Urgent Update for Lanscope Endpoint Vulnerability

Hoplon InfoSec
26 Oct, 2025
Imagine coming to work on a Monday morning only to find out that your enterprise endpoint management system has been hacked without anyone knowing. Because of a serious and ongoing bug in Lanscope Endpoint Manager, many IT teams are now living in a waking nightmare. In this article, we break down the Lanscope endpoint vulnerability, look at how the Lanscope endpoint manager bug is being used, and tell you what you need to do right now.
landscape endpoint vulnerability, is important because it means that there is a direct threat to endpoint security, the risk of remote code execution, and possibly even your whole corporate network. This is not something you can take lightly, whether you manage thousands of desktops, mobile devices, or are part of a global business.
What’s the Lanscope bug?
The vulnerability, which is also known as the landscape endpoint vulnerability,
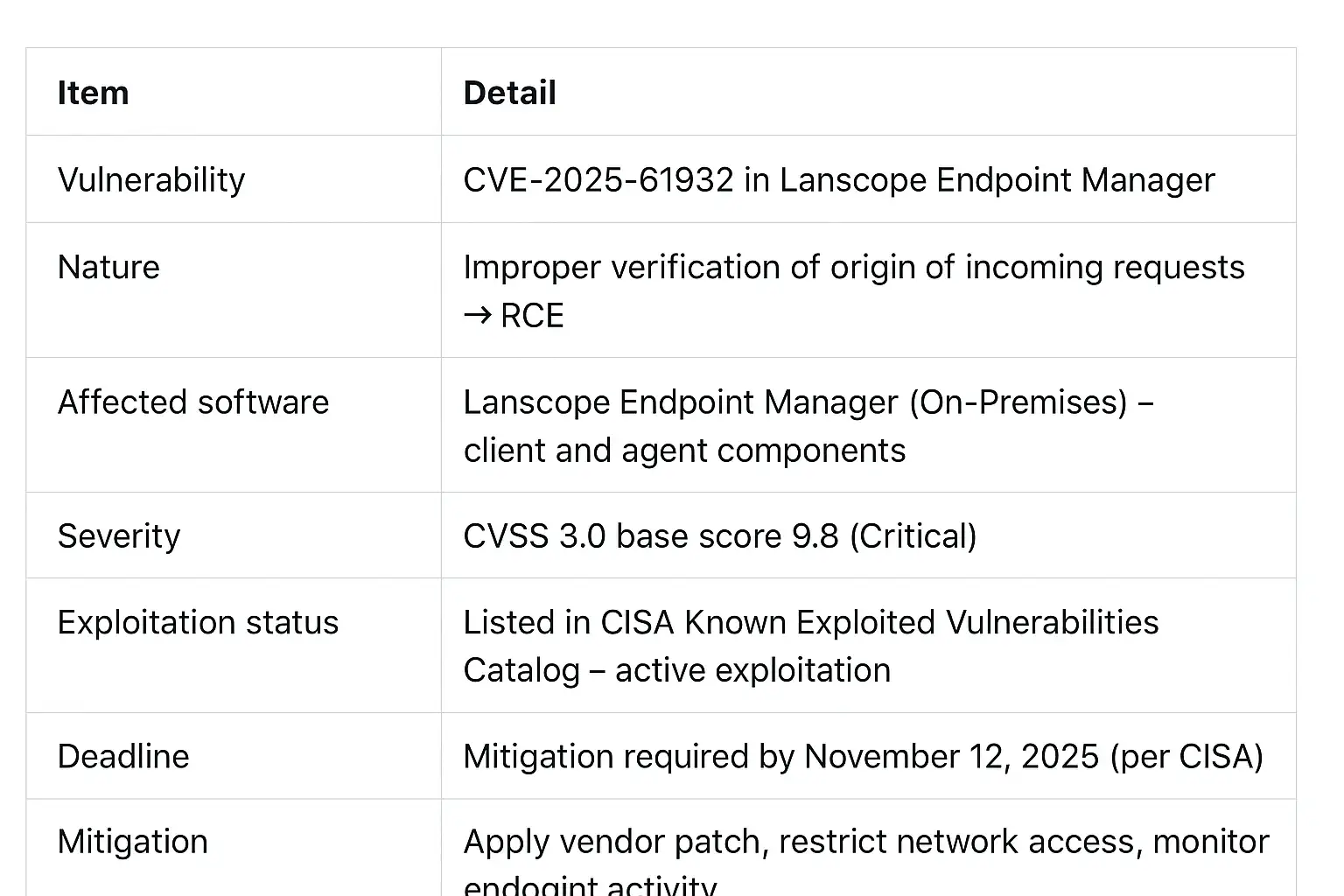
The Lanscope Endpoint Manager exploit takes advantage of a flaw in the on-premises version of Lanscope Endpoint Manager. This vulnerability, known as CVE-2025-61932, lets an attacker run any code they want by sending specially crafted packets.
The official record says that the product's client program (MR) and detection agent (DA) don't check incoming requests' origins correctly. When used, this gives direct access to run remote code without having to log in.
Extent and seriousness
The CVSS 3.0 base score for CVE-2025-61932 is 9.8, which means it is "Critical." This shows how serious it is. Also, this isn't just a theory. The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has put it on its list of known exploited vulnerabilities.
This means that attacks are really happening. Businesses that use this endpoint management software need to take this problem very seriously.
Why the bug is important
In a business, endpoint management software is like the brain of device control. It sends out patches, enforces security policies, and keeps an eye on devices. When that system is hacked, attackers can move sideways, get more access, plant backdoors, or take over data flows. The risk is very high because this landscape endpoint manager bug lets remote code execution (RCE) happen.
Think of it this way: if someone hacked your building's security system (locks, cameras, alarms), they would have full access to the main control panel. That's what a problem with endpoint management software means.
Lanscope exploit.
Confirmed active exploitation
CISA's addition of Lanscope's bug to the list of exploited vulnerabilities shows that attackers are already using the exploit. There aren't many details about the incident yet, but the fact that the vulnerability is out there means that companies should assume that it's only a matter of time before they're targeted if they don't do anything.
Ways and means of attack
The vulnerability is on the network side, which means that an attacker outside the organization could use it without having to log in. Vulnerability intelligence says that it is possible to exploit it by sending specially crafted packets to the system that is vulnerable.
Once an attacker has access to the code, they can run it. In endpoint management software that controls large fleets of devices, a successful exploit could lead to the entire network being compromised. Think about how one bad piece of software could infect a big company.
Think about a business that has 5,000 devices that Lanscope Endpoint Manager controls. The attacker makes a packet, runs code on that server from afar, and now has access to the management console. Then, they send bad agents to all 5,000 endpoints. The damage is done right away: private files are stolen, ransomware is used, or devices are turned into botnet nodes. A single flaw in the software made all of this possible.
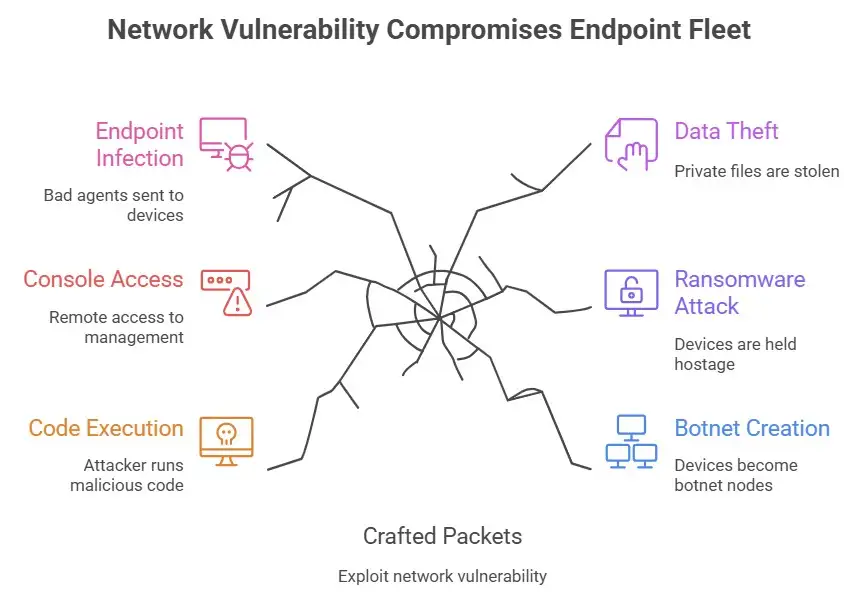
Timeline and History:
In October 2025, the weakness was officially recorded. The JPCERT/CC sent out a warning from Japanese software company MOTEX Inc., which put out a notice on October 20, 2025.
CISA added CVE-2025-61932 to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog on October 22, 2025. The deadline for fixing it was November 12, 2025.
Why this is important now
Companies are under a lot of pressure right now because the patch window is short and attacks are already happening. Delay means a higher chance of a breach. Also, people usually trust endpoint management tools and give them a lot of power, which makes this bug even more dangerous.
Patch Update and Mitigation
Managing patches and taking the right steps
The easiest thing to do is to install the patch or update that MOTEX gives you for Lanscope Endpoint Manager. The vendor's notice lists the versions that are affected, such as version 9.4.7.1 and earlier.
IT teams should treat the bug like a landscape RCE vulnerability and put emergency patching ahead of other updates that are already planned. Getting rid of exposure as soon as possible is very important.
Workaround or mitigation when patching isn't possible right away
If you can't apply the patch right away, think about these ways to make things better:
• Limit network access to the Lanscope Endpoint Manager server by only allowing trusted IPs to connect to it.
• Watch for strange traffic or a lot of management commands coming from outside the network.
• Make sure that logging is turned on and checked for signs of abuse.
• Think about turning off or isolating the agent temporarily until it is patched.
Why patching is necessary
This risk is no longer just a theory because the bug has been confirmed to be used in the real world. It is a zero-day because it has not been patched and is being attacked. The term "landscape endpoint manager zero-day" works here. Not patching right away will only make the network more vulnerable to being hacked, losing data, and hurting your reputation.
Impact on endpoint security
Wider lessons in the flaw of endpoint management software
This incident shows how endpoint management software, which is supposed to be a security tool, can be used to attack. It shows how important it is to have layered security, good patch management, and awareness of endpoint risks.
Reevaluating patching methods
A lot of companies plan to patch during their regular maintenance times. But if you have a bug like this, that schedule might be too slow. It becomes very important to be able to speed up updates, quickly roll them out to all global endpoints, and keep track of compliance.
Risk and supply chain issues that affect the whole network
A compromise can spread quickly because endpoint management tools often have a lot of access and are well integrated. Attackers could use this to gain more access, move sideways, or infect systems that are connected. Companies that use these kinds of tools should assume that "trusted" management software still needs to be watched and made stronger.
Quick Comparison
Why CIOs and security teams must know
It's not just one vendor; it's about trust and control.
When endpoint management software is hacked, the hacker gets the keys to the kingdom. This bug in Lanscope could let attackers send commands, install malware, or turn devices into launchpads, all while pretending to be trusted software.
Everyone uses endpoint management software. A lot of businesses might think their patch status is fine. But this flaw shows that even tools that aren't very well known, like a product from a Japanese company, can be used to attack people all over the world. This is a reminder that all endpoint management tools should be included in inventories, not just the well-known ones.
Once a system is hacked, the damage can be huge: data theft, ransomware, service outages, and damage to reputation. For instance, a compromised endpoint management console could send harmful payloads to user devices, servers, IoT-connected systems, and other places. The risk grows very quickly.
A personal thought
I've worked in enterprise security, and I've seen how "trusted" systems can become blind spots. People think, "The tool is safe because it's from a vendor, and I trust it." But the Lanscope bug is a harsh reminder that any piece of software can be hacked. As soon as you stop thinking of it as "security-immune," you get closer to protecting it.
Best Ways to Keep Your Endpoint Security Up to Date
• Keep a complete list of all the software you use to manage endpoints, including agents, consoles, and servers.
• Before routine updates, make sure to patch and update high-risk, high-privilege systems (like endpoint managers).
• Limit access to management consoles to only trusted administrative hosts and split the network into smaller parts.
• Check and keep an eye on endpoint management logs for strange behavior, like sudden big changes, agent installs, and remote commands.
• Create an incident response plan just for endpoint management compromise. It should assume the worst and move quickly.
• Do regular penetration tests and red-team simulations to see if attackers can get into or change endpoint management systems.
Questions and Answers
Q1: What is the vulnerability in the landscape endpoint?
A: The Lanscope Endpoint vulnerability is a serious bug in Lanscope Endpoint Manager (on-premises) that doesn't check where incoming requests come from correctly. This lets an attacker send packets that are made just for them and run code on the target computer.
Q2: What makes the Lanscope Endpoint Manager exploit different from other bugs?
A: This landscape endpoint manager exploit lets attackers run code from a distance (RCE) without needing to log in or be on the same network. That makes it more dangerous and easier to take advantage of.
Q3: What versions of Lanscope Endpoint Manager are affected?
A: According to vendor notices, the on-premises version of Lanscope Endpoint Manager that is affected is 9.4.7.1 and earlier.
Q4: How can companies quickly reduce this?
A: Organizations should use the patch that MOTEX gave them as soon as they can, limit access to the management console on the network, keep an eye out for strange behavior, and make sure their incident response team is always ready.
Q5: What was the reason for CISA's warning about the Lanscope Endpoint Manager bug?
A: Because CVE-2025-61932 is listed in CISA's Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog and has been confirmed to be actively exploited, the threat is real, and organizations need to take action.
The End
In a world where endpoint security is your first line of defense, the Lanscape endpoint vulnerability isn't just another bug; it's a direct way for attackers to get into your business. The CVE-2025-61932 bug in the Lanscope Endpoint Manager is already being used in real-world cyberattacks, so action must be taken right away.
Your team needs to make this a top priority, from patching to limiting network access, from monitoring to being ready for an incident.
Don't wait for the attack to come to you. Do it now. Make sure your endpoint management infrastructure is safe, apply updates, check access controls, and stay one step ahead of what could be the way into your network. It's time to stop being complacent.
Hoplon Infosec's Endpoint Security service protects your systems from exploits like the lanscope endpoint vulnerability. It does this by quickly patching them, finding threats, and defending them before they happen.
You can also read these important cyber security news articles on our website.
ü Apple Update,
ü Windows Fix,
ü WordPress Issue .
For more Please visit our Homepage and follow us on X (Twitter) and LinkedIn for more cybersecurity news and updates. Stay connected on YouTube, Facebook, and Instagram as well.
Share this :