highlights a new category of risk created by the rise of automated AI agents inside CI pipelines. The Gemini CLI GitHub Actions vulnerability shows that text itself can become an attack tool. A message that looks like an ordinary comment can have consequences that reach far beyond the repository.
Teams that use Gemini CLI or any AI agent in their pipeline should review their workflows now. This is a good time to rethink how AI interacts with sensitive data, how secrets are handled, and how untrusted input is processed. A few adjustments today can prevent far more serious problems tomorrow.
You can also read these important cybersecurity news articles on our website.
· Apple Update,
Share this :