Phantom Stealer Attack: How This Malware Steals Sensitive Data

Hoplon InfoSec
18 Dec, 2025
Is the Phantom Stealer attack a real and growing danger to people and businesses in 2025?
Yes, the answer is yes. As of mid-2025, several reliable cybersecurity reports say that real-world campaigns are still using Phantom Stealer malware to steal passwords, browser cookies, credit card information, and crypto wallet data. Cybersecurity News published one of the most cited investigations in 2025. It showed how Phantom Stealer version 3.5 spread through phishing emails and ISO-based installers.
The Phantom Stealer attack is not just a theoretical threat if you work online, save passwords in your browser, or use a credit card to shop. It's made for people just like you. This malware is quiet, fast, and hard to see. It doesn't lock files or show ransom notes. Instead, it quietly watches and takes what matters most.
The fact that the infection process looks so normal is what makes Phantom Stealer malware so dangerous. A lot of victims don't realize anything is wrong until their accounts are emptied, their sessions are taken over, or they get login alerts from places they don't know. The damage is already done by then.
This article explains how Phantom Stealer works, why it is spreading so quickly, what most top-ranking articles don't say, and what you can do if you think you might have an infection. The goal is to be clear, not scared.

What is the Phantom Stealer attack, and why are security teams worried?
Phantom Stealer is a new type of malware that steals information without causing any visible problems. Its goal is to get sensitive user data. Its success depends on staying hidden for as long as possible, unlike ransomware or wipers.
Security researchers say it is a modular credential-harvesting malware. That means the hackers can change what information it steals without having to rewrite the whole malware. This design choice is why Phantom Stealer 2025 campaigns look more advanced than those of older infostealers.
The Phantom Stealer attack has been seen going after both people and small businesses. Freelancers, people who work from home, people who use cryptocurrency, and small business administrators are all common in incident reports. The thing that all of them have in common is that they store data in a browser.
How Phantom Stealer gets into systems
Phishing is the most common way for people to get infected with Phantom Stealer malware. Attackers send emails that look like bills, shipping notices, software updates, or job-related papers. The attachment is usually an ISO file or a compressed installer that looks like something safe.
Windows automatically mounts the ISO when the user opens the file. There is usually a shortcut or executable file inside that starts the stealing payload. ISO files are a popular way to send things because they don't follow some of the usual rules for scanning email.
There have been campaigns called Operation MoneyMount ISO that have shown this ISO phishing malware attack method. The names may be different in different reports, but the behavior stays the same.

What the Data Phantom Stealer Really Steals
When it is running, Phantom Stealer looks for saved passwords in popular browsers. This includes usernames and passwords that are stored in Chrome, Edge, Firefox, and other Chromium-based browsers.
Its ability to steal cookies from browsers is even more worrisome. Cookies let hackers take over active sessions without needing the password. This is how victims see logins from other countries even after changing their passwords.
The malware also goes after saved credit card information, autofill data, crypto wallet extensions, and tokens for messaging apps. This means that Phantom Stealer is a type of malware that steals data from many different places instead of just one.
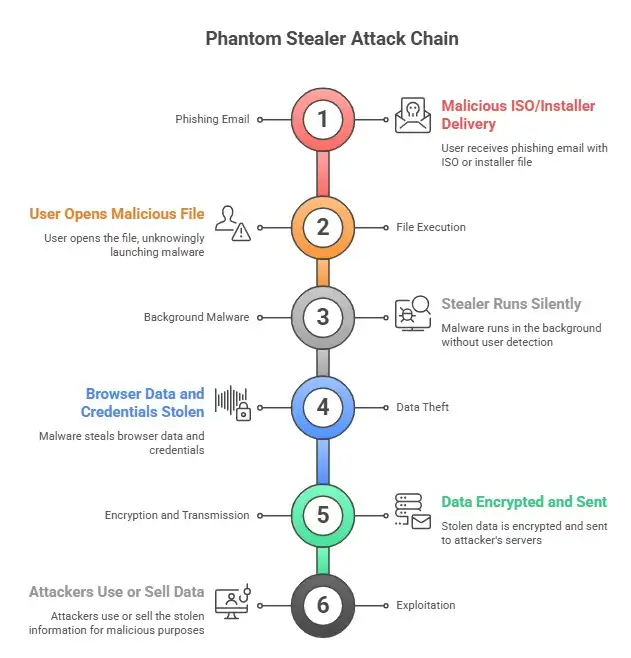
Step-by-step guide to how the Phantom Stealer Attack works
Knowing how the attack chain works can help you understand why so many people miss the warning signs.
• A phishing email sends an ISO or installer file
• The user opens the file, thinking it is real
• The stealer malware runs in the background without the user knowing
• The browser data and credentials are stolen
• The data is encrypted and sent to the attacker's servers
• The attackers use or sell the stolen information
Timing is something that a lot of articles don't talk about. Phantom Stealer often waits to do things or spreads them out over hours. This makes it less likely that antivirus programs that look for sudden behavior changes will find it.
Another thing that people don't think about is persistence. Some versions of Phantom Stealer make scheduled tasks or registry entries so that they can stay alive after a reboot. This is why a simple restart won't get rid of the threat.
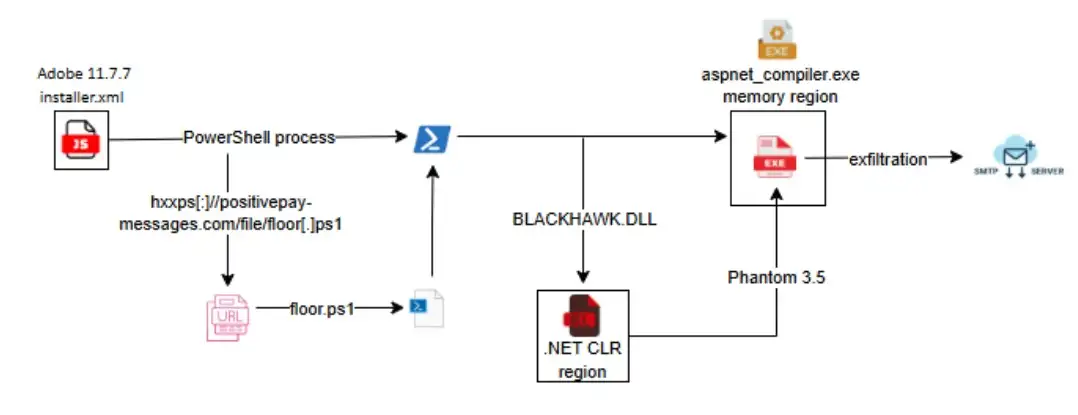
Malware execution sequence (source: labs.k7computing)
Why Phantom Stealer Is More Dangerous Than Older Infostealers
At first glance, comparisons between Phantom Stealer and RedLine or Raccoon make it seem like they do the same things. The difference is in how refined and stealthy they are.
The main thing that Phantom Stealer malware does is steal cookies. This shows that attackers have changed their strategy. You can change your passwords. Session cookies usually can't. This lets attackers get around multi-factor authentication completely.
Another thing to think about is the quality of the distribution. Recent Phantom Stealer attack campaigns use email templates that look clean andbelievable sender domains. This layer of social engineering is often better than the malware itself.

RC4 encryption key and decryption process (source: labs.k7computing )
A Realistic Scenario of Infection
A freelance designer gets an email about a new contract. The attached file is an ISO file that is clearly and professionally labeled. Nothing makes people suspicious.
The designer sees strange activity in a payment account two days later. Changing passwords doesn't stop access. The real issue is that browser cookies are being stolen. The attacker already has everything they need by the time the system is scanned.
Phantom Stealer: A Visual Data Snapshot Types of Data That Are Targeted

There is no one clear sign. Users instead report patterns.
It's normal for accounts to be logged in from new places without warning. Even after you change your password, you may still get security alerts.
Browsers may log you out at random times or act strangely. Some antivirus programs will flag generic trojans without naming Phantom Stealer in particular.
If several different accounts are hacked in a short amount of time, you should think about a Phantom Stealer attack.
How to Get Rid of Phantom Stealer Malware Safe
It takes time to get rid of malware that steals information. When you rush, you often leave things behind.
First, unplug the infected device from the internet. This stops more data from being stolen.
Install a good antivirus program with the most recent signatures. No tool can guarantee detection, but enterprise-grade scanners work better against Phantom Stealer 2025 variants.
If you know for sure that your computer is infected, the safest thing to do is usually to reset the operating system. You should only change your password after the system is clean.
Questions and Answers
What is Phantom Stealer,r and how dangerous is it?
Phantom Stealer is a piece of malware that steals passwords, cookies, and financial information. Its danger comes from being sneaky, not from causing damage.
Can malware really steal cookies from your browser?
Yes. It's now common for malware to steal browser cookies. Cookies can let hackers get into accounts without knowing the password.
How does Phantom Stealer get into systems?
Phishing emails with ISO attachments or fake installers are the most common way for infections to start.
What can I do to keep my accounts safe after an attack?
First, clean the device. Then change your passwords, log out of all active sessions, turn on multi-factor authentication, and keep a close eye on your financial statements.
The Real Lesson from the Phantom Stealer Attack
The Phantom Stealer attack is an example of how cybercrime has changed. Attackers don't need loud malware anymore. They need quiet access and time.
The lesson for users is simple but not easy to accept. There is a real risk that comes with browser ease. Saved passwords and cookies are important things to have.
If you only do one thing today, check how much sensitive information your browser saves and delete some of it on purpose. Awareness is still the best way to protect yourself from Phantom Stealer malware and the many other types of stealer malware that will come after it.
You can also read these important cybersecurity news articles on our website.
· Apple Update,
For more Please visit our Homepage and follow us on X (Twitter) and LinkedIn for more cybersecurity news and updates. Stay connected on YouTube, Facebook, and Instagram as well.
Share this :